|
Thyroid Hormone Binding Ratio
Thyroid hormone binding ratio (THBR) is a thyroid function test that measures the "uptake" of T3 or T4 tracer by thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) in a given serum sample. This provides an indirect and ''reciprocal'' estimate of the available binding sites on TBG within the sample. The results are then reported as a ratio to normal serum. Indications Attempts to correct for changes in thyroid binding globulin due to liver disease, protein losing states, pregnancy or various drugs It is used to calculate free thyroxine index (total T4 x T3 uptake), an estimate of free T4. Free thyroxine index may be calculated with increased diagnostic accuracy using direct TBG measurement when the total hormone concentration is abnormally elevated Examples * In patients with hyperthyroidism, there will be fewer available binding sites on TBG (due to the increased circulating T3 / T4). This will lead to an increased thyroid hormone binding ratio. * In patients with hypothyroidism, there will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Function Tests
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) is a collective term for blood tests used to check the function of the thyroid. TFTs may be requested if a patient is thought to suffer from hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), or to monitor the effectiveness of either thyroid-suppression or hormone replacement therapy. It is also requested routinely in conditions linked to thyroid disease, such as atrial fibrillation and anxiety disorder. A TFT panel typically includes thyroid hormones such as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) and thyroxine (T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) depending on local laboratory policy. Thyroid-stimulating hormone Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) is generally increased in hypothyroidism and decreased in hyperthyroidism,Military Obstetrics & Gynecology > Thyroid Function TestsIn turn citing: Operational Medicine 2001, Health Care in Military Settings, NAVMED P-5139, May 1, 2001, Bureau of Medicine and Surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anticonvulsant, anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The intravenous form, fosphenytoin, is used for status epilepticus that does not improve with benzodiazepines. It may also be used for certain heart arrhythmias or neuropathic pain. It can be taken intravenously or by mouth. The intravenous form generally begins working within 30 minutes and is effective for roughly 24 hours. Blood levels can be measured to determine the proper dose. Common side effects include nausea, stomach pain, loss of appetite, poor coordination, hypertrichosis, increased hair growth, and Gingival hyperplasia, enlargement of the gums. Potentially serious side effects include sleepiness, self harm, liver problems, bone marrow suppression, hypotension, low blood pressure, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and atrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Procedures
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland, thyroid, parathyroid gland, parathyroid, pituitary gland, pituitary, pineal gland, pineal, and adrenal glands, and the (male) testis and (female) ovaries. The hypothalamus, pancreas, and thymus also function as endocrine glands, among other functions. (The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are organs of the Neuroendocrinology#Neuroendocrine system, neuroendocrine system. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamusit is located in the brain adjacent to the pituitary glandis to link the endocrine system to the nervous system via the pituitary gland.) Other organs, such as the kidneys, also have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse. Extraction A venipuncture is useful as it is a minimally invasive way to obtain cells and extracellular fluid ( plasma) from the body for analysis. Blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium that provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues and carries waste products back to the excretory systems f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Dysalbuminemic Hyperthyroxinemia
Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia (FDH) rare genetic condition that is a common cause oeuthyroid hyperthyroxinemiaand is associated with mutations in the human serum albumin gene. It is an autosomal dominant condition that is often mistaken for resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH) syndromes or hyperthyroidism. FDH is characterized by high levels of thyroxine (T4) and normal levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Due to the mutations in the albumin gene, an abnormal albumin protein binds thyroid hormones with a high affinity than normal. This explains why those with familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia have increased T4 levels and normal TSH levels. Signs and symptoms Familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia is usually asymptomatic. The clinical features are not specific and vary from patient to patient. In some cases, symptoms such as those seen in hyperthyroidism have been recorded like: palpitations, weight losstremors and anxiety. Cause The mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylbutazone
Phenylbutazone, often referred to as "bute", is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for the short-term treatment of pain and fever in animals. In the United States and United Kingdom, it is no longer approved for human use (except in the United Kingdom for ankylosing spondylitis), as it can cause severe adverse effects such as suppression of white blood cell production and aplastic anemia. This drug was implicated in the 2013 meat adulteration scandal. Positive phenylbutazone tests in horse meat were uncommon in the UK, however. Uses In humans Phenylbutazone was originally made available for use in humans for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and gout in 1949. However, it is no longer approved, and therefore not marketed, for any human use in the United States. In the UK it is used to treat ankylosing spondylitis, but only when other therapies are unsuitable. In horses Phenylbutazone is the most commonly used NSAID for horses in the United States.McIlwraith C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a active metabolite, metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin for willow tree, from which it was initially identified and derived. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. Uses Medicine Salicylic acid as a medication is commonly used to remove the outermost layer of the skin. As such, it is used to treat warts, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, ringworm, dandruff, and ichthyosis. Similar to other hydroxy acids, salicylic acid is an ingredient in many skincare products for the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, psoriasis, calluses, Corn (medicine), corns, keratosis pilaris, acanthosis nigricans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine, sold under the brand name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other medications and as a Therapy#Lines of therapy, second-line agent in bipolar disorder. Carbamazepine appears to work as well as phenytoin and valproate for focal and generalized seizures. It is not effective for absence seizure, absence or myoclonic seizures. Carbamazepine was discovered in 1953 by Swiss chemist Walter Schindler. It was first marketed in 1962. It is available as a generic medication. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, it was the 185th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Photoswitchable analogues of carbamazepine have been developed to control its pharmacological activity locally and on demand using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the uncontrolled and excessive firing of neurons during seizures and in doing so can also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs have diverse mechanisms of action but many block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GABA transporter type 1, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
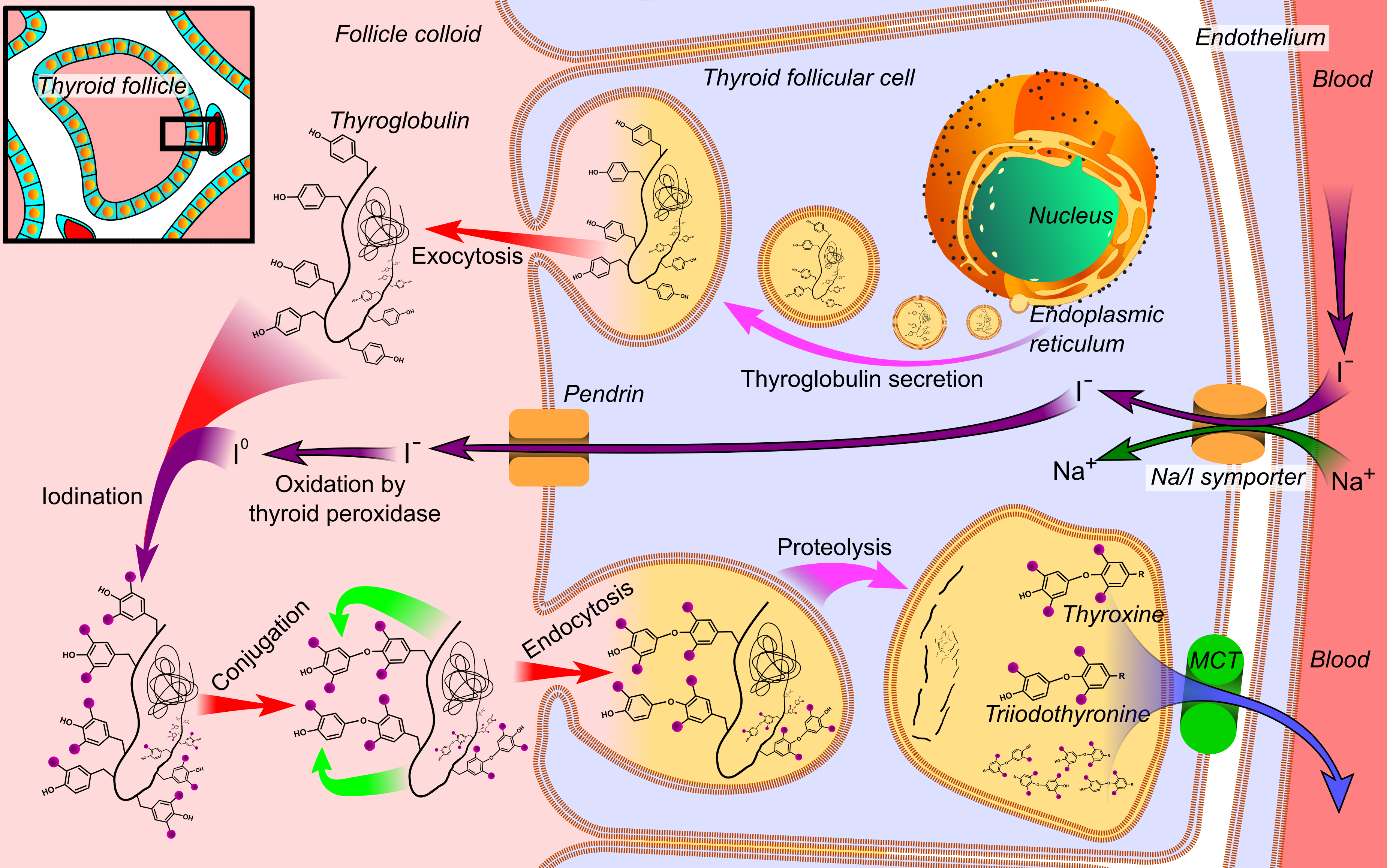
Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine, T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary, Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid, Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid, thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |