|
Thomas Mann
Paul Thomas Mann ( , ; ; 6 June 1875 – 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novellas are noted for their insight into the psychology of the artist and the intellectual. His analysis and critique of the European and German soul used modernized versions of German and Biblical stories, as well as the ideas of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Nietzsche, and Arthur Schopenhauer. Mann was a member of the Hanseaten (class), hanseatic Mann family and portrayed his family and class in his first novel, ''Buddenbrooks''. His older brother was the radical writer Heinrich Mann and three of Mann's six children – Erika Mann, Klaus Mann and Golo Mann – also became significant German writers. When Adolf Hitler Adolf Hitler's rise to power, came to power in 1933, Mann fled to Switzerland. When World War II broke out in 1939, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph And His Brothers
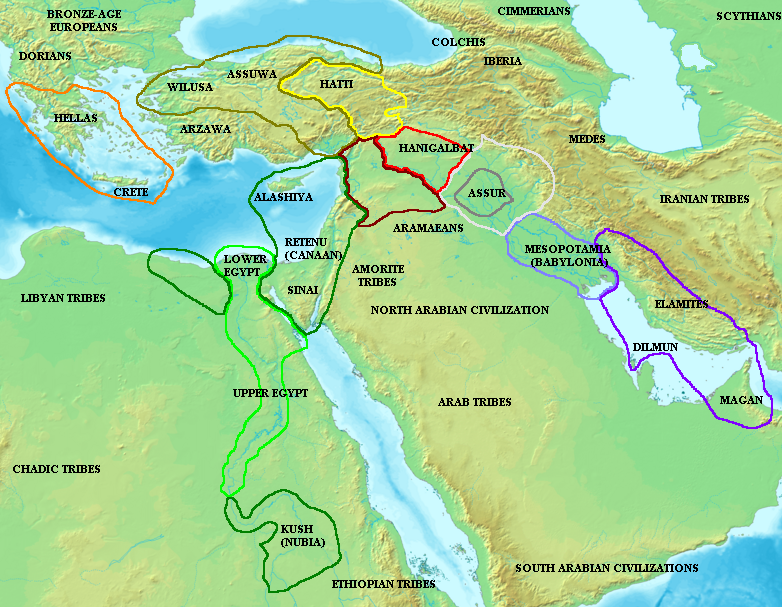
''Joseph and His Brothers'' (, ) is a four-part novel by Thomas Mann, written over the course of 16 years. Mann retells the familiar stories of Genesis, from Jacob to Joseph (chapters 27–50), setting it in the historical context of the Amarna Period. Mann considered it his greatest work. The tetralogy consists of: * ''The Stories of Jacob'' (''Die Geschichten Jaakobs''; written December 1926 to October 1930, Genesis 27–36) * ''Young Joseph'' (''Der junge Joseph''; written January 1931 to June 1932, Genesis 37) * ''Joseph in Egypt'' (''Joseph in Ägypten''; written July 1932 to 23 August 1936, Genesis 38–39) * ''Joseph the Provider'' (''Joseph, der Ernährer''; written 10 August 1940 to 4 January 1943, Genesis 40–50) Themes Mann's presentation of the ancient Orient and the origins of Judaism is influenced by Alfred Jeremias' 1904 ''Das Alte Testament im Lichte des Alten Orients'', emphasizing Babylonian influence in the editing of Genesis, and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 Nobel Prize In Literature
The 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the German author Thomas Mann (1875–1955) "principally for his great novel, Buddenbrooks, which has won steadily increased recognition as one of the classic works of contemporary literature." He is the fourth German author to be awarded the literature prize after Paul von Heyse in 1910 Nobel Prize in Literature, 1910. Laureate Thomas Mann was a prolific writer of fiction and novels who wrote in a variety of genres. He was a merchant's son and was supposed to inherit the family's grain business in Lübeck, but like his older brother Heinrich Mann, Heinrich, he decided to focus on literature. In 1905, he married Katia Mann, Katia Pringsheim, and the couple had six children, four of whom also became significant authors (Erika Mann, Erika, Klaus Mann, Klaus, and Golo Mann, Golo). His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novellas are noted for their insight into the psychology of the artist and the intellectual. His analysis an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Mann
Luiz Heinrich Mann (; March 27, 1871 – March 11, 1950), best known as simply Heinrich Mann, was a German writer known for his sociopolitical novels. From 1930 until 1933, he was president of the fine poetry division of the Prussian Academy of Arts. His fierce criticism of the growing Fascism and Nazism forced him to flee Germany after the Nazis came to power during 1933. He was the elder brother of writer Thomas Mann. Early life Born in Lübeck, as the oldest child of Senator Thomas Johann Heinrich Mann, grain merchant and finance minister of the Free City of Lübeck, a state of the German Empire, and Júlia da Silva Bruhns. He was the elder brother of the writer Thomas Mann with whom he had a lifelong rivalry. The Mann family was an affluent family of grain merchants of the Hanseatic city of Lübeck. After the death of his father, his mother relocated the family to Munich, where Heinrich began his career as a ''freier Schriftsteller'' (free writer). In 1914, he married a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Júlia Da Silva Bruhns
Júlia da Silva Bruhns (14 August 1851, Paraty – 11 March 1923, Weßling) was the Brazilian mother of Thomas and Heinrich Mann and one of the matriarchs of the Mann family. Biography Da Silva Bruhns was born in Paraty, Rio de Janeiro state on Boa Vista sugar plantation. Raised Roman Catholic, she was the daughter of a Lübecker farmer Johann Ludwig Herman Bruhns and his wife Maria Luísa da Silva, herself the daughter of a Portuguese immigrant and landowner and his wife, who was of Criollo descent. Johann had emigrated from Lübeck to Brazil at age 16 and changed his name to João Luis Germano Bruhns. He owned several sugar cane plantations between Santos and Rio de Janeiro. Maria died at age 28 in childbirth when da Silva Bruhns was six. The following year, she, her father, and her four siblings moved to Lübeck, where da Silva Bruhns and her sister, neither of whom spoke German, lived in a boarding house for girls. Their father, meanwhile, returned to Brazil to care for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Mann (scholar)
Michael Thomas Mann (April 21, 1919 – January 1, 1977) was a German-born musician and professor of German literature. Life Born in Munich, Michael Mann was the youngest and sixth child of writer Thomas Mann and Katia Mann. His older siblings were Erika Mann, Erika, Klaus Mann, Klaus, Golo Mann, Golo, Monika Mann, Monika and Elisabeth Mann Borgese, Elisabeth. He was of Jews, Jewish descent from his mother's side. Due to his being the grandson of Júlia da Silva Bruhns, he was also of Portuguese-Indigenous peoples in Brazil, Indigenous Brazilian partial descent. He studied viola and violin in Zürich, Paris and New York City. He was a viola player in the San Francisco Symphony Orchestra from 1942 to 1947 as well as being a solo viola player. Accompanied by pianist Yaltah Menuhin, he made a concert tour in 1951 and recorded the 1948 ''Viola Sonata'' by Ernst Krenek. He was forced to give up professional music due to a neuropathy. Mann gained a master's degree in musicology from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabeth Mann Borgese
Elisabeth Veronika Mann Borgese, (24 April 1918 – 8 February 2002) was an internationally recognized expert on maritime law and policy and the protection of the environment. Called "the mother of the oceans", she received the Order of Canada and awards from the governments of Austria, China, Colombia, Germany, the United Nations and the World Conservation Union. Elisabeth was a child of Nobel Prize–winning German author Thomas Mann and his wife Katia Mann. Born in Germany, Elisabeth experienced displacement due to the rise of the Nazi Party and became a citizen first of Czechoslovakia, then of the United States, and finally of Canada. Elisabeth Mann Borgese worked as a senior fellow at the Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions in Santa Barbara, California and as a university professor at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. She became a proponent of international cooperation and world federalism. In 1968, she was one of the founding memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monika Mann
Monika Mann (7 June 1910 – 17 March 1992) was a Germans, German American author and feature writer. She was born in Munich, German Empire, Germany, the fourth of six children of the Nobel Prize–winning author Thomas Mann and Katia Mann, Katia, née Katharina Pringsheim. She trained as a pianist and her early attempts at a musical career seemed promising, but were not met with success and she instead pursued a career as a writer. She married in 1939 but lost her husband the following year, when the ship on which they were travelling to Canada was sunk by a German submarine. Later that year she joined her family in Princeton, New Jersey, and was granted US citizenship in 1952. Between 1954 and 1986, she lived with her partner Antonio Spadaro in ''Villa Monacone'' on Capri. This was her most productive time as a writer and her books and several magazine articles were written during this period. After the death of her partner she left Capri and spent her last years until her death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golo Mann
Golo Mann (born Angelus Gottfried Thomas Mann; 27 March 1909 – 7 April 1994) was a popular German historian and essayist. After completing a doctorate in philosophy under Karl Jaspers at Heidelberg, in 1933 he fled Hitler's Germany. He followed his father, the writer Thomas Mann, and other members of his family in emigrating first to France, then to Switzerland and, on the eve of war, to the United States. From the late 1950s he re-established himself in Switzerland and West Germany as a literary historian. Mann was perhaps best known for his master work ''German History in the 19th and 20th Century'' (1958). A survey of German political history, it emphasised the nihilistic and aberrant nature of the Hitler regime. In his later years, Mann took issue with historians who sought to contextualise the crimes of the regime by comparing them with those of Stalinism in Soviet Union and with wartime Allied bombing. At the same time he was sharply critical of those, broadly on the lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus Mann
Klaus Heinrich Thomas Mann (18 November 1906 – 21 May 1949) was a German writer and dissident. He was the son of Thomas Mann, a nephew of Heinrich Mann and brother of Erika Mann (with whom he maintained a lifelong close relationship) and Golo Mann. Klaus moved to the United States to escape Nazism, and after training in counterintelligence as one of the Ritchie Boys, he served in Europe during World War II, becoming one of the first outsiders to witness the horrors of the concentration camps. His books '' Escape to Life'' (co-written with his sister Erika Mann), and ''The Turning Point'' have attained a historical importance as frequently cited primary documents of the experience of exile undergone by members of the German intelligentsia and arts community who fled the Third Reich. This genre is referred to as Exilliteratur. He is best known for his 1936 novel, ''Mephisto'', about an actor who sells his soul to the devil, by attaching his career to the rise of the Nazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erika Mann
Erika Julia Hedwig Mann (9 November 1905 – 27 August 1969) was a German actress and writer, daughter of the novelist Thomas Mann. Erika lived a bohemian lifestyle in Berlin and became a critic of National Socialism. After Hitler came to power in 1933, she moved to Switzerland, and married the poet W. H. Auden, purely to obtain a British passport and so avoid becoming stateless when the Germans cancelled her citizenship. She continued to attack Nazism, most notably with her 1938 book ''School for Barbarians'', a critique of the Nazi education system. During World War II, Mann worked for the BBC and became a war correspondent attached to the Allied forces after D-Day. She attended the Nuremberg trials before moving to America to support her exiled parents. Her criticisms of American foreign policy led to her being considered for deportation. After her parents moved to Switzerland in 1952, she also settled there. She wrote a biography of her father and died in Zürich in 1969. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katia Mann
Katia Mann (born Katharina Hedwig Pringsheim; 24 July 1883 – 25 April 1980) was the youngest child and only daughter (among four sons) of the German Jewish mathematician and artist Alfred Pringsheim and his wife Hedwig Pringsheim, who was an actress in Berlin before her marriage. Katia was also a granddaughter of the writer and women's rights activist Hedwig Dohm. Her twin brother Klaus was a conductor, composer, music writer and music pedagogue, active in Germany and Japan. She married the writer Thomas Mann. Life Katia was born in Feldafing near Munich, into one of the wealthiest families in Germany. She was the granddaughter of German-Jewish industrialist Rudolf Pringsheim and the great-niece of the banker Hugo Pringsheim. At the age of 21, in the fall of 1904, she aborted her studies of physics and mathematics on the request of her mother and aunt, to marry the writer Thomas Mann on 11 February 1905, in Munich. She continued her studies as a guest student for another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |