|
Tomb Of 'Ip
The Tomb of 'Ip is an ancient Egyptian tomb chapel that was discovered in 1936 in El Saff, 17 km north of Atfih in Middle Egypt. The decoration of the tomb chapel was copied in the following years, but since then the location of the tomb was lost. The records were published in 1995 by Henry George Fischer in a monograph. No plan was recorded. The decoration of the chapel was painted. It can be assumed that the paintings decorated a tomb chapel cut into the rocks at El Saff. The left wall of the tomb chapel shows on the left, Ip and his wife are sitting in front of an offering table (the table was already destroyed when the scene was copied). His wife is called ''she who is known to the king, the revered one before Hathor, lady of Atfih''. Her name is Menkhet Henut. Above them is a text mainly listing the titles of Ip and of his wife. In front of this was painted a long offering list, also much destroyed when found. On the far right are shown servants and fishermen in a boat. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Saff
El Saff () is a city in the Giza Governorate, Egypt. Its population was estimated at 59,000 people in 2018. Background El Saff is a Markaz and city located about 30 km south of Helwan, which includes more than 30 villages, and it follows the Giza Governorate, although it is located on the eastern shore of the Nile River, opposite Al-Ayyat B center. The West is the Nile River, and from the east is the Eastern desert. The city is known for the clay brick factories that spread widely over the area and the villages of Askar, Al-Wadi, and Abu Abu Sa’id. The most famous cities in El Saff Markaz: * El Saff El Balad village * Ghamza AL Kubra village * Al Akhsas village * El Shobak El Sharqy village * Kafr Tarchan village * Askar village * El Wadi village * Al Aquas wel Fahmyen village *Nazlet El Eryan village *El Shorfa village *El Desmy village Most of the villages and areas of the center are located to the east and west of the desert road to Upper Egypt, which connects the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
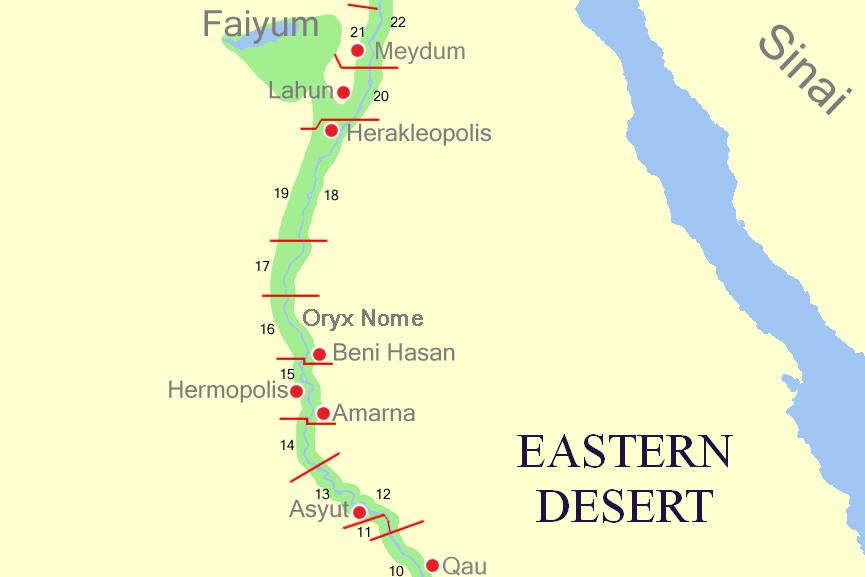
Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis, Egypt, Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed "#Heptanomis, Heptanomis" (; Greek language, Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a "nome (Egypt), nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaid, Thebaïd from the Nile Delta, Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atfih
Atfih ( ' , ''Tpeh or Tpēh'') is a town in Middle Egypt. It was part of the now defunct Helwan Governorate from April 2008 to April 2011, after which it was reincorporated into the Giza Governorate. As of 2001, it has a population of 106,300 inhabitants. Etymology The name is derived from Ancient Egyptian ''Tp-jhw'', meaning ''the first of the cows'', referring to Hathor. The name became ''Petpeh'' in Coptic, from which the Arabic version ''Atfih'' () is derived. The city was also known in Greco-Roman Egypt as Aphroditopolis. Location Atfih is located in the area of ancient Maten, Upper Egypt's northernmost nome. History Ancient history Atfih was known as ''Per-nebet tep-ihu'' in antiquity and Busiris (Aphroditopolis) to the Romans. Some of the Ancient Egyptian monuments discovered in the town include an animal necropolis, Greco-Roman tombs, and sepulchers of cows in huge limestone tombs. About 17 km North was found the Tomb of 'Ip, who lived around 2000 B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry George Fischer
Henry George Fischer (May 10, 1923 – January 11, 2006) was an American Egyptologist and poet. Biography Born on May 10, 1923, in Philadelphia, Fischer graduated from Princeton University in 1945, after that he was sent teaching English at the American University of Beirut. Returned in the USA, he became an assistant at the University of Pennsylvania Museum and in 1955 he received a Ph.D. from the same university. Shortly after he joined an expedition to Egypt and later he became an assistant professor of Egyptology at Yale University. In 1958 he started working as an assistant curator at the New York Metropolitan Museum of Art, forming a bond with this place that will last for his entire life. In 1963 he became associate curator and in 1964, head of the Department of Egyptology. Since the same year until 1970 Fischer was a member of the committee for the salvage of Abu Simbel temples from being submerged by the Lake Nasser following construction of the Aswan Dam: the sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathor
Hathor (, , , Meroitic language, Meroitic: ') was a major ancient Egyptian deities, goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the mother goddess, symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. She was one of several goddesses who acted as the Eye of Ra, Ra's feminine counterpart, and in this form, she had a vengeful Aspect (religion), aspect that protected him from his enemies. Her beneficent side represented music, dance, joy, love, sexuality, and maternal care, and she acted as the consort of several male deities and the mother of their sons. These two aspects of the goddess exemplified the women in ancient Egypt, Egyptian conception of femininity. Hathor crossed boundaries between worlds, helping deceased ancient Egyptian conception of the soul, souls in the transition to the ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleventh Dynasty
The Eleventh Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty XI; ) is a well-attested group of rulers. Its earlier members before Pharaoh Mentuhotep II are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, whereas the later members are considered part of the Middle Kingdom. They all ruled from Thebes in Upper Egypt. Characteristics The relative chronology of the 11th Dynasty is well established by contemporary attestations and, except for count Intef and Mentuhotep IV, by the Turin canon.mirror Manetho's statement that the 11th Dynasty consisted of 16 kings, who reigned for 43 years is contradicted by contemporary inscriptions and the evidence of the Turin King List, whose combined testimony establishes that this kingdom consisted of seven kings who ruled for a total of 143 years. However, his testimony that this dynasty was based at Thebes is verified by the contemporary evidence. It was during this dynasty that all of ancient Egypt was united under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Of The Eleventh Dynasty Of Egypt
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |