|
The Skystone
''The Skystone'' is a historical fiction novel written by Jack Whyte, which was first published in 1992. The story is told by a Roman Officer called Publius Varrus, who is an expert blacksmith as well as a soldier. In the early fifth century, amid the violent struggles between the people of Britain and the invading Saxons, Picts and Scots, he and his former General, Caius Britannicus, forge the government and military system that will become known as the Round Table, and initiate a chain of events that will lead to the coronation of the High King known as Arthur. Plot summary ;Invasion: The book begins with Publius Varrus laying its framework: he is retelling his history and the history of the Roman withdrawal from Britain. He then begins by talking about an ambush by Celts where he and Caius Britannicus are injured. While thinking about his time spent with Britannicus recovering from these injuries, his thoughts lead to their meeting: Britannicus had been a captive of Berbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Whyte
Jack Whyte (March 15, 1940February 22, 2021) was a Scottish-Canadian novelist of historical fiction. Born and raised in Scotland, he moved to Canada in 1967. He resided in Kelowna, British Columbia. Early life Whyte was born in Scotland on March 15, 1940. He resided there until relocating to Canada in 1967. He was employed at a local school for one year, where he taught English. He subsequently worked as an author, musician, and actor. He and his wife, Beverley, initially lived in Alberta before settling in Kelowna in 1996. Writings Whyte's major work was a series of historical novels retelling the story of King Arthur against the backdrop of Roman Britain. This version of the popular legend eschews the use of magic to explain Arthur's ascent to power and instead relies on the historical condition (with some artistic licence) of post-Roman Britain to support the theory that Arthur was meant to counter the anarchy left by the End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman departure from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primus Pilus
The ''primus pilus'' ( "first maniple of triarii") or ''primipilus'' was the senior centurion of the first cohort in a Roman legion, a formation of five double-strength centuries of 160 men each; he was a career soldier and advisor to the legate. The ''primus pilus'' would remain in command for one year. They could continue to serve in the army after their term ended if there was a vacancy in command or if they wished to become an independent commander of an ''auxilia'' unit or the '' praefectus castrorum''. During the Roman Empire, the emperor Claudius created the office of ''primus pilus iterum''. To become the ''primus pilus iterum'' an officer must have formerly served as a tribune in the '' vigiles'', ''cohortes urbanae'', or Praetorian Guard. The ''primus pilus iterum'' would hold the responsibility of a praefectus castrorum but with higher pay. The ''primus pilus'' was a well paid position. They could accumulate enough wealth to become part of the equestrian class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Military Engineering
Roman military engineering was of a scale and frequency far beyond that of its contemporaries. Indeed, military engineering was in many ways endemic in Roman military culture, as demonstrated by each Roman legionary having as part of his equipment a shovel, alongside his ''gladius'' (sword) and '' pila'' (javelins). Workers, craftsmen, and artisans, known collectively as ''fabri'', served in the Roman military. Descriptions of early Roman army structure (initially by phalanx, later by legion) attributed to king Servius Tullius state that two ''centuriae'' of ''fabri'' served under an officer, the ''praefectus fabrum''. Roman military engineering took both routine and extraordinary forms, the former a part of standard military procedure, and the latter of an extraordinary or reactive nature. Proactive and routine military engineering The Roman legionary fortified camp Each Roman legion had a legionary fort as its permanent base. However, when on the march, particularly in enem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Commerce
Roman commerce was a major sector of the Roman economy during the later generations of the Republic and throughout most of the imperial period. Fashions and trends in historiography and in popular culture have tended to neglect the economic basis of the empire in favor of the lingua franca of Latin and the exploits of the Roman legions. The language and the legions were supported by trade and were part of its backbone. The Romans were businessmen, and the longevity of their empire was caused by their commercial trade. Whereas in theory members of the Roman Senate and their sons were restricted when engaging in trade, the members of the equestrian order were involved in businesses despite their upper-class values, which laid the emphasis on military pursuits and leisure activities. Plebeians and freedmen held shop or manned stalls at markets, and vast numbers of slaves did most of the hard work. The slaves were themselves also the subject of commercial transactions. Probably becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. The druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks. The earliest known references to the druids date to the 4th century BC. The oldest detailed description comes from Julius Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (50s BC). They were described by other Roman writers such as Cicero, Cicero (44) I.XVI.90. Tacitus, and Pliny the Elder. Following the Roman invasion of Gaul, the druid orders were suppressed by the Roman government under the 1st-century AD emperors Tiberius and Claudius, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
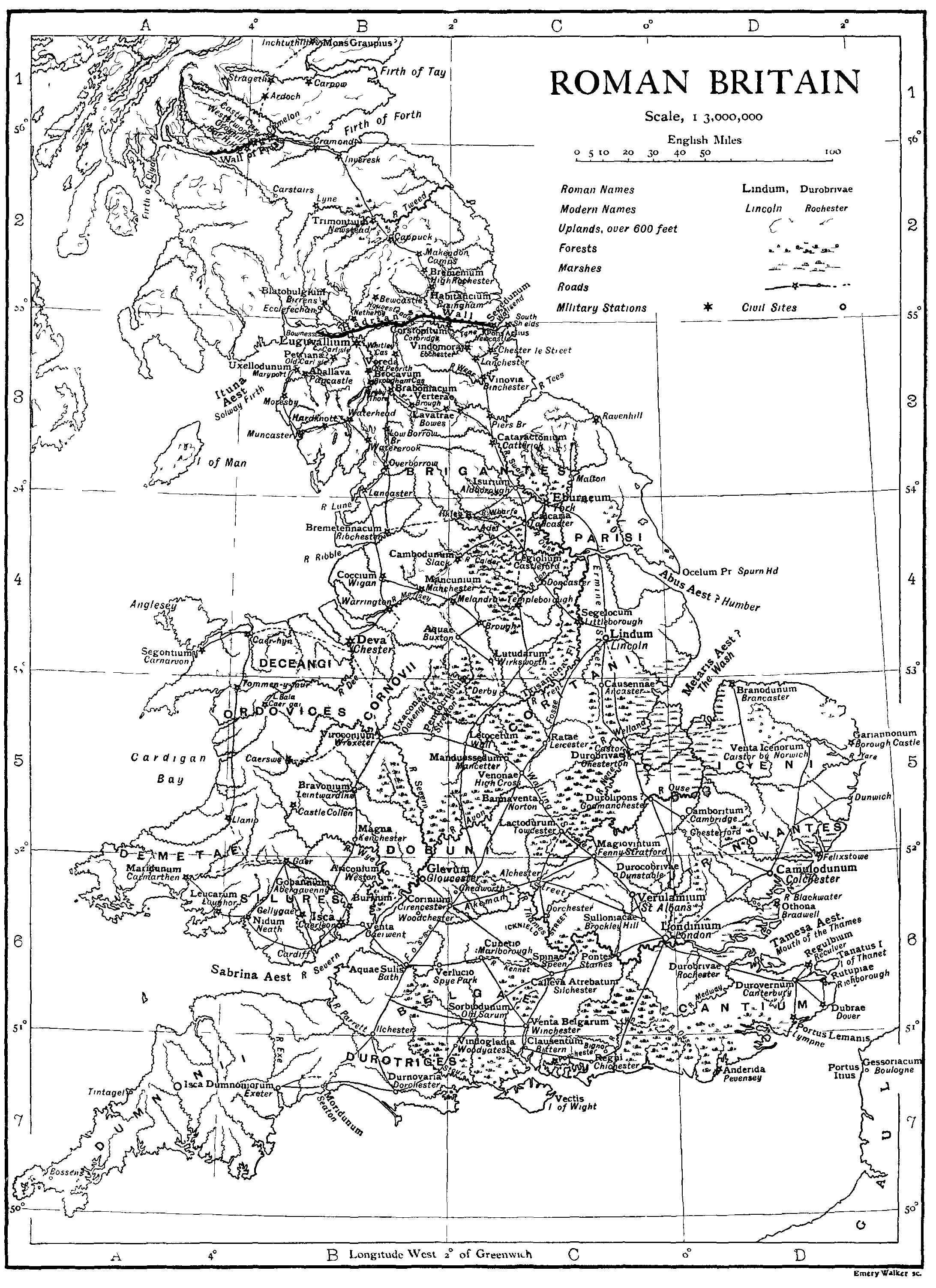
Aquae Sulis
Aquae Sulis (Latin for ''Waters of Sulis'') was a small town in the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia. Today it is the England, English city of Bath, Somerset. The Antonine Itinerary register of Roman roads lists the town as ''Aquis Sulis.'' Ptolemy records the town as ''Aquae calidae'' (warm waters) in his 2nd-century work ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geographia'', where it is listed as one of the cities of the Belgae#Great Britain, Belgae. Development Baths and temple complex The Romans probably began building a formal temple complex at Aquae Sulis in the AD 60s. The Romans had probably arrived in the area shortly after their arrival in Britain in AD 43 and there is evidence that their military road, the Fosse Way, crossed the River Avon (Bristol), river Avon at Bath. An early Roman military presence has been found just to the North-East of the bath complex in the Walcot, Bath, Walcot area of modern Bath. Not far from the crossing point of their road, they would have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verulamium
Verulamium was a town in Roman Britain. It was sited southwest of the modern city of St Albans in Hertfordshire, England. The major ancient Roman route Watling Street passed through the city, but was realigned in medieval times to bring trade to St Albans. It was about a day's walk from London. A large portion of the Roman city remains unexcavated, being now park and agricultural land, although due to ploughing on the privately owned agricultural half of the city a lot of damage has been done, as proven by parts of mosaic floors that have been found on the surface, and results of ground penetrating radar show outlines of buildings as smudges rather than clearly defined walls like those protected by the parkland. Part of the Roman city has been built upon, such as the small settlement around the Anglo-Saxon St Michael's Church. Much of the site and its environs is now a scheduled monument. History Before the Romans established their settlement, there was already a tribal ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. This material culture was found throughout Gaul and as far east as modern-day southern Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary. Warbands led by the Gaul Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennos Battle of the Allia, sacked Rome in 387 BC, becoming the only time Rome was conquered by a foreign enemy in 800 years. However, Gallia Cisalpina was conquered by the Romans in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagaudae
Bagaudae (also spelled bacaudae) were groups of peasant insurgents in the western parts of the late antiquity, later Roman Empire, who arose during the Crisis of the Third Century and persisted until the very Decline of the Roman Empire, end of the Western Empire, particularly in the less-Romanised areas of Gallia and Hispania. They were affected by the depredations of the late Roman state, wealthy landowners, and clerics. The invasions, military anarchy, and disorders of the third century provided a chaotic and ongoing degradation of the regional power structure within a declining Empire. During the chaos, the ''bagaudae'' achieved some temporary and scattered successes under the leadership of members of the underclass as well as former members of local ruling elites. Etymology The name probably means 'fighters' in Gaulish language, Gaulish. C. E. V. Nixon assesses the ''bagaudae'', from the official Imperial viewpoint, as "bands of brigands who roamed the countryside looting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in northeastern Essex, England. It is the second-largest settlement in the county, with a population of 130,245 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 Census. The demonym is ''Colcestrian''. Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first Colonia (Roman), major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colchester therefore claims to be Britain's first city. It has been an important military base since the Roman Empire, Roman era, with Colchester Garrison currently housing the 16th Air Assault Brigade (United Kingdom), 16th Air Assault Brigade. On the River Colne, Essex, River Colne, Colchester is northeast of London. It is connected to London by the A12 road (England), A12 road and the Great Eastern Main Line railway. Colchester is less than from London Stansted Airport and from the port of Harwich. Attractions in and around the city include St Botolph's Priory, Colchester Zoo, and several art galleries. Colchester Castle was constructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Theodosius
Count Theodosius (; died 376), Flavius Theodosius or Theodosius the Elder (), was a senior military officer serving Valentinian I () and the Western Roman Empire during Late Antiquity. Under his command the Roman army defeated numerous threats, incursions, and usurpations. Theodosius was patriarch of the imperial Theodosian dynasty () and father of the emperor Theodosius the Great (). Appointed '' comes rei militaris per Britannias'' (commander of mobile military forces for the Diocese of the Britains) by Valentinian, Theodosius put down the Great Conspiracy (367–368) and the usurpation of Valentinus. After restoring order in Britain he returned to continental Europe and fought against the Alemanni; as Valentinian's ''magister equitum'' (Master of Horse) he successfully invaded Alemannic territory (371 or 370). In 372 Theodosius led a successful campaign against the Sarmatians. Within the same year Firmus, a Mauritanian prince, rebelled against Roman rule with the help o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Londinium
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. Most twenty-first century historians think that it was originally a settlement established shortly after the Roman conquest of Britain, Claudian invasion of Britain, on the current site of the City of London, around 47–50 AD, but some defend an older view that the city originated in a defensive enclosure constructed during the Claudian invasion in 43 AD. Its earliest securely-dated structure is a timber drain of 47 AD. It had almost certainly been granted colony () status prior to the complete replanning of the city's street plan attending the erection of the great second forum around the year 120.Merrifieldp. 68./ref> By this time, Britain's provincial administration had also almost certainly been moved to Londinium from Camulodunum (now Colchester in Essex). The precise date of this change is unknown, and no surviving source explicitly states that Londinium w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |