|
Thirlwall's Law
Thirlwall's law (named after Anthony Thirlwall) states that if long-run balance of payments equilibrium on current account is a requirement, and the real exchange rate stays relatively constant, then the long run growth of a country can be approximated by the ratio of the growth of exports to the income elasticity of demand for imports (Thirlwall, 1979). If the real exchange rate varies considerably, but the price elasticities of demand for imports and exports are low, the long run growth of the economy will then be determined by the growth of world income times the ratio of the income elasticity of demand for exports and imports which are determined by the structural characteristics of countries. One important example of this is that if developing countries produce mainly primary products and low value manufactured goods with a low income elasticity of demand, while developed countries specialise in high income elasticity manufactured goods the developing countries will grow at a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Thirlwall
Anthony Philip Thirlwall (21 April 1941 – 8 November 2023) was a British economist who was Professor of Applied Economics at the University of Kent. He made major contributions to regional economics; the analysis of unemployment and inflation; balance of payments theory, and to growth and development economics with particular reference to developing countries. He was the author of the bestselling textbook ''Economics of Development: Theory and Evidence'' (Palgrave Macmillan) now in its ninth edition. He was also the biographer and literary executor of the famous Cambridge economist Nicholas Kaldor. Perhaps his most notable contribution was to show that if long-run balance of payments equilibrium is a requirement for a country, its growth of national income can be approximated by the ratio of the growth of exports to the income elasticity of demand for imports ( Thirlwall's Law). Early life and education Anthony Philip Thirlwall was born on 21 April 1941. He was educated at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Of Payments
In international economics, the balance of payments (also known as balance of international payments and abbreviated BOP or BoP) of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time (e.g., a quarter or a year) and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. In other words, it is economic transactions between countries during a period of time. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services. The balance of payments consists of three primary components: the current account, the financial account, and the capital account. The current account reflects a country's net income, while the financial account reflects the net change in ownership of national assets. The capital account reflects a part that has little effect on the total, and represents the sum of unilateral capital account transfers, and the acquisitions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
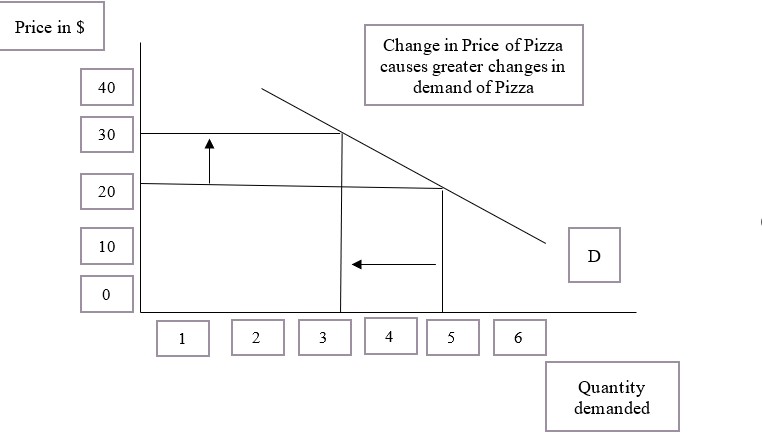
Price Elasticities
In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another. For example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10% increase in price will cause the quantity demanded to fall by 20%. Elasticity in economics provides an understanding of changes in the behavior of the buyers and sellers with price changes. There are two types of elasticity for demand and supply, one is inelastic demand and supply and the other one is elastic demand and supply. Introduction The concept of price elasticity was first cited in an informal form in the book '' Principles of Economics'' published by the author Alfred Marshall in 1890. Subsequently, a major study of the price elasticity of supply and the price elasticity of demand for US products was undertaken by Joshua Levy and Trevor Pollock in the late 1960s. Elasticity is an important concept in neoclassical economic theory, and enables in the understanding of various economic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Harrod
Sir Henry Roy Forbes Harrod (13 February 1900 – 8 March 1978) was an English economist. He is best known for writing '' The Life of John Maynard Keynes'' (1951) and for the development of the Harrod–Domar model, which he and Evsey Domar developed independently. He is also known for his ''International Economics'', a former standard textbook of international economics, the first edition of which contained some observations and ruminations (wanting in subsequent editions) that would foreshadow theories developed independently by later scholars (such as the Balassa–Samuelson effect). Biography Harrod was born in London to businessman Henry Dawes Harrod and novelist Frances Forbes-Robertson. He attended St Paul's School and then Westminster School. Harrod attended New College in Oxford on a history scholarship. After a brief period in the Artillery, he gained a first in literae humaniores in 1921, and a first in modern history the following year. Afterwards he spent some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Trade Multiplier
Foreign may refer to: Government * Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries * Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries ** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government ** Foreign office and foreign minister * United States state law, a legal matter in another state Science and technology * Foreign accent syndrome, a side effect of severe brain injury * Foreign key, a constraint in a relational database Arts and entertainment * Foreign film or world cinema, films and film industries of non-English-speaking countries * Foreign music or world music * Foreign literature or world literature * ''Foreign Policy'', a magazine Music * "Foreign", a song by Jessica Mauboy from her 2010 album ''Get 'Em Girls'' * "Foreign" (Trey Songz song), 2014 * "Foreign", a song by Lil Pump from the album ''Lil Pump'' Other uses * Foreign corporation, a corporation that can do business outside its jurisdiction * Foreign language, a language not spoken by the people of a cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Development Economics
Development economics is a branch of economics that deals with economic aspects of the development process in low- and middle- income countries. Its focus is not only on methods of promoting economic development, economic growth and structural change but also on improving the potential for the mass of the population, for example, through health, education and workplace conditions, whether through public or private channels. Development economics involves the creation of theories and methods that aid in the determination of policies and practices and can be implemented at either the domestic or international level. This may involve restructuring market incentives or using mathematical methods such as intertemporal optimization for project analysis, or it may involve a mixture of quantitative and qualitative methods. Common topics include growth theory, poverty and inequality, human capital, and institutions. Unlike in many other fields of economics, approaches in development econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eponymous Laws Of Economics
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovations, biological nomenclature, astronomical objects, works of art and media, and tribal names. Various orthographic conventions are used for eponyms. Usage of the word The term ''eponym'' functions in multiple related ways, all based on an explicit relationship between two named things. ''Eponym'' may refer to a person or, less commonly, a place or thing for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. ''Eponym'' may also refer to someone or something named after, or believed to be named after, a person or, less commonly, a place or thing. A person, place, or thing named after a particular person share an eponymous relationship. In this way, Elizabeth I of England is the eponym of the Elizabethan era, but the Elizabethan e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |