|
Token (railway Signalling)
In railway signalling, a token is a physical object which a train driver is required to have or see before entering onto a particular section of single track. The token is clearly endorsed with the names of the section to which it belongs. A token system is more commonly used for single lines because of the greater risk of collision in the event of a mistake being made by a signaller or traincrew than on double lines. Principle The operation of a bidirectional single track line has the hazard of two trains colliding. The simplest way to prevent such collisions is to have only one train in the section at any given time. Such a system is known as "one-engine-in-steam” (OES) or “one-train working" (OTW). This system is used on some branches of rail networks, and on heritage railways. The main disadvantage is that it restricts the number of train movements that can be made. For a larger railway system, it becomes exceptionally limiting in the level of operations that it all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
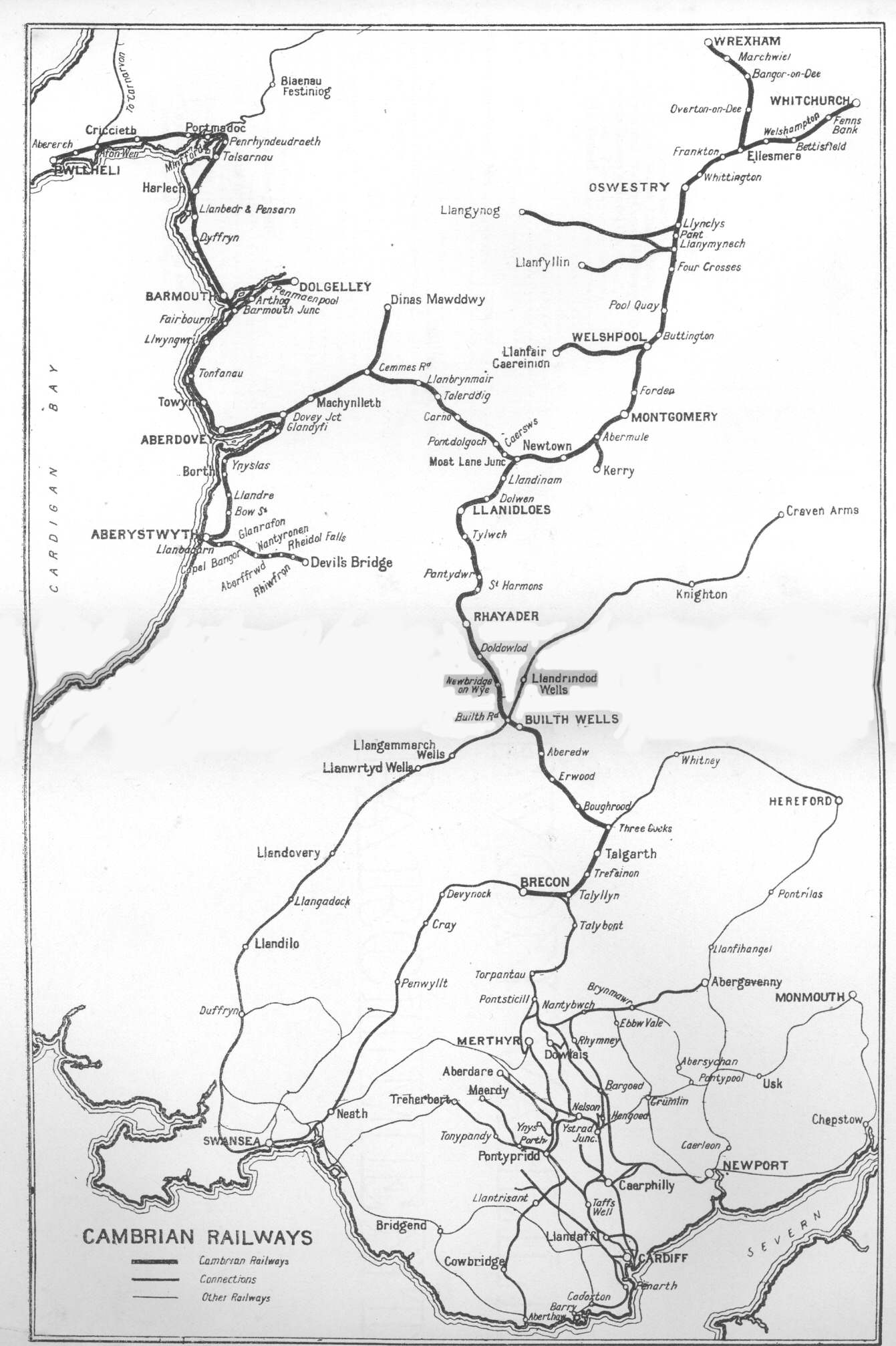
Cambrian Railways
The Cambrian Railways owned of Railway track, track over a large area of mid Wales. The system was an amalgamation of a number of railways that were incorporated in 1864, 1865 and 1904. The Cambrian connected with two larger railways with connections to the northwest of England via the London and North Western Railway, and the Great Western Railway for connections between London and Wales. The Cambrian Railways amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1922 as a result of the Railways Act 1921. The name is continued today in the route known as the Cambrian Line. History Creation of the Cambrian Railways: 1864 The Cambrian Railways Company was created on 25 July 1864 when the (27 & 28 Vict. c. cclxii) received royal assent. The company was formed by amalgamating most of the railway companies in mid Wales: the Oswestry and Newtown Railway, the Llanidloes and Newtown Railway, the Newtown and Machynlleth Railway and the Oswestry, Ellesmere and Whitchurch Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Coast Railway Line, New South Wales
The North Coast railway line is the primary rail route in the Mid North Coast and Northern Rivers regions of New South Wales, Australia, and forms a major part of the Sydney–Brisbane rail corridor. The line begins at Maitland, New South Wales, Maitland and ends at Roma Street railway station in Brisbane, although freight services terminate at the yard at Acacia Ridge, Queensland, Acacia Ridge on the outskirts of Brisbane. Along the way, the railway passes through the towns of Dungog railway station, Dungog, Gloucester railway station, New South Wales, Gloucester, Wingham railway station, New South Wales, Wingham, Taree railway station, Taree, Kendall railway station, Kendall, Wauchope railway station, Wauchope, Kempsey railway station, Kempsey, Macksville railway station, Macksville, Nambucca Heads railway station, Nambucca Heads, Urunga railway station, Urunga, Sawtell railway station, Sawtell, Coffs Harbour railway station, Coffs Harbour, Grafton railway station, New South W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Northern Railway Line
The Main North Line (also known as the Great Northern Railway) is a major railway in New South Wales, Australia, running from Strathfield railway station, Strathfield in Sydney to Armidale railway station, Armidale. The 1980s saw the line closed progressively north of Armidale; passenger services north of Tamworth railway station, New South Wales, Tamworth were cancelled in 1990 but were reintroduced as far as the former two years later. The Sydney–Brisbane rail corridor now branches off the Great Northern Railway after Maitland railway station, Maitland and follows the North Coast railway line, New South Wales, North Coast line. Description of route The line starts as a branch off the Main Suburban railway line, Main Suburban line at Strathfield in Sydney. The line heads north as a quadruple track electrified line to Rhodes, crossing the John Whitton Bridge over the Parramatta River as a double track line. At West Ryde the line again expands out to four tracks through to E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Southern Railway Line
The Main Southern Railway (or Great Southern Railway) is a major railway in New South Wales, Australia. It runs from Sydney to Albury, near the Victorian border. The line passes through the Southern Highlands, Southern Tablelands, South West Slopes and Riverina regions. Description of route The Main Southern Railway commences as an electrified pair of tracks in the Sydney metropolitan area. Since 1924, the line branches from the Main Suburban railway line at Lidcombe and runs via Regents Park to Cabramatta, where it rejoins the original route from Granville. The line then heads towards Campbelltown and Macarthur, the current limit of electrification and suburban passenger services. The electrification previously extended to Glenlee Colliery, but this was removed following the cessation of electric haulage of freight trains in the 1990s. The line continues as a double non-electrified track south through the Southern Highlands towns of Mittagong and Goulburn to Junee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductor (rail)
A conductor (North American English) or guard (Commonwealth English) is a train crew member responsible for operational and safety duties that do not involve actual operation of the train/locomotive. The role is common worldwide under various job titles, although on many railroads the role has been discontinued. The ''conductor'' title is most common in North America. In Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries, the conductor (also sometimes known as ''train manager'') is someone who sells and/or inspects tickets. The responsibilities of the role typically include the following: * ensuring that the train follows applicable safety rules and practices * making sure that the train stays on schedule starting from the stations * opening and closing power operated doors * selling and checking tickets, and other customer service duties * ensuring that any cars and cargo are picked up and dropped off properly * completing en-route waybill, paperwork * directing the train's moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverness Railway Station
Inverness railway station serves the Scottish city of Inverness. It is the terminus of the Highland Main Line, the Aberdeen–Inverness line (of which the Inverness and Nairn Railway is now a part), the Kyle of Lochalsh line and the Far North Line. The Aberdeen and Perth lines diverge at ''Millburn Junction'' a short distance beyond Welsh's Bridge. Platforms 1–4 are from (measured via ); Millburn Junction, from Perth (or via ). The station is the zero point for the Far North Line and platforms 5–7 are along this line; Rose Street Junction, along the line, is from Perth. History Inverness station was opened on 5 November 1855 as the western terminus of the Inverness and Nairn Railway to designs by the architect, Joseph Mitchell. The station originally comprised a single covered passenger platform with three lines of rails, one for arrivals, one for departures and a spare line for carriages. In 1857 the railway company erected a clock in front of the station fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeen Railway Station
Aberdeen railway station is the main railway station in Aberdeen, Scotland. It is the busiest railway station in Scotland north of the major cities of Edinburgh and Glasgow. It is located on Guild Street in the city centre, next to Union Square. The station is managed by ScotRail. Inter-city, regional, local and sleeper train services are provided to all parts of Great Britain by ScotRail, Caledonian Sleeper, CrossCountry and London North Eastern Railway. The station is the northern terminus of the Dundee–Aberdeen line and the southern terminus of the Aberdeen–Inverness line, and is measured from Carlisle via Perth. History Pre-nationalisation The station currently standing was built and opened in 1867, although the station today has been significantly redeveloped from the original. The station and the new Denburn Valley Line enabled the main line from the south and the commuter line from Deeside to connect with the line from the north. The lines from the south h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great North Of Scotland Railway
The Great North of Scotland Railway (GNSR) was one of the two smallest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping, operating in the north-east of the country. Formed in 1845, it carried its first passengers the from Kittybrewster, in Aberdeen, to Huntly on 20 September 1854. By 1867 it owned of line and operated over a further . The early expansion was followed by a period of forced economy, but in the 1880s the railway was refurbished, express services began to run and by the end of that decade there was a suburban service in Aberdeen. The railway operated its main line between Aberdeen and and two routes west to , connections could be made at both Keith and Elgin for Highland Railway services to Inverness. There were other junctions with the Highland Railway at and , and at Aberdeen connections for journeys south over the Caledonian Railway, Caledonian and North British Railways. Its eventual area encompassed the three Scottish counties of Aber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland & Great Northern Joint Railway
The Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway (M&GNJR) was a railway network in England, in the area connecting southern Lincolnshire, the Isle of Ely and north Norfolk. It developed from several local independent concerns and was incorporated in 1893. It was jointly owned by the Midland Railway and the Great Northern Railway, and those companies had long sponsored and operated the predecessor companies. The area directly served was agricultural and sparsely populated, but seaside holidays had developed and the ran many long-distance express trains to and from the territory of the parent companies, as well as summer local trains for holidaymakers. It had the longest mileage of any joint railway in the United Kingdom. In the grouping of 1923, the two joint owners of the were absorbed into two separate companies (the Midland into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway and the Great Northern into the London and North Eastern Railway). The maintained a distinct identity which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway
The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway (S&DJR, also known as the S&D, S&DR or SDJR), was an English railway line jointly owned by the Midland Railway (MR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) that grew to connect Bath (in north-east Somerset) and Bournemouth (then in Hampshire; now in south-east Dorset), with a branch in Somerset from Evercreech Junction to Burnham-on-Sea and Bridgwater. Strictly speaking, its main line only ran from Bath Junction to Broadstone, as the Bath to Bath Junction section was wholly owned by the MR and the Broadstone to Bournemouth section was owned by the LSWR. Brought under joint ownership in 1876, the S&DJR was used for freight and local passenger traffic over the Mendip Hills, and for weekend holiday traffic to Bournemouth. Criticised as the "Slow and Dirty" or the "Slow and Doubtful", it closed in 1966 as part of the Beeching axe despite protests from the local community. Overview The initial Somerset and Dorset Railway (S&DR) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Railway History
''Australian Railway History'' is a monthly magazine covering railway history in Australia, published by the New South Wales Division of the Australian Railway Historical Society on behalf of its state and territory Divisions. History and profile It was first published in 1937 as the ''Australasian Railway and Locomotive Historical Society Bulletin''. It was renamed ''ARHS Bulletin'' in 1952. In January 2004, the magazine was re-branded as ''Australian Railway History''. Historically, the magazine had a mix of articles dealing with historical material and items on current events drawn from its affiliate publications. Today, it contains only historical articles, two or three of them being in-depth. References Publication details *''Australian Railway History: bulletin of the Australian Railway Historical Society'' Redfern, New South Wales Vol. 55, no. 795 (Jan. 2004)- *''Bulletin (Australian Railway Historical Society The Australian Railway Historical Society (AR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |