|
Tisserand's Parameter
Tisserand's parameter (or Tisserand's invariant) is a number calculated from several orbital elements (semi-major axis, orbital eccentricity, and inclination) of a relatively small object and a larger " perturbing body". It is used to distinguish different kinds of orbits. The term is named after French astronomer Félix Tisserand who derived it and applies to restricted three-body problems in which the three objects all differ greatly in mass. Definition For a small body with semi-major axis a\,\!, orbital eccentricity e\,\!, and orbital inclination i\,\!, relative to the orbit of a perturbing larger body with semimajor axis a_P, the parameter is defined as follows: :T_P\ = \frac + 2\cos i\sqrt Tisserand invariant conservation In the three-body problem, the quasi-conservation of Tisserand's invariant is derived as the limit of the Jacobi integral away from the main two bodies (usually the star and planet). Numerical simulations show that the Tisserand invariant of orbit-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics. A real orbit and its elements change over time due to gravitational Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations by other objects and the effects of general relativity. A Kepler orbit is an idealized, mathematical approximation of the orbit at a particular time. When viewed from an inertial frame, two orbiting bodies trace out distinct trajectories. Each of these trajectories has its Focus (geometry), focus at the common center of mass. When viewed from a non-inertial frame centered on one of the bodies, only the trajectory of the opposite body is apparent; Keplerian elements describe these non-inertial trajectories. An orbit has two sets of Keplerian elements depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattered Disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small Solar System bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc objects (SDOs) have orbital eccentricities ranging as high as 0.8, inclinations as high as 40°, and perihelia greater than . These extreme orbits are thought to be the result of gravitational "scattering" by the gas giants, and the objects continue to be subject to perturbation by the planet Neptune. Although the closest scattered-disc objects approach the Sun at about 30–35 AU, their orbits can extend well beyond 100 AU. This makes scattered disc objects among the coldest and most distant objects in the Solar System. The innermost portion of the scattered disc overlaps with a torus-shaped region of orbiting objects traditionally called the Kuiper belt, but its outer limits reach much farther away from the Sun and farther abov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kozai Mechanism
In celestial mechanics, the Kozai mechanism is a dynamical phenomenon affecting the orbit of a binary system perturbed by a distant third body under certain conditions. The mechanism is also named von Zeipel-Kozai-Lidov, Lidov–Kozai, Kozai–Lidov, etc., and may be termed an ''effect'', ''oscillation'', ''cycle'', or ''resonance''. This effect causes the orbit's argument of pericenter to oscillate about a constant value, which in turn leads to a periodic exchange between its eccentricity and inclination. The process occurs on timescales much longer than the orbital periods. It can drive an initially near-circular orbit to arbitrarily high eccentricity, and ''flip'' an initially moderately inclined orbit between a prograde and a retrograde motion. The effect has been found to be an important factor shaping the orbits of irregular satellites of the planets, trans-Neptunian objects, extrasolar planets, and multiple star systems. It hypothetically promotes black hole mergers. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximum amplitude response in the system. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases. All systems, including molecular systems and particles, tend to vibrate at a natural frequency depending upon their structure; when there is very little damping this frequency is approximately equal to, but slightly above, the resonant frequency. When an Oscillation, oscillat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conserved Quantity
A conserved quantity is a property or value that remains constant over time in a system even when changes occur in the system. In mathematics, a conserved quantity of a dynamical system is formally defined as a function of the dependent variables, the value of which remains constant along each trajectory of the system. Not all systems have conserved quantities, and conserved quantities are not unique, since one can always produce another such quantity by applying a suitable function, such as adding a constant, to a conserved quantity. Since many laws of physics express some kind of conservation, conserved quantities commonly exist in mathematical models of physical systems. For example, any classical mechanics model will have mechanical energy as a conserved quantity as long as the forces involved are conservative. Differential equations For a first order system of differential equations :\frac = \mathbf f(\mathbf r, t) where bold indicates vector quantities, a scala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-body Problem
In physics, specifically classical mechanics, the three-body problem is to take the initial positions and velocities (or momenta) of three point masses orbiting each other in space and then calculate their subsequent trajectories using Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. Unlike the two-body problem, the three-body problem has no general closed-form solution, meaning there is no equation that always solves it. When three bodies orbit each other, the resulting dynamical system is chaotic for most initial conditions. Because there are no solvable equations for most three-body systems, the only way to predict the motions of the bodies is to estimate them using numerical methods. The three-body problem is a special case of the -body problem. Historically, the first specific three-body problem to receive extended study was the one involving the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. In an extended modern sense, a three-body problem is any problem in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamiltonian Mechanics
In physics, Hamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of Lagrangian mechanics that emerged in 1833. Introduced by Sir William Rowan Hamilton, Hamiltonian mechanics replaces (generalized) velocities \dot q^i used in Lagrangian mechanics with (generalized) ''momenta''. Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena. Hamiltonian mechanics has a close relationship with geometry (notably, symplectic geometry and Poisson structures) and serves as a Hamilton–Jacobi equation, link between classical and quantum mechanics. Overview Phase space coordinates (''p'', ''q'') and Hamiltonian ''H'' Let (M, \mathcal L) be a Lagrangian mechanics, mechanical system with configuration space (physics), configuration space M and smooth Lagrangian_mechanics#Lagrangian, Lagrangian \mathcal L. Select a standard coordinate system (\boldsymbol,\boldsymbol) on M. The quantities \textstyle p_i(\boldsymbol,\boldsymbol,t) ~\stackrel~ / are called ''m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Eugène Delaunay
Charles-Eugène Delaunay (; 9 April 1816 – 5 August 1872) was a French astronomer and mathematician. His lunar motion studies were important in advancing both the theory of planetary motion and mathematics. Life Born in Lusigny-sur-Barse, France, to Jacques-Hubert Delaunay and Catherine Choiselat, Delaunay studied under Jean-Baptiste Biot at the Sorbonne. He worked on the mechanics of the Moon as a special case of the three-body problem. He published two volumes on the topic, each of 900 pages in length, in 1860 and 1867. The work hints at chaos in the system, and clearly demonstrates the problem of so-called "small denominators" in perturbation theory. His infinite series expression for finding the position of the Moon converged too slowly to be of practical use but was a catalyst in the development of functional analysisO'Connor & Edmund and computer algebra. Delaunay became director of the Paris Observatory in 1870 but drowned in a boating accident near Cherbourg, Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large. The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financial support of Charles Scribner, as a printing press to serve the Princeton community in 1905. Its distinctive building was constructed in 1911 on William Street in Princeton. Its first book was a new 1912 edition of John Witherspoon's ''Lectures on Moral Philosophy.'' History Princeton University Press was founded in 1905 by a recent Princeton graduate, Whitney Darrow, with financial support from another Princetonian, Charles Scribner II. Darrow and Scribner purchased the equipment and assumed the operations of two already existing local publishers, that of the ''Princeton Alumni Weekly'' and the Princeton Press. The new press printed both local newspapers, university documents, '' The Daily Princetonian'', and later added book publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate-mass Black Hole
An intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH) is a class of black hole with mass in the range of one hundred to one hundred thousand (102–105) solar masses: significantly higher than stellar black holes but lower than the hundred thousand to more than one billion (105–109) solar mass supermassive black holes. Several IMBH candidate objects have been discovered in the Milky Way galaxy and others nearby, based on indirect gas cloud velocity and accretion disk spectra observations of various evidentiary strength. Observational evidence The gravitational wave signal GW190521, which occurred on 21 May 2019 at 03:02:29 UTC, and was published on 2 September 2020, resulted from the merger of two black holes. They had masses of 85 and 65 solar masses and merged to form a black hole of 142 solar masses, with 8 solar masses radiated away as gravitational waves. Before that, the strongest evidence for IMBHs came from a few low-luminosity active galactic nuclei. Due to their activity, these gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
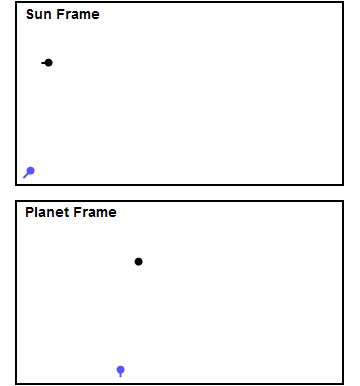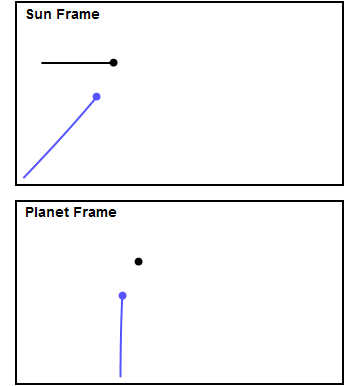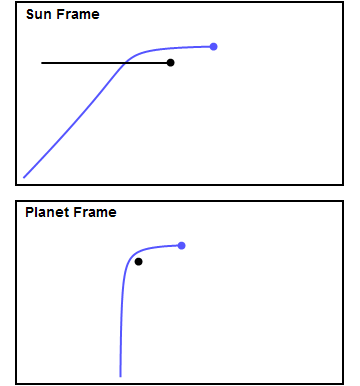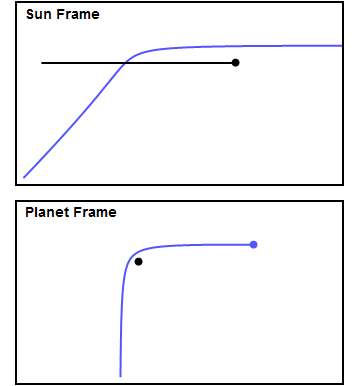
Gravity Assist
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby (spaceflight), flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the Course (navigation), path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and linear momentum by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's laws of motion#Newton's third law, Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon, and it was used by inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |