|
TK 2000
The TK 2000 microcomputer, produced by the Brazilian company Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda, was presented to the public during the 1983 Computer Fair and launched in 1984. It was a clone of the Microprofessor II manufactured by Multitech. Based on the 6502 CPU, the machine was partially compatible with Apple II Plus software and hardware. Some software was developed specifically for the machine, including productivity programs and games. In 1985 the TK2000/II was released and in 1987 the machine was discontinued. Details * CPU - MOS Technology 6502 at 1,02 MHz * Memory - 16 KB ROM, 64 KB RAM (expandable to 128KB) * Sound - one channel, up to 4 octaves with tones and semitones, 5 different tempos for each note, by software. * Video - 280 x 192 with 8 colors, low-resolution mode emulates 16 colors through dithering. * Keyboard - mechanical, 54 keys with QWERTY layout. * Expansion - 1 slot * Interfaces / Ports - TV output, RGB monitor, printer, joystick * Storage - cassette reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC game, gaming. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. The term home computer has also been used, primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s. The advent of personal computers and the concurrent Digital Revolution have significantly affected the lives of people. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with computers. While personal computer users may develop their applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
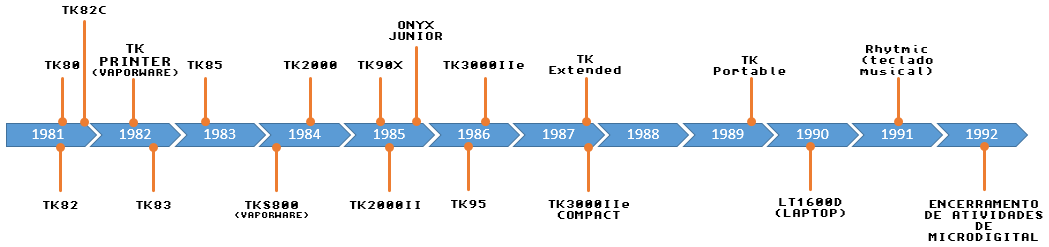
Microdigital Eletronica
Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda. was a Brazilian computer company in the 1980s, based in São Paulo. History Established in 1981 by the brothers George and Tomas Kovari (whose initials were the TK of the domestic computers line made by the company), its first product was the TK80, a clone of the British microcomputer Sinclair ZX80. The company reached its height around 1985, with the launching of the TK90X (clone of the ZX Spectrum) and the TK 2000/II'''', a personal computer partially compatible (at Applesoft BASIC level) with the Apple II+. At this time, it had approximately 400 employees in three plants (two in São Paulo (state), São Paulo and one in the Zona Franca de Manaus) and more than 700 peddlers spread for all Brazil. Although the logo of the company is identical to the earlier Microdigital Ltd of the United Kingdom the company is not related. Line of products A not extensive list of Microdigital's products: Home computers * TK80 (1981) * TK82 (1981) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprofessor II
Micro-Professor II (MPF-II) is an Apple II clones, Apple II clone introduced in 1982 by Multitech (later renamed to Acer Inc., Acer). It is Multitech second branded computer product and also one of the earliest Apple II clones. The MPF II doesn't look like most other computers, with its case being a slab with a small chiclet keyboard on the lower part. In 1983, the Micro-Professor II had a retail price of £269.00 in the UK and 2995French franc, FF in France. One key feature of the MPF-II was its Chinese BASIC, a version of Chinese language, Chinese-localized BASIC based and compatible with Applesoft BASIC. Versions of the machine sold in Europe, Northern America, India, Singapore, and Australia didn't have Chinese Language localisation, localization. Peripherals for the machine included a two floppy disk Disk controller, drive controller and a Thermal printing, thermal printer. Differences from Apple II The MPF-II is not entirely compatible with the Apple II, not having its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acer Inc
Acer Inc. (; ) is a Taiwanese Multinational corporation, multinational company that produces computer hardware and electronics, headquartered in Xizhi District, New Taipei City, Taiwan. Its products include desktop computer, desktop PCs, laptop PCs (Laptop, clamshells, 2-in-1 PC, 2-in-1s, Convertible laptop, convertibles and Chromebooks), tablet computer, tablets, server (computing), servers, storage devices, virtual reality devices, displays, smartphones, televisions and peripherals, as well as Gaming computer, gaming PCs and accessories under its Predator brand. Acer is the Market share of personal computer vendors, world's sixth-largest personal computer vendor by unit sales. In the early 2000s, Acer implemented a new business model, shifting from a manufacturer to a designer, marketer, and distributor of products, while performing production processes via contract manufacturers.Centre for Research on Multinational Corporations, Bart Sleb, 2005 Currently, in addition to its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOS Technology 6502
The MOS Technology 6502 (typically pronounced "sixty-five-oh-two" or "six-five-oh-two") William Mensch and the moderator both pronounce the 6502 microprocessor as ''"sixty-five-oh-two"''. is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit microprocessor that was designed by a small team led by Chuck Peddle for MOS Technology. The design team had formerly worked at Motorola on the Motorola 6800 project; the 6502 is essentially a simplified, less expensive and faster version of that design. When it was introduced in 1975, the 6502 was the least expensive microprocessor on the market by a considerable margin. It initially sold for less than one-sixth the cost of competing designs from larger companies, such as the 6800 or Intel 8080. Its introduction caused rapid decreases in pricing across the entire processor market. Along with the Zilog Z80, it sparked a series of projects that resulted in the home computer microcomputer revolution, revolution of the early 1980s. Home video game consoles and home com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II Plus
The Apple II Plus (stylized as Apple ][+ or apple ][ plus) is the second model of the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Inc., Apple Computer. It was sold from June 1979 to December 1982. Approximately 380,000 II Pluses were sold during its four years in production before being replaced by the Apple IIe in January 1983. Features Memory The Apple II Plus shipped with 16 KB, 32 KB or 48 KB of main RAM, expandable to 64 KB by means of the Language Card, an expansion card that could be installed in the computer's slot 0. The Apple's MOS Technology 6502, 6502 microprocessor could support a maximum of 64 KB of address space, and a machine with 48 KB RAM reached this limit because of the additional 12 KB of read-only memory and 4 KB of I/O addresses. For this reason, the extra RAM in the language card was bank switching, bank-switched over the machine's built-in ROM, allowing code loaded into the additional memory to be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOS Technology
MOS Technology, Inc. ("MOS" being short for Metal Oxide Semiconductor), later known as CSG (Commodore Semiconductor Group) and GMT Microelectronics, was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Audubon, Pennsylvania. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers. History Three former General Instrument executives, John Paivinen, Mort Jaffe and Don McLaughlin, formed MOS Technology in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania in 1969. The Allen-Bradley Company was looking to provide a second source for electronic calculators and their chips designed by Texas Instruments (TI). In 1970 Allen-Bradley acquired a majority interest in MOS Technology. In the early 1970s, TI decided to release their own line of calculators, instead of selling just the chips inside them, and introduced them at a price that was lower than the price of the chipset alone. Many early chip companies were reliant on sales of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QWERTY
QWERTY ( ) is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top letter row of the keyboard: . The QWERTY design is based on a layout included in the Sholes and Glidden typewriter sold via E. Remington and Sons from 1874. QWERTY became popular with the success of the Remington No. 2 of 1878 and remains in ubiquitous use. History The QWERTY layout was devised and created in the early 1870s by Christopher Latham Sholes, a newspaper editor and printer who lived in Kenosha, Wisconsin. In October 1867, Sholes filed a patent application for his early writing machine he developed with the assistance of his friends Carlos Glidden and Samuel W. Soule, Samuel W. Soulé. The first model constructed by Sholes used a piano-like keyboard with two rows of characters arranged alphabetically as shown below: - 3 5 7 9 N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 2 4 6 8 . A B C D E F G H I J K L M Sholes struggled for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baud
In telecommunications and electronics, baud (; symbol: Bd) is a common unit of measurement of symbol rate, which is one of the components that determine the speed of communication over a data channel. It is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second or pulses per second. It is the number of distinct symbol changes (signalling events) made to the transmission medium per second in a digitally modulated signal or a bd rate line code. Baud is related to '' gross bit rate'', which can be expressed in bits per second (bit/s). If there are precisely two symbols in the system (typically 0 and 1), then baud and bits per second are equivalent. Naming The baud unit is named after Émile Baudot, the inventor of the Baudot code for telegraphy, and is represented according to the rules for SI units. That is, the first letter of its symbol is uppercase (Bd), but when the unit is spelled out, it should be written in lowercase (baud) except when it begins a sentence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applesoft BASIC
Applesoft BASIC is a dialect of Microsoft BASIC, developed by Marc McDonald and Ric Weiland, supplied with Apple II computers. It supersedes Integer BASIC and is the BASIC in Read-only memory, ROM in all Apple II series computers after the original Apple II model. It is also referred to as FP BASIC (from floating-point arithmetic, floating point) because of the Apple DOS command FP used to invoke it, instead of INT for Integer BASIC. Applesoft BASIC was supplied by Microsoft and its name is derived from the names of both Apple Computer and Microsoft. Apple employees, including Randy Wigginton, adapted Microsoft's interpreter for the Apple II and added several features. The first version of Applesoft was released in 1977 on cassette tape and lacked proper support for high-resolution graphics. Applesoft II, which was made available on cassette and disk and in the ROM of the Apple II Plus and subsequent models, was released in 1978. It is this latter version, which has some synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple DOS
Apple DOS is the disk operating system for the Apple II computers from late 1978 through early 1983. It was superseded by ProDOS in 1983. Apple DOS has three major releases: DOS 3.1, DOS 3.2, and DOS 3.3; each one of these three releases was followed by a second, minor "bug-fix" release, but only in the case of Apple DOS 3.2 did that minor release receive its own version number, Apple DOS 3.2.1. The best-known and most-used version is Apple DOS 3.3 in the 1980 and 1983 releases. Prior to the release of Apple DOS 3.1, Apple users had to rely on audio cassette tapes for data storage and retrieval. Version history When Apple Computer introduced the Apple II in April 1977, the new computer had no disk drive or disk operating system (DOS). Although Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak designed the Disk II controller late that year, and believed that he could have written a DOS, his co-founder Steve Jobs decided to outsource the task. The company considered using Digital Research's CP/M, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microdigital Eletrônica
Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda. was a Brazilian computer company in the 1980s, based in São Paulo. History Established in 1981 by the brothers George and Tomas Kovari (whose initials were the TK of the domestic computers line made by the company), its first product was the TK80, a clone of the British microcomputer Sinclair ZX80. The company reached its height around 1985, with the launching of the TK90X (clone of the ZX Spectrum) and the TK 2000/II'''', a personal computer partially compatible (at Applesoft BASIC level) with the Apple II+. At this time, it had approximately 400 employees in three plants (two in São Paulo (state), São Paulo and one in the Zona Franca de Manaus) and more than 700 peddlers spread for all Brazil. Although the logo of the company is identical to the earlier Microdigital Ltd of the United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northweste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |