|
Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. Thermostats are used in any device or system that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature. Examples include building heating, central heating, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, as well as kitchen equipment including ovens and refrigerators and medical and scientific incubators. In scientific literature, these devices are often broadly classified as thermostatically controlled loads (TCLs). Thermostatically controlled loads comprise roughly 50% of the overall electricity demand in the United States. A thermostat operates as a "closed loop" control device, as it seeks to reduce the error between the desired and measured temperatures. Sometimes a thermostat combines both the sensing and control action elements of a controlled system, such as in an automotive thermostat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wax Thermostatic Element
The wax thermostatic element was invented in 1934 by Sergius Vernet (1899–1968). Its principal application is in automotive thermostats used in the engine cooling system. The first applications in the plumbing and HVAC, heating industries were in Sweden (1970) and in Switzerland (1971). Wax thermostatic elements transform heat energy into mechanical energy using the thermal expansion of waxes when they melt. This wax motor principle also finds applications besides engine cooling systems, including heating system thermostatic radiator valves, plumbing, industrial, and agriculture. Automotive thermostats The internal combustion engine cooling thermostat maintains the temperature of the engine near its optimum operating temperature by regulating the flow of coolant to an air cooled radiator (engine cooling), radiator. This regulation is now carried out by an internal thermostat. Conveniently, both the sensing element of the thermostat and its control valve may be placed at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeywell Round Thermostat
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building automation, industrial automation, and energy and sustainability solutions (ESS). Honeywell also owns and operates Sandia National Laboratories under contract with the U.S. Department of Energy. Honeywell is a Fortune 500 company, ranked 115th in 2023. In 2024, the corporation had a global workforce of approximately 102,000 employees. As of 2023, the current chairman and chief executive officer is Vimal Kapur. The corporation's name, Honeywell International Inc., is a product of the merger of Honeywell Inc. and AlliedSignal in 1999. The corporation headquarters were consolidated with AlliedSignal's headquarters in Morristown, New Jersey. The combined company chose the name "Honeywell" because of the considerable brand recognition. Honeywell was a component of the Dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerator
A refrigerator, commonly shortened to fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermal insulation, thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so that its inside is cooled to a temperature below the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential Food preservation, food storage technique around the world. The low temperature reduces the reproduction rate of bacteria, so the refrigerator lowers the rate of Food spoilage, spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. The optimal temperature range for perishable food storage is .Keep your fridge-freezer clean and ice-free ''BBC''. 30 April 2008 A freezer is a specialized refrigerator, or portion of a refrigerator, that maintains its contents’ temperature below the freezing point of water. The refrigerator replaced the icebox, which had been a common househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Heating
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses. Domestically, water is traditionally heated in vessels known as ''water heaters'', ''kettles'', ''cauldrons'', ''pots'', or ''coppers''. These metal vessels that heat a batch of water do not produce a continual supply of heated water at a preset temperature. Rarely, hot water occurs naturally, usually from natural hot springs. The temperature varies with the consumption rate, becoming cooler as flow increases. Appliances that provide a continual supply of hot water are called ''water heaters'', ''hot water heaters'', ''hot water tanks'', ''boilers'', ''heat exchangers'', ''geysers'' (Southern Africa and the Arab world), or ''calorifiers''. These names depend on region, and whether they heat Drinking water, potable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallic Strip
A bimetallic strip or bimetal strip is a strip that consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated. The different expansion rates cause the strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. Thus, a bimetal strip converts a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled. Common applications include temperature sensing (thermometer) and regulation (thermostat). The invention of the bimetallic strip is generally credited to John Harrison, an eighteenth-century clockmaker who made it for his third marine chronometer (H3) of 1759 to compensate for temperature-induced changes in the balance spring. Harrison's invention is recognized in the memorial to him in Westminster Abbey, England. Characteristics The strip consists of two st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
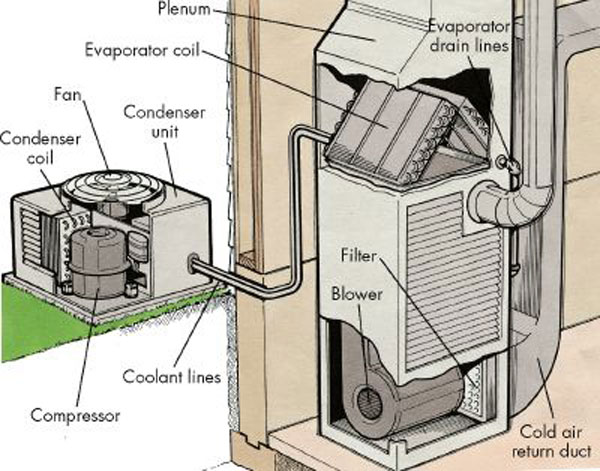
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature, and in some cases, also controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or through other methods, such as passive cooling and ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners but use a reversing valve, allowing them to both heat and cool an enclosed space. Air conditioners, which typically use vapor-compression refrigeration, range in size from small units used in vehicles or single rooms to massive units that can cool large buildings. Air source heat pumps, which can be used for heating as well as cooling, are becoming increasingly common in cool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermocouple
A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of the Seebeck effect, and this voltage can be interpreted to measure temperature. Thermocouples are widely used as list of temperature sensors, temperature sensors. Commercial thermocouples are inexpensive, interchangeable, are supplied with standard Electrical connector, connectors, and can measure a wide range of temperatures. In contrast to most other methods of temperature measurement, thermocouples are self-powered and require no external form of excitation. The main limitation with thermocouples is accuracy; system errors of less than one degree Celsius (°C) can be difficult to achieve. Thermocouples are widely used in science and industry. Applications include temperature measurement for kilns, gas turbine exhaust, diesel engines, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of the moment often form a loop or hysteresis curve, where there are different values of one variable depending on the direction of change of another variable. This history dependence is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive and the remanence that retains a record of the Earth's magnetic field magnitude in the past. Hysteresis occurs in ferromagnetic and ferroelectricity, ferroelectric materials, as well as in the deformation (mechanics), deformation of rubber bands and shape-memory alloys and many other natural phenomena. In natural systems, it is often associated with irreversible process, irreversible thermodynamic change such as phase transitions and with internal friction; and dissipation is a common side effect. Hysteresis can be fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oven
upA double oven A ceramic oven An oven is a tool that is used to expose materials to a hot environment. Ovens contain a hollow chamber and provide a means of heating the chamber in a controlled way. In use since antiquity, they have been used to accomplish a wide variety of tasks requiring controlled heating. Because they are used for a variety of purposes, there are many different types of ovens. These types differ depending on their intended purpose and based upon how they generate heat. Ovens are often used for cooking, usually baking, sometimes broiling; they can be used to heat food to a desired temperature. Ovens are also used in the manufacturing of ceramics and pottery; these ovens are sometimes referred to as kilns. Metallurgical furnaces are ovens used in the manufacturing of metals, while glass furnaces are ovens used to produce glass. There are many methods by which different types of ovens produce heat. Some ovens heat materials using the combustion of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
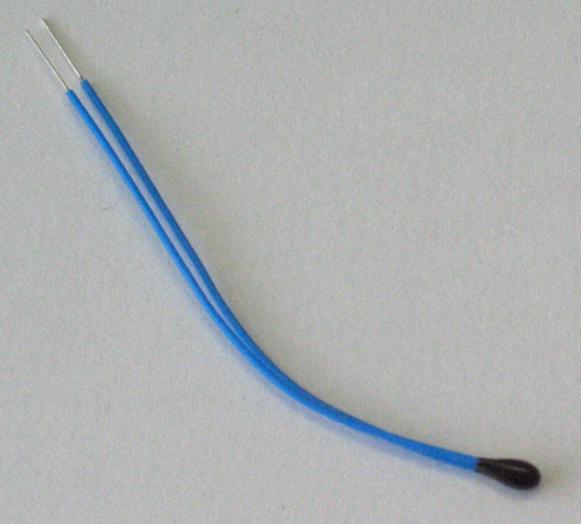
Thermistor
A thermistor is a semiconductor type of resistor in which the resistance is strongly dependent on temperature. The word ''thermistor'' is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''. The varying resistance with temperature allows these devices to be used as temperature sensors, or to control current as a function of temperature. Some thermistors have decreasing resistance with temperature, while other types have increasing resistance with temperature. This allows them to be used for limiting current to cold circuits, e.g. for inrush current protection, or for limiting current to hot circuits, e.g. to prevent thermal runaway. Thermistors are categorized based on their conduction models. ''Negative-temperature-coefficient'' (NTC) thermistors have ''less'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures, while ''positive-temperature-coefficient'' (PTC) thermistors have ''more'' resistance at ''higher'' temperatures. NTC thermistors are widely used as inrush current limiters and temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |