|
Tail Vibration
Tail vibration is a common behavior in some snakes where the tail is vibrated rapidly as a defensive response to a potential predator. Tail vibration is distinct from caudal luring, where the tail is twitched in order to attract prey. While rattlesnakes are perhaps the most famous group of snakes to exhibit tail vibration behavior, many other snake groups—particularly those in the Colubridae and Viperidae families—are known to vibrate their tails. Description Process Tail vibration involves the rapid shaking of the tail in response to a predatory threat. The behavior is particularly widespread among New World species of Viperidae and Colubridae.Allf, Bradley C., Paul AP Durst, and David W. Pfennig. "Behavioral Plasticity and the Origins of Novelty: The Evolution of the Rattlesnake Rattle." The American Naturalist 188.4 (2016): 475–483Young, Bruce A. "Snake bioacoustics: toward a richer understanding of the behavioral ecology of snakes." The Quarterly review of biology 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snakes
Snakes are elongated Limbless vertebrate, limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
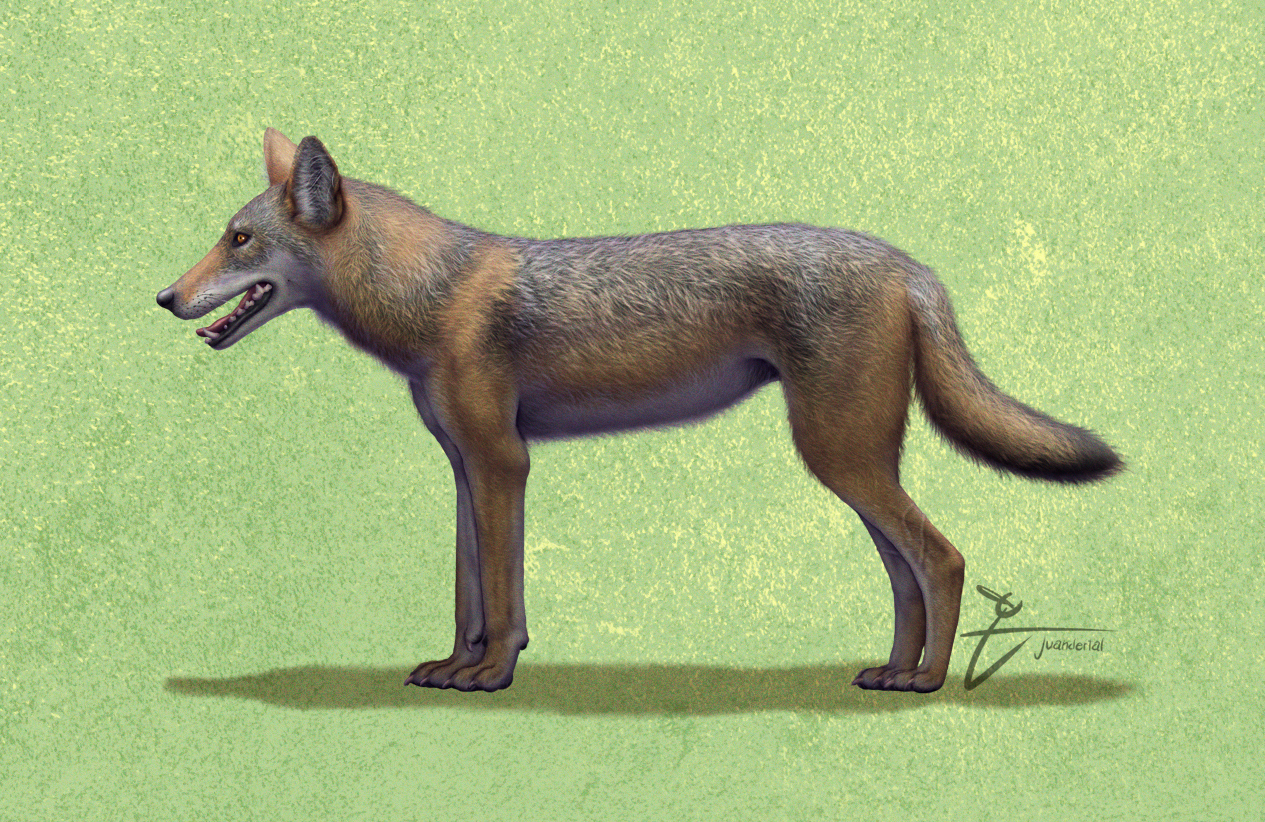
Wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though grey wolves, as popularly understood, only comprise Wild type, naturally-occurring wild subspecies. The wolf is the largest wild Neontology, extant member of the family Canidae, and is further distinguished from other ''Canis'' species by its less pointed ears and muzzle, as well as a shorter torso and a longer tail. The wolf is nonetheless related closely enough to smaller ''Canis'' species, such as the coyote and the golden jackal, to produce fertile Canid hybrid, hybrids with them. The wolf's fur is usually mottled white, brown, grey, and black, although subspecies in the arctic region may be nearly all white. Of all members of the genus ''Canis'', the wolf is most Generalist and specialist species, specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Luring
Caudal luring is a form of aggressive mimicry characterized by the waving or wriggling of the predator's tail to attract prey. This movement attracts small animals who mistake the tail for a small worm or other small animal. When the animal approaches to prey on the worm-like tail, the predator will strike. This behavior has been recorded in snakes, sharks, and eels. Mimicry The tail of a species may serve various functions, such as aggression, defense and feeding. Caudal luring behavior was first recorded in 1878 and is an instance of aggressive mimicry. Predators attract their prey by moving their caudal section to mimic a small animal, such as a worm, and attract prey animals. The prey is intrigued by caudal movement and will investigate assuming it is their own prey, and the predator will strike. Species Snakes Caudal luring behavior is found in over 50 different snake species. It is most common in boas, pythons, tropidophiids, colubrids and elapids of the genus '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to: * Extant hereditary titles * Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English * Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extinct, such as an extant species * Extant Theatre Company, a disability arts organisation * Extant (TV series), ''Extant'' (TV series), an American television series * Hank Hall, also known as Extant, a DC Comics supervillain See also * Extent (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Parsimony (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics and computational phylogenetics, maximum parsimony is an optimality criterion under which the phylogenetic tree that minimizes the total number of character-state changes (or minimizes the cost of differentially weighted character-state changes). Under the maximum-parsimony criterion, the optimal tree will minimize the amount of homoplasy (i.e., convergent evolution, parallel evolution, and evolutionary reversals). In other words, under this criterion, the shortest possible tree that explains the data is considered best. Some of the basic ideas behind maximum parsimony were presented by James S. Farris in 1970 and Walter M. Fitch in 1971. Maximum parsimony is an intuitive and simple criterion, and it is popular for this reason. However, although it is easy to ''score'' a phylogenetic tree (by counting the number of character-state changes), there is no algorithm to quickly ''generate'' the most-parsimonious tree. Instead, the most-parsimonious tree must be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocerastes Urarachnoides
The spider-tailed horned viper (''Pseudocerastes urarachnoides'') is a species of viper, a venomous snake, in the family Viperidae and genus '' Pseudocerastes''. The genus is commonly known as "false-horned vipers". The species is endemic to western Iran and over the border region with Iraq. It was originally described by scientists as ''Pseudocerastes persicus'', attributing the tail to either a parasite, deformity, or tumors. Another specimen was found in 2003. ''P. urarachnoides'' was officially described in 2006. The head looks very similar to that of other ''Pseudocerastes'' species in the region, but the spider-tailed horned viper has a unique tail with a bulb-like end that is bordered by long drooping scales that give it the appearance of a spider. (''Pseudocerastes urarachnoides'', new species). The tail tip is waved around and used to lure insectivorous birds to within striking range. Etymology The specific name, ''urarachnoides'', is derived from Ancient Greek ( οὐ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Plasticity
Behavioral plasticity is the change in an organism's behavior that results from exposure to stimuli, such as changing environmental conditions. Behavior can change more rapidly in response to changes in internal or external stimuli than is the case for most morphological traits and many physiological traits. As a result, when organisms are confronted by new conditions, behavioral changes often occur in advance of physiological or morphological changes. For instance, larval amphibians changed their antipredator behavior within an hour after a change in cues from predators, but morphological changes in body and tail shape in response to the same cues required a week to complete. Background For many years, ethologists have studied the ways that behavior can change in response to changes in external stimuli or changes in the internal state of an organism. In a parallel literature, psychologists studying learning and cognition have spent years documenting the many ways that experiences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vipers
Vipers are snakes in the family Viperidae, found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, New Zealand, Ireland, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipers), hinged fangs that permit deep envenomation of their prey. Three subfamilies are currently recognized. They are also known as viperids. The name "viper" is derived from the Latin word ''vipera'', -''ae'', also meaning viper, possibly from ''vivus'' ("living") and ''parere'' ("to beget"), referring to the trait viviparity (giving live birth) common in vipers like most of the species of Boidae. The earliest known vipers are believed to have diverged from the rest of the clade Caenophidia in the early Eocene. Description All viperids have a pair of relatively long solenoglyphous (hollow) fangs that are used to inject venom from glands located towards the rear of the upper jaws, just behind the eyes. Each of the two fangs is at the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
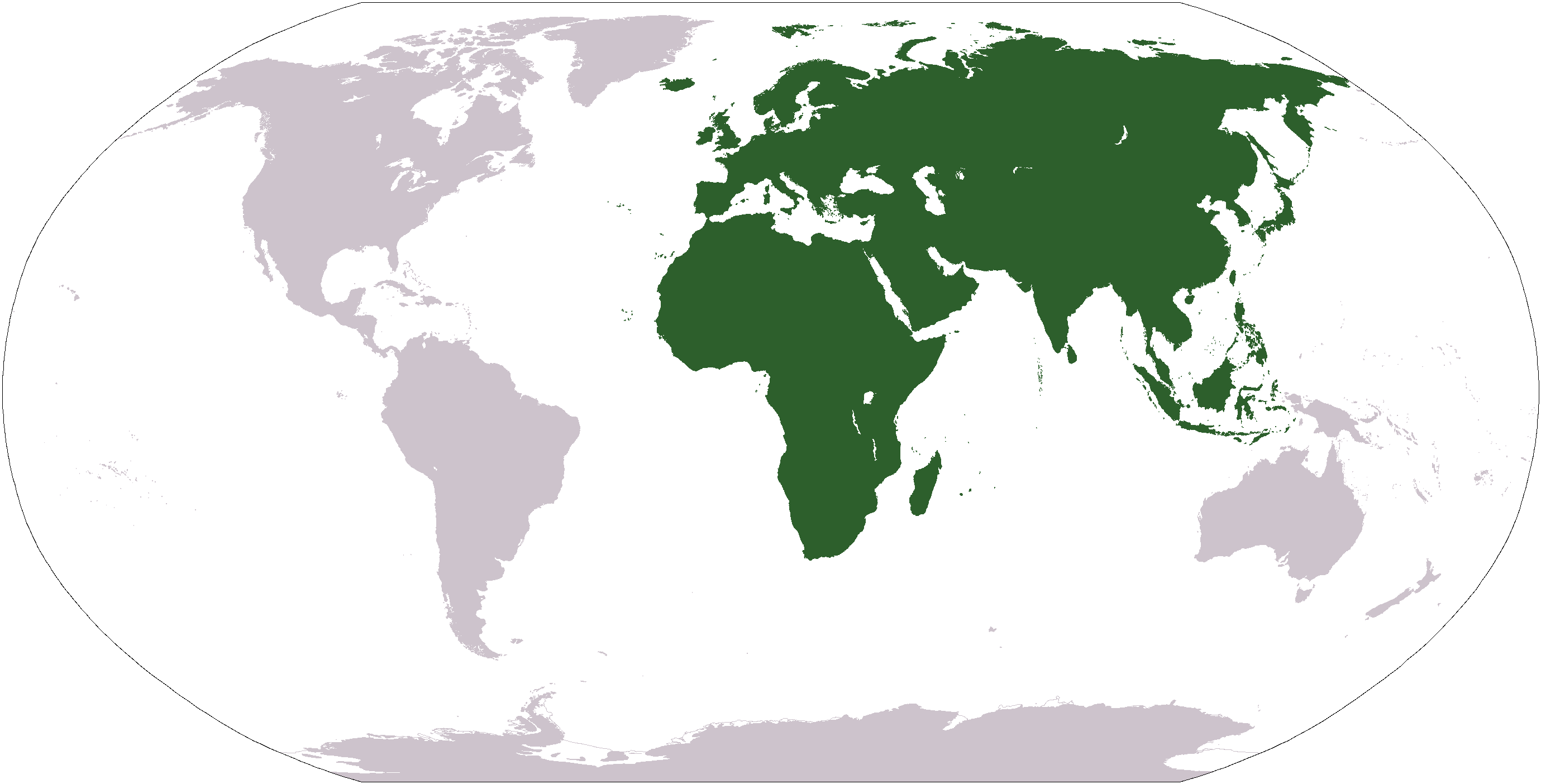
Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously thought of by the Europeans as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituophis Catenifer
:Common names: Pacific gopher snake, coast gopher snake, western gopher snake Wright AH, Wright AA. 1957. ''Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada''. 2 volumes. Comstock Publishing Associates. (7th printing, 1985). 1,105 pp. . (''Pituophis catenifer'', pp. 588-609, Figures 171.-175., Map 46.) ( more here). ''Pituophis catenifer'' is a species of non-venomous colubrid snake endemic to North America. Nine subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominotypical subspecies, ''P. c. catenifer'', described here. This snake is often mistaken for the prairie rattlesnake (''Crotalus viridus''), but can be easily distinguished from a rattlesnake by the lack of a tail rattle, no black-and-white banding on its tail, and by the shape of its head, which is narrower than a rattlesnake's. Additionally, rattlesnakes (and indeed most vipers) possess a large venom gland located behind each eye, giving their heads a much rounder, more angular shape, as opposed to the more cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |