|
Transition Metal Oxalate Complex
Transition metal oxalate complexes are coordination complexes with oxalate (C2O42−) ligands. Some are useful commercially, but the topic has attracted regular scholarly scrutiny. Oxalate (C2O42-) is a kind of dicarboxylate ligand. As a small, symmetrical dinegative ion, oxalate commonly forms five-membered MO2C2 chelate rings. Mixed ligand complexes are known, e.g., o(C2O4)(NH3)4sup>κ+. Homoleptic complexes Homoleptic oxalato complexes are common, e.g., those with the formula (κ2-C2O4)3sup>n-: M = V(III), Mn(III), Cr(III), Tc(IV), Fe(III), Ru(III), Co(III), Rh(III), Ir(III). These anions are chiral (D3 symmetry), and some have been resolved into their component enantiomers. Some early metals form tetrakis complexes of the type (κ2-C2O4)4sup>n- M = Nb(V), Zr(IV), Hf(IV), Ta(V), Bimetallic complexes Oxalate is often a bridging ligand forming bi- and polynuclear complexes with (κ2,κ'2-C2O4)M2 cores. Illustrative binuclear complexes are 2(C2O4)5sup>2- M = Fe(II) and Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (C2O4(CH3)2). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a stepwise manner; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is (p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and only tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Ferrioxalate
Potassium ferrioxalate, also called potassium trisoxalatoferrate or potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate(III) is a chemical compound with the formula []. It often occurs as the trihydrate . Both are crystalline compounds, lime green in colour.A. Saritha, B. Raju, M. Ramachary, P. Raghavaiah, and K. A. Hussain (2012) "Synthesis, crystal structure and characterization of chiral, three-dimensional anhydrous potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate(III)", ''Physica B: Condensed Matter'', volume 407, issue 21, pages 4208-4213. The compound is a salt consisting of ferrioxalate anions, , and potassium cations . The anion is a transition metal complex consisting of an iron atom in the +3 oxidation state and three bidentate oxalate ions anions acting as ligands. Potassium acts as a counterion, balancing the −3 charge of the complex. In solution, the salt dissociates to give the ferrioxalate anion, []3−, which appears fluorescent green in color. The ferrioxalate anion is quite stable in the da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin, sold under the brand name Eloxatin among others, is a cancer medication (platinum-based antineoplastic class) used to treat colorectal cancer. It is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include numbness, feeling tired, nausea, diarrhea, and low blood cell counts. Other serious side effects include allergic reactions. Use in pregnancy is known to harm the baby. Oxaliplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications. It is believed to work by blocking the duplication of DNA. Oxaliplatin was patented in 1976 and approved for medical use in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Oxaliplatin is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, typically along with folinic acid (leucovorin) and fluorouracil in a combination known as FOLFOX or along with capecitabine in a combination known as CAPOX or XELOX. Advanced colorectal cancer Oxaliplatin by itself has modest activity against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
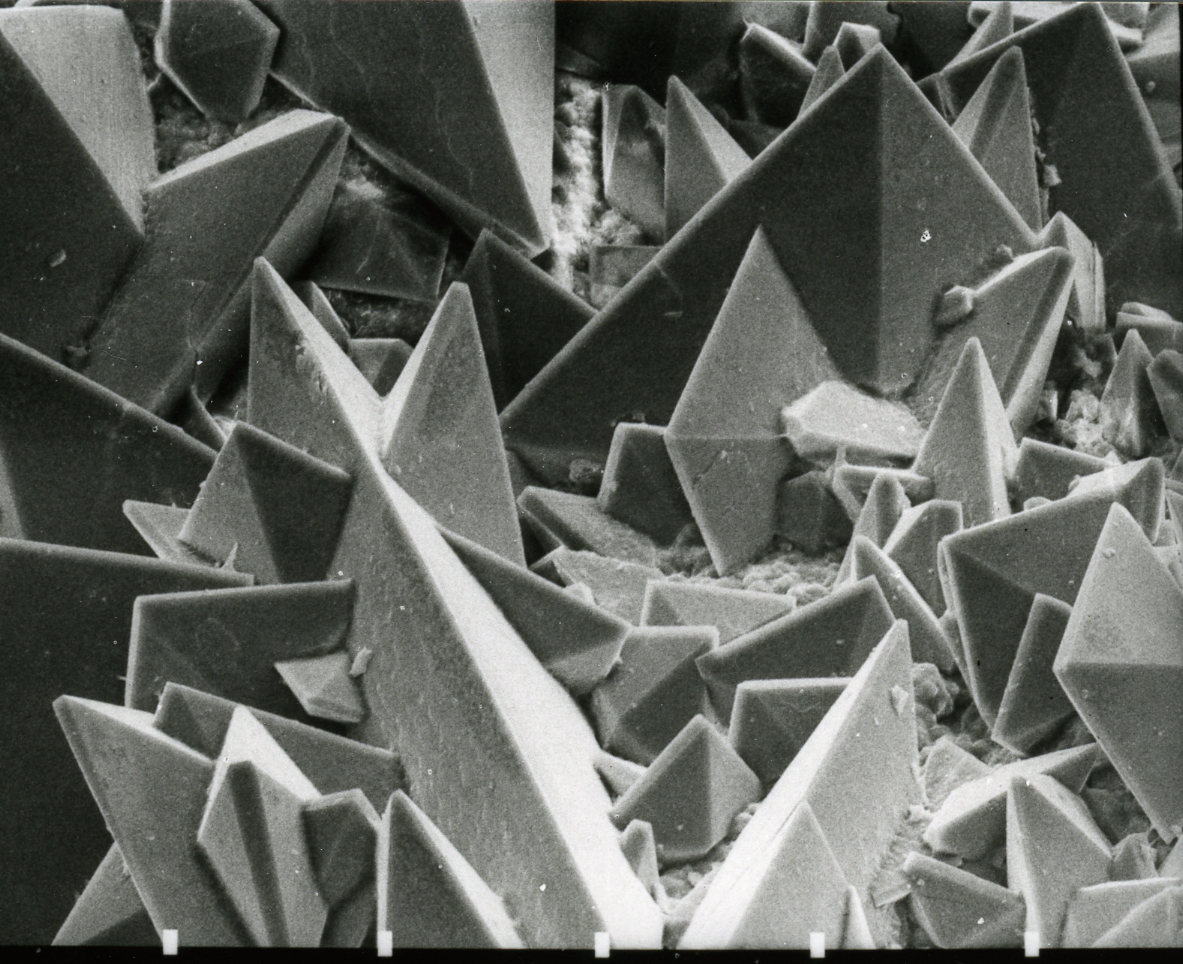
Potassium Ferrioxalate Large Crystals
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinometry
Actinometers are instruments used to measure the heating power of radiation. They are used in meteorology to measure solar radiation as pyranometers, pyrheliometers and net radiometers. An actinometer is a chemical system or physical device which determines the number of photons in a beam integrally or per unit time. This name is commonly applied to devices used in the ultraviolet and visible wavelength ranges. For example, solutions of iron(III) oxalate can be used as a chemical actinometer, while bolometers, thermopiles, and photodiodes are physical devices giving a reading that can be correlated to the number of photons detected. History The actinometer was invented by John Herschel in 1825; he introduced the term ''actinometer'', the first of many uses of the prefix ''actin'' for scientific instruments, effects, and processes. The actinograph is a related device for estimating the actinic power of lighting for photography. Chemical actinometry Chemical actinometry invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalatonickelate
The oxalatonickelates are a class of compounds that contain nickel complexed by oxalate groups. They form a series of double salts, and include clusters with multiple nickel atoms. Since oxalate functions as a bidentate ligand it can satisfy two coordinate positions around the nickel atom, or it can bridge two nickel atoms together. The shape around the nickel atom is octahedral for diaquabis(oxalato)nickelate. The colour of this is green due to the Ni(–O–)6 chromophore. The absorption in infrared is at 8,300 9,060 13,400, 15,260, and 26,160 cm−1. The ligand field parameters are 10 Dq=8800 cm−1 and B=1000 cm−1. Because the Ni2+ ion resembles many other divalent metal A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ... ions, it can be substituted by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligands
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acid A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...ic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


4-3D-balls.png)

