|
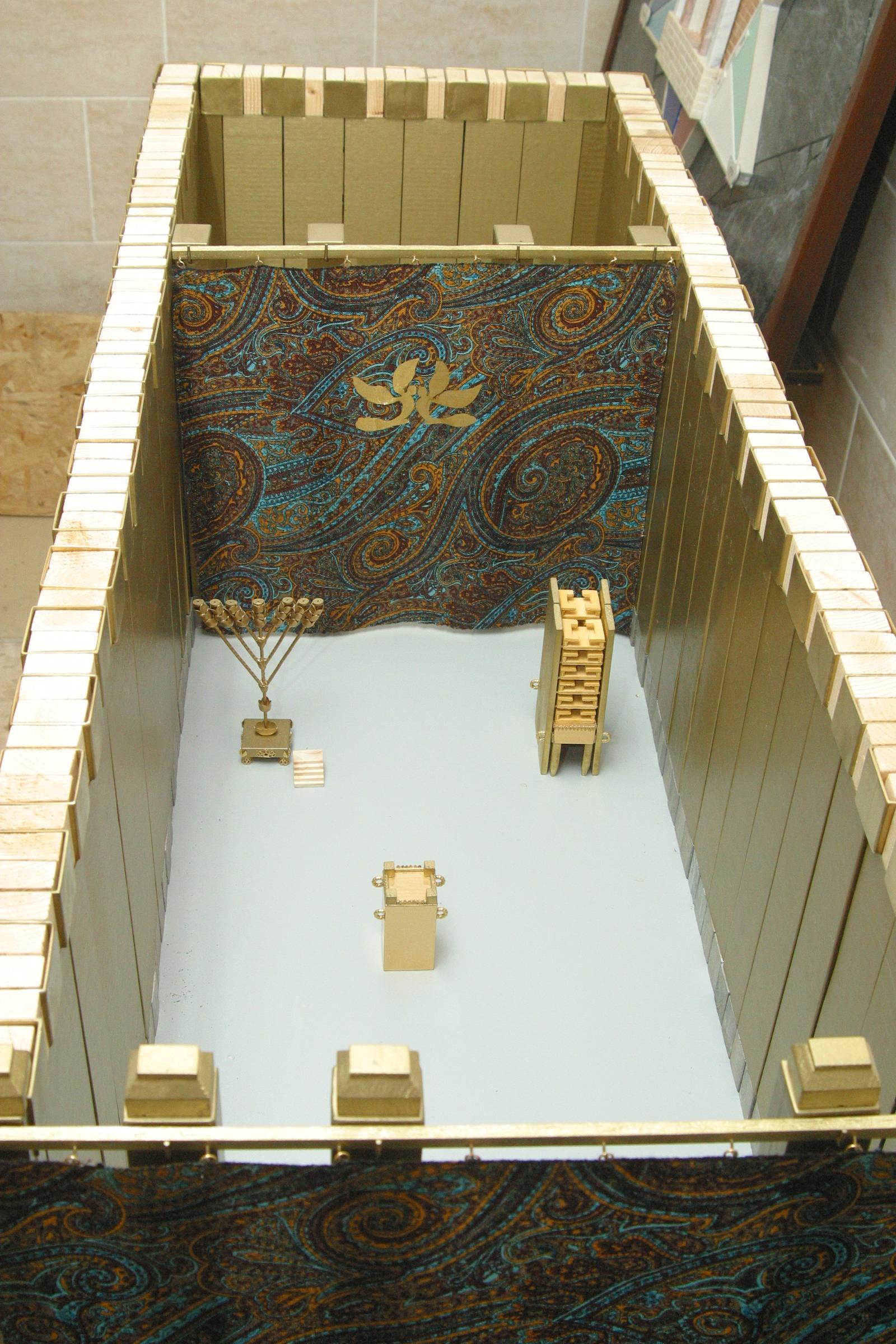
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instructed at biblical Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai to construct and transport the tabernacle with the Israelites on their journey through the wilderness and their subsequent conquest of the Promised Land. After 440 years, Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem superseded it as the dwelling-place of God. The main source describing the tabernacle is the biblical Book of Exodus, specifically Exodus 25–31 and 35–40. Those passages describe an inner sanctuary, the Holy of Holies, created by the veil suspended by four pillars. This sanctuary contained the Ark of the Covenant, with its cherubim-covered mercy seat. An outer sanctuary (the "Holy Place") contained a gold lamp-stand or candlestick. On the north side stood a table, on which lay the showbread. On th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Of Holies
The Holy of Holies ( or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also ''hadDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where the Shekhinah (God in Judaism, God's presence) appeared. According to Hebrew tradition, the area was defined by four pillars that held up the veil of the covering, under which the Ark of the Covenant was held above the floor. According to the Hebrew Bible, the Ark contained the Ten Commandments, which were given by God to Moses on Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai. The first Temple in Jerusalem, called Solomon's Temple, was said to have been built by Solomon, King Solomon to keep the Ark. Ancient Judaism, Jewish traditions viewed the Holy of Holies as the spiritual junction of Heaven and Earth, the "axis mundi". As a part of the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem, the Holy of Holies was situated somewhere on Temple Mount; its precise location in the Mount being a matter of dispute, with some classical Jewish sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menorah (Temple)
The Temple menorah (; , Tiberian Hebrew ) is a seven-branched candelabrum that is described in the Hebrew Bible and later ancient sources as having been used in the Tabernacle and the Temple in Jerusalem. Since ancient times, it has served as a symbol representing the Jews and Judaism in both the Land of Israel and the Jewish diaspora. It became the State of Israel's official emblem when it was founded in 1948. According to the Hebrew Bible, the menorah was made out of pure gold, and the only source of fuel that was allowed to be used to light the lamps was fresh olive oil. The menorah was placed in the Tabernacle. Biblical tradition holds that Solomon's Temple was home to ten menorahs, which were later plundered by the Babylonians; the Second Temple is also said to have been home to a menorah. Following the Roman destruction of Jerusalem and the Temple in 70 CE, the menorah was taken to Rome; the Arch of Titus, which still stands today, famously depicts the menorah being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew language, Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yəṣīʾat Mīṣrayīm'': ) is the Origin myth#Founding myth, founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four of the five books of the Torah, Pentateuch (specifically, Book of Exodus, Exodus, Book of Leviticus, Leviticus, Book of Numbers, Numbers, and Book of Deuteronomy, Deuteronomy). The narrative of the Exodus describes a history of Egyptian bondage of the Israelites followed by their exodus from Egypt through a Crossing the Red Sea, passage in the Red Sea, in pursuit of the Promised Land under the leadership of Moses. The story of the Exodus is central in Judaism. It is recounted daily in List of Jewish prayers and blessings, Jewish prayers and celebrated in festivals such as Passover. Early Christians saw the Exodus as a typology (theology), typological prefiguration of Resurrection of Jesus, resurrection and Salvation in Christianity, salvation by Jesus. The Exodus is also recounted in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark Of The Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant, also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, was a religious storage chest and relic held to be the most sacred object by the Israelites. Religious tradition describes it as a wooden storage chest decorated in solid gold accompanied by an ornamental lid known as the mercy seat, Seat of Mercy. According to the Book of Exodus and Books of Kings, First Book of Kings in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, the Ark contained the Tablets of Stone, Tablets of the Law, by which Yahweh, God delivered the Ten Commandments to Moses at Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai. According to the Book of Exodus, the Book of Numbers, and the Epistle to the Hebrews in the New Testament, it also contained Aaron's rod and a pot of manna. The biblical account relates that approximately one year after the Israelites' The Exodus, exodus from Egypt, the Ark was created according to the pattern that God gave to Moses when the Israelites were encamped at the foot of Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Menorah
The Temple menorah (; , Tiberian Hebrew ) is a seven-branched candelabrum that is described in the Hebrew Bible and later ancient sources as having been used in the Tabernacle and the Temple in Jerusalem. Since ancient times, it has served as a symbol representing the Jews and Judaism in both the Land of Israel and the Jewish diaspora. It became the State of Israel's official emblem when it was founded in 1948. According to the Hebrew Bible, the menorah was made out of Gold#Religion, pure gold, and the only source of fuel that was allowed to be used to light the lamps was olive oil#Judaism, fresh olive oil. The menorah was placed in the Tabernacle. Biblical tradition holds that Solomon's Temple was home to ten menorahs, which were later plundered by the Judah's revolts against Babylon, Babylonians; the Second Temple is also said to have been home to a menorah. Following the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), Roman destruction of Jerusalem and the Temple in 70 CE, the menorah was taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Ancient Roman Religion
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on later juridical and religious vocabulary in Europe, particularly of the Christian Church. This glossary provides explanations of concepts as they were expressed in Latin pertaining to Religion in ancient Rome, religious practices and beliefs, with links to articles on major topics such as priesthoods, forms of divination, and rituals. For theonyms, or the names and epithets of gods, see List of Roman deities. For public religious holidays, see Roman festivals. For temples see the List of Ancient Roman temples. Individual landmarks of religious Topography of ancient Rome, topography in ancient Rome are not included in this list; see Roman temple. __NOTOC__ Glossary A abominari The verb ''abominari'' ("to avert an omen", from ''ab-'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Showbread
Showbread (), in the King James Version shewbread, in a Biblical or Jewish context, refers to the cakes or loaves of bread which were always present, on a specially-dedicated table, in the Temple in Jerusalem as an offering to God. An alternative, and more appropriate, translation would be ''presence bread'',''Jewish Encyclopedia''. since the Bible requires that the bread be constantly in the presence of God (). Biblical references Within the Torah, the showbread is mentioned exclusively by the Priestly Code and Holiness Code, but certain sections of the Bible, including the Books of Chronicles, Books of Samuel, and Books of Kings, also describe aspects of them. In the Holiness Code, the showbread is described as twelve cakes baked from fine flour, arranged in two rows on a table; each cake was to contain "two tenth parts of an ephah" of flour (; approximately 5 pounds or 2 kg). The biblical regulations specify that cups of frankincense were to be placed upon the rows of cake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from ; ''Šəmōṯ'', 'Names'; ) is the second book of the Bible. It is the first part of the narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites, in which they leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of Yahweh, their deity, who according to the story Chosen people, chose them as his people. The Israelites then journey with the prophet Moses to biblical Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai, where Yahweh gives the Ten Commandments and they enter into a Mosaic covenant, covenant with Yahweh, who promises to make them a "holy nation, and a kingdom of priests" on condition of their faithfulness. He gives them laws and instructions to build the Tabernacle, the means by which he will come from heaven and dwell with them and lead them in a holy war to conquer Canaan (the "Promised Land"), which has earlier, according to the Book of Genesis, been promised to the "seed" of Abraham, the patriarch of the Israelites. Though traditionally Mosaic authorship, ascri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
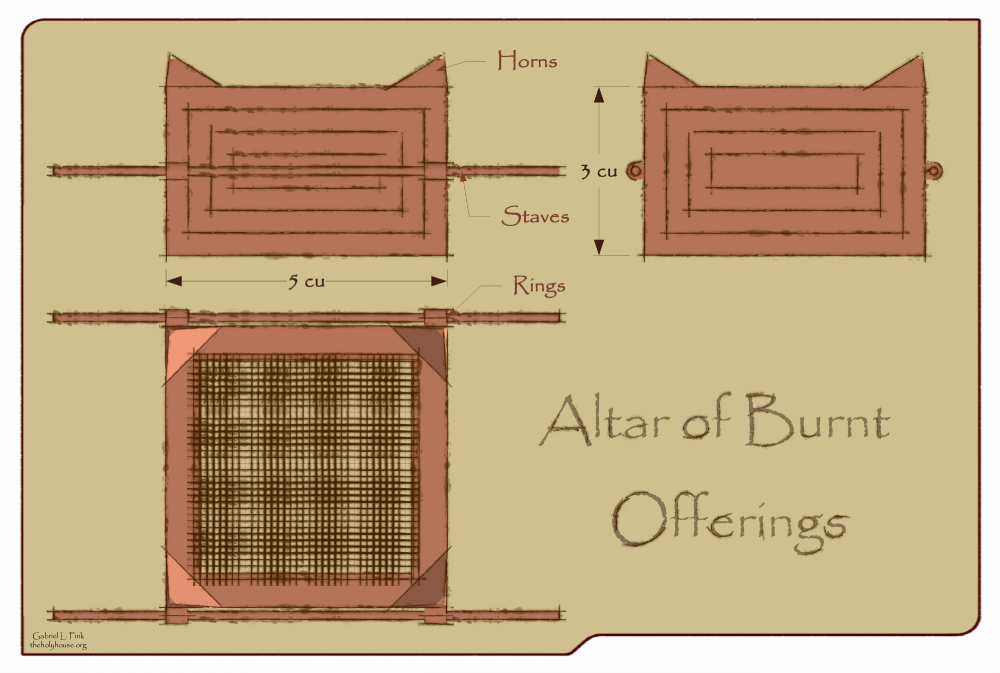
Altar (Bible)
Altars (, ''mīzbēaḥ'', "a place of slaughter or sacrifice") in the Hebrew Bible were typically made of earth () or unwrought stone (). Altars were generally erected in conspicuous places (; ; ; ; ). The first time the word altar is mentioned and recorded in the Hebrew Bible is that it was erected by Noah, it does specify that there was an altar in (). Other altars were erected by Abraham (; ; ;), by Isaac (), by Jacob (; ), by Moses (), and by Saul (1 Samuel 14:35). After the theophany on Biblical Mount Sinai, in the Tabernacle, and afterwards in the Temple in Jerusalem, only two altars are mentioned: the Altar of Burnt Offering and the Altar of Incense. Altar of burnt offering The first altar was the Altar of Burnt Offering (''mizbeach ha'olah''; ), also called the Brasen Altar (), the Outer Altar (''mizbeach hachitzona''), the Earthen Altar (''mizbeach adamah''), the Great Altar (''mizbeach hagedola'') and the Table of the Lord (). This was the outdoor altar and stood in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritanism, and one of the most important prophets in Christianity, Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islam, the Manifestation of God (Baháʼí Faith)#Known messengers, Baháʼí Faith, and Table of prophets of Abrahamic religions, other Abrahamic religions. According to both the Bible and the Quran, God in Abrahamic religions, God dictated the Mosaic Law to Moses, which he Mosaic authorship, wrote down in the five books of the Torah. According to the Book of Exodus, Moses was born in a period when his people, the Israelites, who were an slavery, enslaved minority, were increasing in population; consequently, the Pharaohs in the Bible#In the Book of Exodus, Egyptian Pharaoh was worried that they might ally themselves with New Kingdom of Egypt, Eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altar Of Incense
Altars (, ''mīzbēaḥ'', "a place of slaughter or sacrifice") in the Hebrew Bible were typically made of earth () or unwrought stone (). Altars were generally erected in conspicuous places (; ; ; ; ). The first time the word altar is mentioned and recorded in the Hebrew Bible is that it was erected by Noah, it does specify that there was an altar in (). Other altars were erected by Abraham (; ; ;), by Isaac (), by Jacob (; ), by Moses (), and by Saul (1 Samuel 14:35). After the theophany on Biblical Mount Sinai, in the Tabernacle, and afterwards in the Temple in Jerusalem, only two altars are mentioned: the Altar of Burnt Offering and the Altar of Incense. Altar of burnt offering The first altar was the Altar of Burnt Offering (''mizbeach ha'olah''; ), also called the Brasen Altar (), the Outer Altar (''mizbeach hachitzona''), the Earthen Altar (''mizbeach adamah''), the Great Altar (''mizbeach hagedola'') and the Table of the Lord (). This was the outdoor altar and stood in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |