|
Tolman Electronic Parameter
The Tolman electronic parameter (TEP) is a measure of the electron donating or withdrawing ability of a ligand. It is determined by measuring the frequency of the A1 C-O vibrational mode (ν(CO)) of a (pseudo)-C3v Molecular symmetry, symmetric complex, [LNi(CO)3] by infrared spectroscopy, where L is the ligand of interest. [LNi(CO)3] was chosen as the model compound because such complexes are readily prepared from tetracarbonylnickel(0). The shift in ν(CO) is used to infer the electronic properties of a ligand, which can aid in understanding its behavior in other complexes. The analysis was introduced by Chadwick A. Tolman. : The A1 carbonyl band is rarely obscured by other bands in the analyte's infrared spectrum. Carbonyl is a small ligand so steric factors do not complicate the analysis. Upon coordination of CO to a metal, ν(CO) typically decreases from 2143 cm−1 of free CO. This shift can be explained by Pi backbonding, π backbonding: the metal forms a π bond with the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
A1 Stretch Of Ni(CO)3L
A1, A-1, A01 or A.1. may refer to: Arts and entertainment Film * ''A-1 Headline'', a 2004 Hong Kong film * (English title: ''Our Man in Jamaica''), a 1965 Italian film * ''A1'', a 1999 Syrian film; see List of Syrian films * ''A1'' (2019 film), Indian Tamil film Games * ''A1 – Slave Pits of the Undercity'', a component of ''Scourge of the Slave Lords'' adventure module for ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * Larsen's Opening (ECO code: A01), a chess move * A1, a square on a chessboard Music and dance * A1, a part in contra dance choreography * A-1 Sound Studios, a recording studio owned by Herb Abramson * A-1, an American rap group behind the album ''Mash Confusion'' * A-One (band), a Mandopop group * A1 (group), a British–Norwegian boy band * A1 x J1, a British hip hop duo Albums * ''A1'', an album by Ertuğ Ergin * ''A1'', an album by Tony Cetinski * ''A One'', an album by Ayumi Hamasaki * ''A1'' (album), a 2002 album by the British–Norwegian band A1 Radio * CHIN (AM) (promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
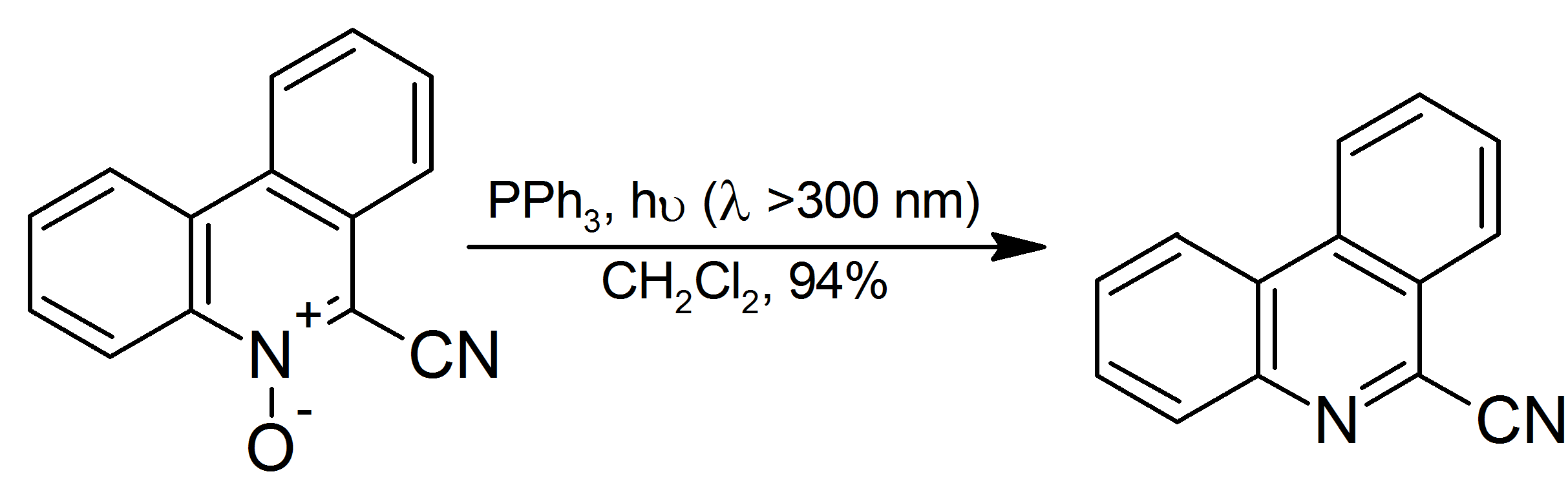
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (Metal carbonyl, metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganics, metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organometallics
''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Citation Reports by Thomson Reuters. Since 2015 Paul Chirik is the editor-in-chief of ''Organometallics''. He is an American chemist and the Edwards S. Sanford Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, and associate director for external partnerships of the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment. He writes about the catalysis of hydrocarbons. Past editors-in-chief are Dietmar Seyferth and John Gladysz. Retrieved on 2014-07-30. This journal is indexed in |
Tolman Cone Angle
In coordination chemistry, the ligand cone angle (θ) is a measure of the steric bulk of a ligand in a transition metal coordination complex. It is defined as the solid angle formed with the metal at the vertex of a cone and the outermost edge of the van der Waals spheres of the ligand atoms at the perimeter of the base of the cone. Tertiary phosphine ligands are commonly classified using this parameter, but the method can be applied to any ligand. The term ''cone angle'' was first introduced by Chadwick A. Tolman, a research chemist at DuPont. Tolman originally developed the method for phosphine ligands in nickel complexes, determining them from measurements of accurate physical models. Asymmetric cases The concept of cone angle is most easily visualized with symmetrical ligands, e.g. PR3. But the approach has been refined to include less symmetrical ligands of the type PRR′R″ as well as diphosphines. In such asymmetric cases, the substituent angles' half angles, , are ave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metal Carbonyl
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic materials. A metal conducts electricity at a temperature of absolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
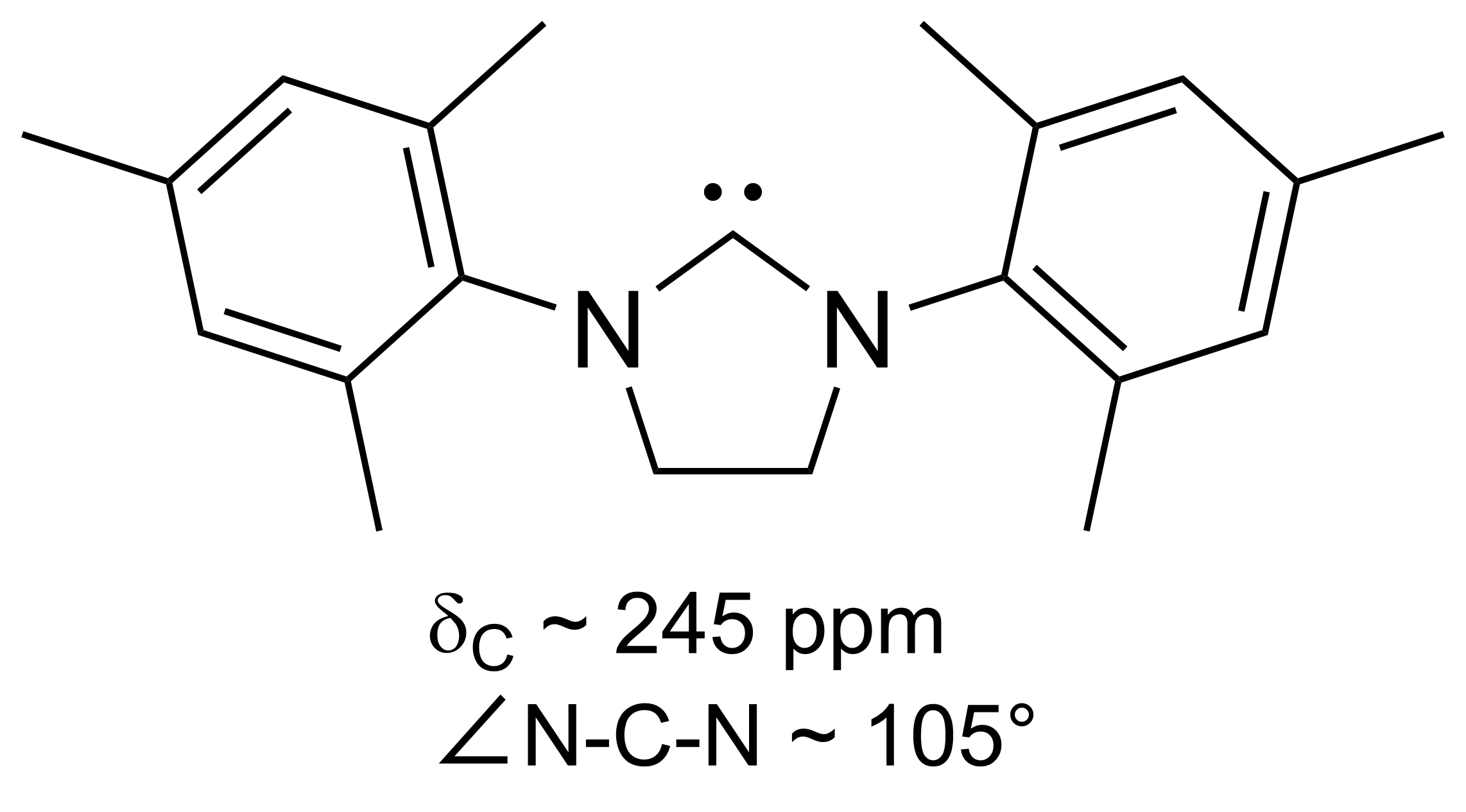
N-heterocyclic Carbene
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with octet rule, incomplete octet (a carbene), but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moieties. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the ''N''-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), in which nitrogen atoms flank the formal carbene. Modern theoretical analysis suggests that the term "persistent carbene" is in fact a misnomer. Persistent carbenes do not in fact have a carbene electronic structure in their ground state, but instead an ylide stabilized by Aromaticity, aromatic resonance or steric shielding. Excitation to a carbene structure then accounts for the carbene-like dimerization that some persistent carbenes undergo over the course of days. Persistent carbenes in general, and Arduengo carbenes in particular, are popular ligands in organometallic chemistry. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phosphorus Trifluoride
Phosphorus trifluoride (formula P F3), is a colorless and odorless gas. It is highly toxic and reacts slowly with water. Its main use is as a ligand in metal complexes. As a ligand, it parallels carbon monoxide in metal carbonyls, and indeed its toxicity is due to its binding with the iron in blood hemoglobin in a similar way to carbon monoxide. Physical properties Phosphorus trifluoride has an F−P−F bond angle of approximately 96.3°. Gaseous PF3 has a standard enthalpy of formation of −945 kJ/mol (−226 kcal/ mol). The phosphorus atom has a nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shift of 97 ppm (downfield of H3PO4). Properties Phosphorus trifluoride hydrolyzes especially at high pH, but it is less hydrolytically sensitive than phosphorus trichloride. It does not attack glass except at high temperatures, and anhydrous potassium hydroxide may be used to dry it with little loss. With hot metals, phosphides and fluorides are formed. With Lewis base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phosphorus Trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride. History Phosphorus trichloride was first prepared in 1808 by the French chemists Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis Jacques Thénard by heating calomel (Hg2Cl2) with phosphorus. Later during the same year, the English chemist Humphry Davy produced phosphorus trichloride by burning phosphorus in chlorine gas. Preparation World production exceeds one-third of a million tonnes. Phosphorus trichloride is prepared industrially by the reaction of chlorine with white phosphorus, using phosphorus trichloride as the solvent. In this continuous process PCl3 is removed as it is formed in order to avoid the formation of PCl5. :P4 + 6 Cl2 → 4 PCl3 Structure and spectroscopy It has a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Triethyl Phosphite
Triethyl phosphite (TEP) is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphite ester, with the formula P(OCH2CH3)3, often abbreviated P(OEt)3. It is a colorless, malodorous liquid. It is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis. The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three ethoxide groups. Its 31P NMR spectrum features a signal at around +139 ppm vs phosphoric acid standard. Triethylphosphite is prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with ethanol in the presence of a base, typically a tertiary amine: :PCl3 + 3 EtOH + 3 R3N → P(OEt)3 + 3 R3NH + 3 Cl− In the absence of the base, the reaction of ethanol and phosphorus trichloride affords diethylphosphite ((EtO)2P(O)H). Of the many related compounds can be prepared similarly, triisopropyl phosphite is an example (b.p. 43.5 °C/1.0 mm; CAS# 116-17-6). Reactions Triethyl phosphite can react with electrophiles in a Michaelis–Arbuzov rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tris(4-fluorophenyl)phosphine
Tris, or tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, or known during medical use as tromethamine or THAM, is an organic compound with the formula (HOCH2)3CNH2. It is extensively used in biochemistry and molecular biology as a component of buffer solutions such as in TAE and TBE buffers, especially for solutions of nucleic acids. It contains a primary amine and thus undergoes the reactions associated with typical amines, e.g., condensations with aldehydes. Tris also complexes with metal ions in solution. In medicine, tromethamine is occasionally used as a drug, given in intensive care for its properties as a buffer for the treatment of severe metabolic acidosis in specific circumstances. Some medications are formulated as the "tromethamine salt" including Hemabate (carboprost as trometamol salt), and "ketorolac trometamol". In 2023 a strain of ''Pseudomonas hunanensis'' was found to be able to degrade TRIS buffer. Since Tris' pKa is more strongly temperature dependent, its use is not recom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tris(4-methoxyphenyl)phosphine
Tris(4-methoxyphenyl)phosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH3OC6H4)3P. Several isomers of this formula are known, but the symmetrical derivative with methoxy groups in the 4-position is most studied. The compound is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.{{cite journal , doi=10.1039/j19680003133, title=Hydroformylation of alkenes by use of rhodium complex catalysts, year=1968, last1=Evans, first1=D., last2=Osborn, first2=J. A., last3=Wilkinson, first3=G., journal=Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical, page=3133 Related ligands *Triphenylphosphine Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a l ... * 2-(Diphenylphosphino)anisole References Tertiary phosphines 4-Methoxyphenyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |