|
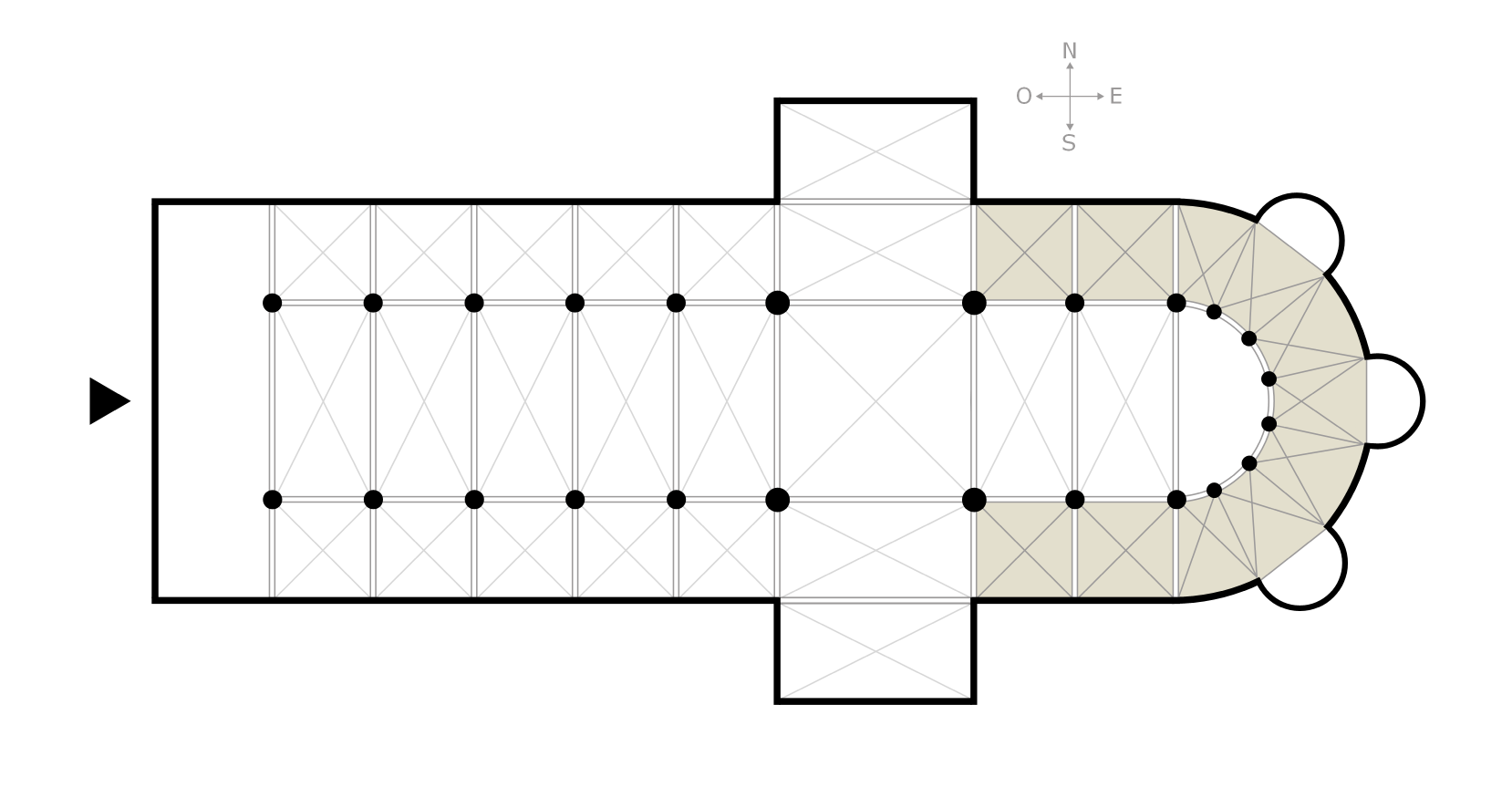
Toledo Cathedral
The Primatial Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption (), is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Toledo, Spain. It is the seat of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Toledo. Since 1088, it holds the honorific title of Primatial, granted by Urban II, establishing a higher rank over the rest in the Iberian Peninsula. The cathedral of Toledo is one of the three 13th-century High Gothic cathedrals in Spain and is considered, in the opinion of some authorities, to be the magnum opus of the Gothic style in Spain. It was begun in 1226 under the rule of Ferdinand III, and the last Gothic contributions were made in the 15th century when, in 1493, the vaults of the central nave were finished during the time of the Catholic Monarchs. It was modeled after the Bourges Cathedral, although its five naves plan is a consequence of the constructors' intention to cover all of the sacred space of the former city mosque with the cathedral, and of the former '' sahn'' with the cloister. It al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primacy Of The Spains
The Primacy of the Spains (; , ) is the primate (bishop), primacy of the Iberian Peninsula, historically known as Hispania or in the plural as the Spains. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Braga, Archbishop of Braga, in Portugal, has claimed this primacy over the whole Iberian Peninsula since the middle ages, however today his primacy is only recognized in Portugal. The Archdiocese of Toledo, Archbishop of Toledo in Spain has claimed the Primacy of Spain, as the primate above all other episcopal sees in Spain. In addition, the Archdiocese of Tarragona, Archbishop of Tarragona in Catalonia also makes use of the title. The Archbishops in Braga, Toledo and Tarragona, if raised to the rank of cardinal (Catholicism), cardinal, are known as Cardinal-Primates. Primacy of Braga The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Braga, Archbishop of Braga has claimed the title of ''Primate of the Spains'' () both for being the oldest diocese on the Iberian Peninsula and for its role in the christiani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toledo, Spain
Toledo ( ; ) is a city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality of Spain, the capital of the province of Toledo and the ''de jure'' seat of the government and parliament of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. Toledo is primarily located on the right (north) bank of the Tagus in central Iberian Peninsula, Iberia, nestled in a bend of the river. Built on a previous Carpetanian settlement, Toledo developed into an important Roman city of Hispania, later becoming the capital (''civitas regia'') of the Visigothic Kingdom and seat of a Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Toledo, powerful archdiocese. Often unsubmissive to Emirate of Córdoba, Umayyad central rule during the Islamic period, Toledo (طليطلة) nonetheless acquired a status as a major cultural centre (promoting productive cultural exchanges between the Ummah and the Latin Christendom), which still retained after the Fitna of al-Andalus, collapse of the caliphate and the crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourges Cathedral
Bourges Cathedral ( French: ''Cathédrale Saint-Étienne de Bourges'') is a Roman Catholic church located in Bourges, France. The cathedral is dedicated to Saint Stephen and is the seat of the Archbishop of Bourges. Built atop an earlier Romanesque church from 1195 until 1230, it is largely in the High Gothic or Classic Gothic architectural style and was constructed at about the same time as Chartres Cathedral. The cathedral is particularly known for the great size and unity of its interior, the sculptural decoration of its portals, and the large collection of 13th century stained glass windows. Owing to its quintessential Gothic architecture, the cathedral was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992. History Earlier cathedrals The walled city of Avaricum, the capital of the Gallic tribe of the Bituriges, was conquered by Julius Caesar in 54 B.C. and became the capital of the Gallo-Roman province of Aquitaine. Christianity was brought by Saint Ursinus of Bourges in abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reccared
Reccared I (or Recared; ; ; 559 – December 601; reigned 586–601) was the king of the Visigoths, ruling in Hispania, Gallaecia and Septimania. His reign marked a climactic shift in history, with the king's renunciation of Arianism in favour of Nicene Christianity in 587. Reign Reccared was the younger son of Liuvigild, King Leovigild by his first wife. Like his father, Reccared had his capital at Toledo, Spain, Toledo. The Visigothic kings and nobles were traditionally Arianism, Arian Christians, while the Hispano-Roman population were Chalcedonian Christianity, Chalcedonian Christians. The bishop Leander of Seville was instrumental in converting the elder son and heir of Leovigild, Hermenegild, to Chalcedonianism. Leander supported his rebellion and was exiled for his role. When King Leovigild died, within a few weeks of April 21, 586, bishop Leander was swift to return to Toledo. The new king had been associated with his father in ruling the kingdom and was acclaimed king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arianism
Arianism (, ) is a Christology, Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is considered Heresy in Christianity, heretical by most modern mainstream branches of Christianity. It is held by a minority of modern denominations, although some of these denominations hold related doctrines such as Socinianism, and some shy away from use of the term Arian due to the term's historically negative connotations. Modern denominations sometimes connected to the teaching include Jehovah's Witnesses, some individual churches within the Churches of Christ (including the movement's founder Barton W. Stone), as well as some Hebrew Roots Christians and Messianic Judaism, Messianic Jews (although many Messianic Jews also follow Nicene Christianity). It is first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter who preached and studied in Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Councils Of Toledo
From the 5th century to the 7th century AD, about thirty synods, variously counted, were held at Toledo (''Concilia toletana'') in what would come to be part of Spain. The earliest, directed against Priscillianism, assembled in 400. The "third" synod of 589 marked the epoch-making conversion of King Reccared from Arianism to Catholic Chalcedonian Christianity. The " fourth", in 633, probably under the presidency of the noted Isidore of Seville, regulated many matters of discipline and decreed uniformity of liturgy throughout the kingdom. The Britonia of Galicia accepted the Latin liturgical rite. The "twelfth" council in 681 assured to the archbishop of Toledo the primacy of Hispania (present Iberian Peninsula). As nearly one hundred early canons of Toledo found a place in the '' Decretum Gratiani'', they exerted an important influence on the development of ecclesiastical law. The later synod of 1565 and 1566 concerned itself with the execution of the decrees of Trent; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group united under the command of Alaric I. Their exact origins are believed to have been diverse but they probably included many descendants of the Thervingi who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and Alaric's Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under Alaric, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sack of Rome (410), sacked Rome in August 410. The Visigoths were subsequently settled in southern Gaul as ''foederati'' to the Romans, a relationship that was established in 418. This developed as an independent kingdom with its Capital city, capital at Toulou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FP Toledo Cathedral 2025 - Visigothic Consecration
FP may refer to: Arts, media and entertainment Music * Fortepiano, an early version of the piano * Fortepiano (musical dynamic), an Italian musical term meaning 'loud soft' * Flux Pavilion, a British dubstep artist * Francis Poulenc, an early 20th century pianist and composer ** FP (catalogue) - of his compositions. * "FP", song by Arcángel and Rauw Alejandro from ''Sentimiento, Elegancia y Más Maldad'', 2023 Publications * ''Financial Post'', a Canadian business newspaper, published from 1907 to 1998, now ''National Post'' * ''Foreign Policy'', a bimonthly American magazine founded in 1970 Other media * Facepunch Studios, a British video game company * ''The FP'', a 2011 comedy film * Fast Picket, a class of fictional artificially intelligent starship in The Culture universe of late Scottish author Iain Banks Science and technology Computing * FP (complexity), in computational complexity theory, a complexity class * FP (programming language) designed by John Backus in the 1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vault (architecture)
In architecture, a vault (French ''voûte'', from Italian ''volta'') is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the Keystone (architecture), keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or Circular segment, segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed. The Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaeans (ca. 18th century BC, 1800–1050s BC, 1050 BC) were known for their Tholos (architecture), tholos tombs, also called beehive tombs, which were underground structures with conical vaults. This type of vault is one of the earliest evidences of curved brick architecture without the use of ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triforium
A triforium is an interior Gallery (theatre), gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be located as a separate level below the clerestory. Masonry triforia are generally vaulting, vaulted and separated from the central space by Arcade (architecture), arcades. Early triforia were often wide and spacious, but later ones tend to be shallow, within the thickness of an inner wall, and may be blind arcades not wide enough to walk along. The outer wall of the triforium may itself have windows (glazed or unglazed openings), or it may be solid stone. A narrow triforium may also be called a "blind-storey", and looks like a row of window frames. History ''Triforium'' is derived from the Latin ''tres'', ''tria'' 'three' and ''foris'' 'door, entrance'; its Greek language, Greek equivalent is τρίθυρον, which originally r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |