|
Tas1r2
T1R2 - Taste receptor type 1 member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAS1R2'' gene. The sweet taste receptor is predominantly formed as a dimer of T1R2 and T1R3 by which different organisms sense this taste. In songbirds, however, the T1R2 monomer does not exist, and they sense the sweet taste through the umami taste receptor (T1R1 and T1R3) as a result of an evolutionary change that it has undergone. Structure and molecular function Both T1R2 and T1R3 receptors belongs to the class C G protein-coupled receptor family that features a common structure comprised a large extracellular domain, called the venus flytrap domain (VFD), which is connected to a 7-helix TMD by a cysteine-rich domain (CRD). The canonical activation mechanism of class C GPCRs follows a multiple-step process that requires communication between the VFDs (housing the orthosteric-binding site) and the TMDs via the CRDs. Although the main binding site for most sweet compounds was found to resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taste Receptor
A taste receptor or tastant is a type of cellular receptor that facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locations. Molecules which give a sensation of taste are considered "sapid". Vertebrate taste receptors are divided into two families: * Type 1, sweet, first characterized in 2001: – * Type 2, bitter, first characterized in 2000: In humans there are 25 known different bitter receptors, in cats there are 12, in chickens there are three, and in mice there are 35 known different bitter receptors. Visual, olfactive, "sapictive" (the perception of tastes), trigeminal (hot, cool), mechanical, all contribute to the perception of ''taste''. Of these, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 ( TRPV1) vanilloid receptors are responsible for the perception of heat from some molecules such as capsaicin, and a CMR1 receptor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living Organism, organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its Stereoisomerism, stereoisomer L-glucose, -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumvallate Papilla
Lingual papillae (: papilla, ) are small structures on the upper surface of the tongue that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circumvallate (or vallate), fungiform, filiform, and foliate. All except the filiform papillae are associated with taste buds. Structure In living subjects, lingual papillae are more readily seen when the tongue is dry. There are four types of papillae present on the tongue in humans: Filiform papillae Filiform papillae () are the most numerous of the lingual papillae. They are fine, small, cone-shaped papillae found on the anterior surface of the tongue. They are responsible for giving the tongue its texture and are responsible for the sensation of touch. Unlike the other kinds of papillae, filiform papillae do not contain taste buds. They cover most of the front two-thirds of the tongue's surface. They appear as very small, conical or cyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase
A phospholipase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes phospholipids into fatty acids and other lipophilic substances. There are four major classes, termed A, B, C, and D, which are distinguished by the type of reaction which they catalyze: *Phospholipase A ** Phospholipase A1 – cleaves the ''sn''-1 acyl chain (where ''sn'' refers to stereospecific numbering). ** Phospholipase A2 – cleaves the ''sn''-2 acyl chain, releasing arachidonic acid. * Phospholipase B – cleaves both ''sn''-1 and ''sn''-2 acyl chains; this enzyme is also known as a lysophospholipase. * Phospholipase C – cleaves before the phosphate, releasing diacylglycerol and a phosphate-containing head group. PLCs play a central role in signal transduction, releasing the second messenger inositol triphosphate. * Phospholipase D – cleaves after the phosphate, releasing phosphatidic acid and an alcohol. Types C and D are considered phosphodiesterases. Endothelial lipase is primarily a phospholipase. Phospho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Receptor Potential
Transient receptor potential channels (TRP channels) are a group of ion channels located mostly on the plasma membrane of numerous animal cell types. Most of these are grouped into two broad groups: Group 1 includes TRPC ( "C" for canonical), TRPV ("V" for vanilloid), TRPVL ("VL" for vanilloid-like), TRPM ("M" for melastatin), TRPS ("S" for soromelastatin), TRPN ("N" for mechanoreceptor potential C), and TRPA (channel), TRPA ("A" for ankyrin). Group 2 consists of TRPP ("P" for polycystic) and TRPML ("ML" for mucolipin). Other less-well categorized TRP channels exist, including yeast channels and a number of Group 1 and Group 2 channels present in non-animals. Many of these channels mediate a variety of sensations such as pain, temperature, different kinds of taste, pressure, and vision. In the body, some TRP channels are thought to behave like microscopic thermometers and used in animals to sense hot or cold. Some TRP channels are activated by molecules found in spices like garlic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol or inositol phospholipid is a biomolecule. It was initially called "inosite" when it was discovered by Léon Maquenne and Johann Joseph von Scherer in the late 19th century. It was discovered in bacteria but later also found in eukaryotes, and was found to be a signaling molecule. The biomolecule can exist in 9 different isomers. It is a lipid which contains a phosphate group, two fatty acid chains, and one inositol sugar molecule. Typically, the phosphate group has a negative charge (at physiological pH values). As a result, the molecule is amphiphilic. The production of the molecule is limited to the endoplasmic reticulum. History of phospatidylinositol Phosphatidylinositol (PI) and its derivatives have a rich history dating back to their discovery by Johann Joseph von Scherer and Léon Maquenne in the late 19th century. Initially known as " inosite" based on its sweet taste, the isolation and characterization of inositol laid the groundwork for und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
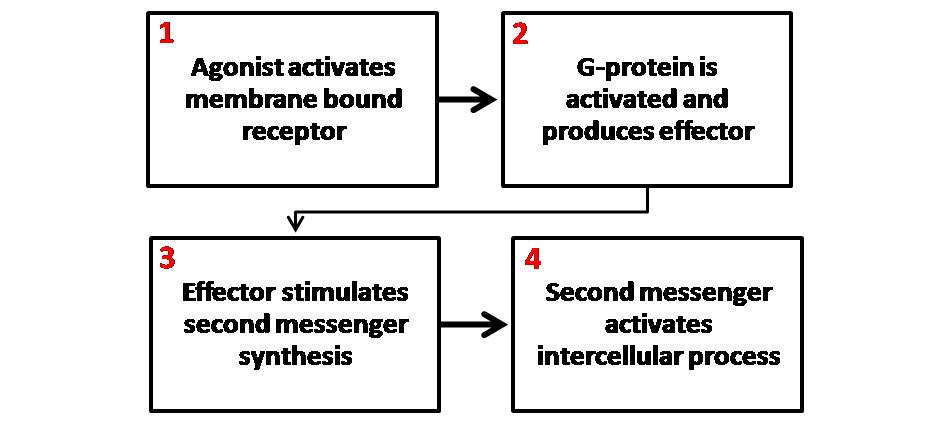
Second Messenger Systems
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or neurotransmitters, such as epinephrine, growth hormone, and serotonin. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic molecules, these first messenger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in response to the binding of membrane-impermeable peptide hormones to the external cell surface. Through protein kinases activation, cGMP can relax smooth muscle. cGMP concentration in urine can be measured for kidney function and diabetes detection. History Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) research began after cGMP and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) were identified as cellular components and potentially involved with cellular regulation. Upon the synthesis of cGMP in 1960, progress rapidly spread in the understanding of regulation and effects of cGMP. Earl W. Sutherland received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Medicine for his work with cAMP and secondary messengers. This award sparked extensive research into cAMP, while cGMP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenylyl Cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction: :ATP = 3′,5′-cyclic AMP + diphosphate It has key regulatory roles in essentially all Cell (biology), cells. It is the most Polyphyly, polyphyletic known enzyme: six distinct classes have been described, all catalysis, catalyzing the same reaction but representing unrelated gene Gene family, families with no known Sequence homology, sequence or structural homology. The best known class of adenylyl cyclases is class III or AC-III (Roman numerals are used for classes). AC-III occurs widely in eukaryotes and has important roles in many human Tissue (biology), tissues. All classes of adenylyl cyclase Catalysis, catalyse the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic adenosine monophosphate, 3',5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP) and pyrophosphate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptors
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large protein family, group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell (biology), cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminus, N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |