|
Tiburtia Gens
The gens Tiburtia was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Hardly any members of this gens are mentioned in history, but a large number are known from inscriptions. Origin The nomen ''Tiburtius'' is derived from the earlier cognomen ''Tiburtes'', referring to an inhabitant of the ancient city of Tibur in Latium. This indicates that the Tiburtii claimed descent from a Tiburtine family that settled at Rome, or else obtained Roman citizenship at an early period. Chase classifies the nomen among those gentilicia that either originated at Rome, or which cannot be shown to have come from anywhere else. Praenomina The main praenomina of the Tiburtii were '' Lucius'' and ''Gaius'', the two most common names at all periods of Roman history. While a number of other common praenomina are found amongst the inscriptions of this gens, the only ones that appear more than once are ''Aulus'', ''Marcus'', '' Publius'', and ''Titus''. Members * Aulus Tiburtius A. l. Timiso, one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebeian
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary. Etymology The precise origins of the group and the term are unclear, but may be related to the Greek, ''plēthos'', meaning masses. In Latin, the word is a singular collective noun, and its genitive is . Plebeians were not a monolithic social class. Those who resided in the city and were part of the four urban tribes are sometimes called the , while those who lived in the country and were part of the 31 smaller rural tribes are sometimes differentiated by using the label . ( List of Roman tribes) In ancient Rome In the annalistic tradition of Livy and Dionysius, the distinction between patricians and plebeians was as old as Rome itself, instituted by Romulus' appointment of the first hundred senators, whose descendants became the patriciate. Modern hypotheses d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria. Etruscan Etruria The ancient people of Etruria are identified as Etruscans. Their complex culture centered on numerous city-states that arose during the Villanovan period in the ninth century BCE, and they were very powerful during the Orientalizing Archaic periods. The Etruscans were a dominant culture in Italy by 650 BCE,Rix, Helmut. "Etruscan." In ''The Ancient Languages of Europe,'' ed. Roger D. Woodard. Cambridge University Press, 2008, pp. 141–164. surpassing other ancient Italic peoples such as the Ligures. Their influence may be seen beyond Etruria's confines in the Po River Valley and Latium, as well as in Campania and through their contact with the Greek colonies in Southern Italy (including Sicily). Indeed, at some Etruscan tombs, such as those of the Tumulus di Montefortini at Comeana (see Carm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ateste
Ateste (modern Este, Italy) was an ancient town of Venetia, at the southern foot of the Euganean hills, 43 feet above sea-level and 22 miles southwest of Patavium (modern Padua). The site was occupied in very early times, as archaeology begun in the late 19th century showed. Overview Large cemeteries have been excavated, which show three different periods from the 8th century BCE down to the Roman domination: * I. Italic cremation burials closely approximating to the Villanova type; * II. Venetic period, when tombs are constructed of blocks of stone, and situlae (bronze buckets), sometimes elaborately decorated, are often used to contain the funerary urns; * III. Gallic period (beginning in the 4th century BCE), when tombs are much poorer, ossuaries being of badly baked rough clay, with traces of Gallic influence characteristic of La Tène culture; cremation also continues. The many important objects found in these excavations are preserved in the local museum.G. Ghirardini in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
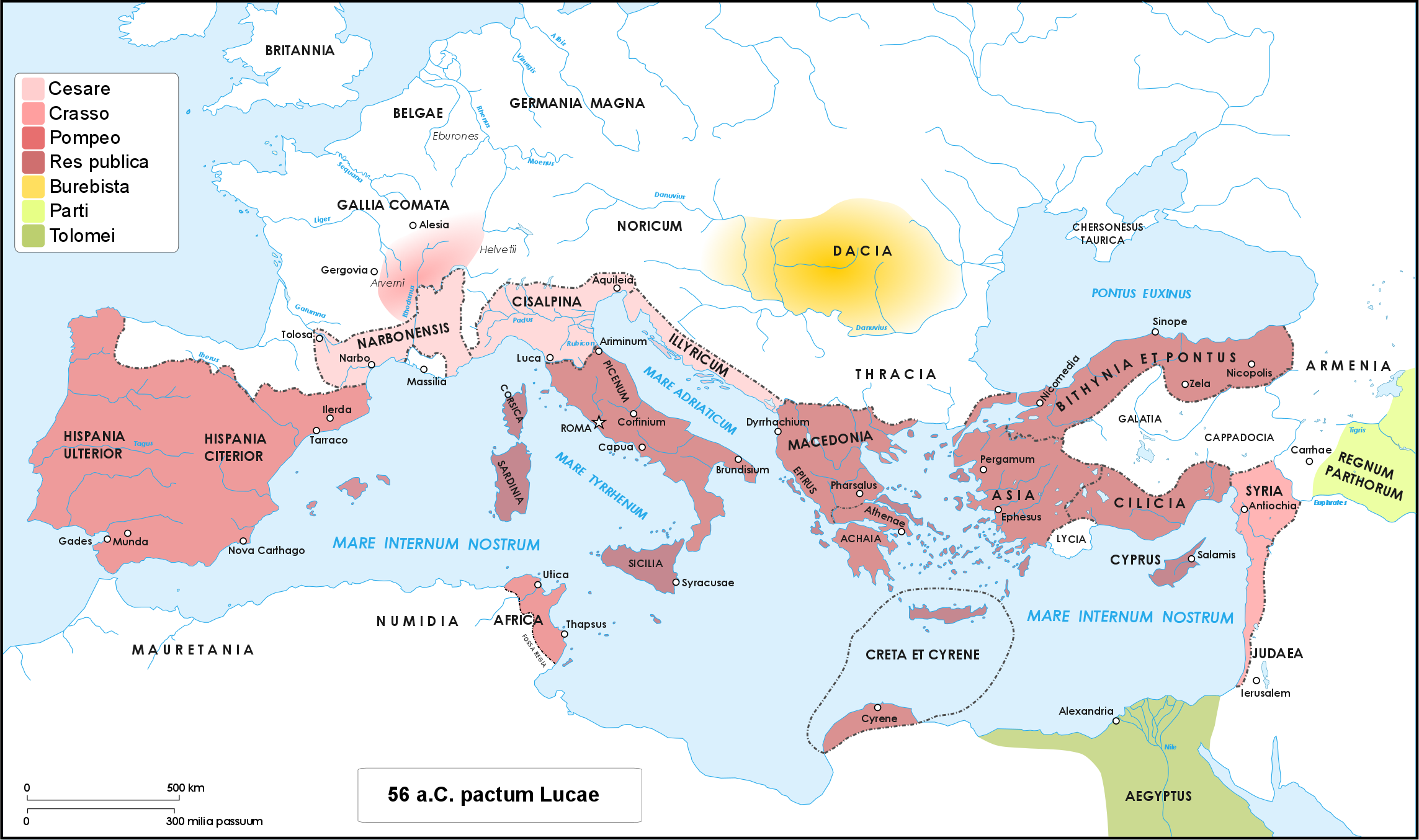
Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the first Roman province north of the Alps, and as Gallia Transalpina ("Transalpine Gaul"), distinguishing it from Cisalpine Gaul in Northern Italy. It became a Roman province in the late 2nd century BC. Gallia Narbonensis was bordered by the Pyrenees Mountains on the west, the Cévennes to the north, the Alps on the east, and the Gulf of Lion on the south; the province included the majority of the Rhone catchment. The western region of Gallia Narbonensis was known as Septimania. The province was a valuable part of the Roman Empire, owing to the Greek colony of Massalia, its location between the Spanish provinces and Rome, and its financial output. Names The province of Gallia Transalpina ("Transalpine Gaul") was later renamed Galli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarante
Quarante (; oc, Cranta) is a commune in the Hérault department in the Occitanie region in southern France. Quarante is a hilltop medieval village from the Gallo-Roman era, just 1km from the famous 17th century Canal du Midi, 8km from Capestang, 25km from Béziers, and 35km from the Mediterranean Sea. The closest train station and regional airport is in Béziers, and 59km to the north is the city of Carcassonne, famous for its medieval walled citadel. International airports within an hour are; Carcassonne, Perpignan, Montpellier, and with Toulouse being two hours away. Installed on a Roman oppidum, the town had a significant occupation during those times, as evidenced by the artifacts found and available for viewing in the local museum. The Sainte-Marie de Quarante Abbey, built in 902, is located in the town square. You can still see the original rempart walls, towers and prison in the ancient town center on the stone roads from the 12th and 13th centuries on Rue des Remparts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Vatinius
Publius Vatinius was a Roman politician during the last decades of the Republic. He served as a Caesarian-allied plebeian tribune in the year 59 – he was the tribune that proposed the law giving Caesar his Gallic command – and later fought on that side of the civil war. Caesar made him consul in 47 BC; he later fought in Illyricum for the Caesarians and celebrated a triumph for his victories there in 42 BC. Biography Many details about Vatinius' life emerge from Cicero's claims, which "must be taken with a grain of salt and understood as a piece of rhetorical invective, in which an orator would do anything to discredit his opponent, including the use of half-truths and exaggerations". Early political life Vatinius did not appear to have had consular ancestors, making him a ''novus homo''. His first recorded position was a quaestorship in 63 BC, the same year Marcus Tullius Cicero was consul. He was elected last to the quaestorship. Cicero claims he was allotte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Labienus
Titus Labienus (c. 10017 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul, mentioned frequently in the accounts of his military campaigns, Labienus chose to oppose him during the Civil War and was killed at Munda. He was the father of Quintus Labienus. Biography Early career As his praetorship was in 60 or 59 BC, Titus Labienus most likely was born around 100 BC.Tyrrell(3) Many sources suggest that he came from the town of Cingulum in Picenum. His family was of equestrian status. He most likely had early ties with Pompey during his time as a patron for Picenum and his desire to rise in military rank. His early service was c. 78–75 BC in Cilicia under Publius Servilius Vatia Isauricus fighting pirates and the Isaurian hill tribes. Tribune of the Plebs, Trial of Gaius Rabirius In 63 BC, Titus Labienus was a tribun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeius
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of Rome from republic to empire. He was (for a time) a student of Roman general Sulla as well as the political ally, and later enemy, of Julius Caesar. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving the dictator Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–82 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first Roman consulship without following the traditional ''cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as Roman consul on three occasions. He celebrated three Roman triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, the Third Servile War, the Third Mithridatic War, and in vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apsus
The Seman is a major river in western Albania. It is formed by the confluence of the rivers Devoll and Osum, a few km west of Kuçovë. It is long ( with its longest source river Devoll) and its drainage basin is . Its average discharge is . It meanders generally westwards through a flat lowland. Near Fier it receives Gjanica from the left. It flows into the Adriatic Sea at the southern margin of the Divjakë-Karavasta National Park. Name In classical antiquity, the Seman River was known as the ''Apsus'', which is a derivative of the Indo-European root ''*ăp-'' "water, river". The Illyrian hydronym ''Apsus'', corresponds to ''Apsias'', a river name in southern Italy brought by Illyrian migrations (Iapygians) in the region. The contemporary Albanian name ''Seman/Semen'' ( definite form: ''Semani/Semeni''), which is used to indicate the lower course of the river, evolved from ''*Apson-'' through Albanian phonetic changes. Also the contemporary Albanian name ''Osum The Osum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centurion
A centurion (; la, centurio , . la, centuriones, label=none; grc-gre, κεντυρίων, kentyríōn, or ) was a position in the Roman army during classical antiquity, nominally the commander of a century (), a military unit of around 80 legionaries. In a Roman legion, centuries were grouped into cohorts and commanded by their senior-most centurion. The prestigious first cohort was led by the '' primus pilus'', the most senior centurion in the legion and its fourth-in-command who was next in line for promotion to Praefectus Castrorum, and the primi ordines who were the centurions of the first cohort. A centurion's symbol of office was the vine staff, with which they disciplined even Roman citizens, who were otherwise legally protected from corporal punishment by the Porcian Laws. Centurions also served in the Roman navy. After the 107 BC Marian reforms of Gaius Marius, centurions were professional officers. In Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, the Byzantine army's cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |