|
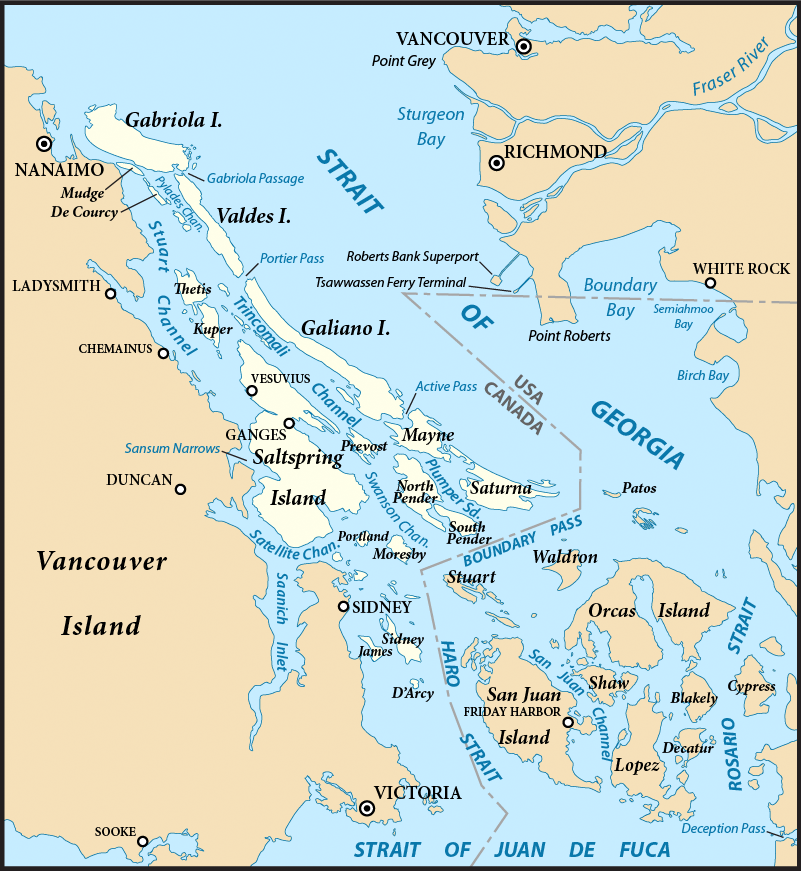
T'Sou-ke People
The T'Sou-ke Nation of the Coast Salish peoples, is a band government whose reserve community is located on Vancouver Island, in the province of British Columbia, Canada. In February 2013, the T'Sou-ke Nation had 251 registered members, with two reserves around the Sooke Basin on the Strait of Juan de Fuca at the southern end of Vancouver Island, with a total area of 67 hectares (165 acres). The T'Souk-e people are the namesake of the town of Sooke, British Columbia and its surrounding harbour and basin. Etymology The spelling ''T'Sou-ke'' is an exoticization of ''Sooke'', which derives from the name of the area around Sooke Harbor. It may be from the Klallam form (now pronounced ), or a relic of an earlier Northern Straits pronunciation. The current Saanich form is , pronounced . Alternate anglicizations have included ''Soke'', ''Sok'', ''Tsohke'', and ''Sock''. Language The language of the T'Sou-ke Nation is the T'Sou-ke dialect of the Northern Straits Salish languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east; the territories of Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north; the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south, and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.7million as of 2025, it is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, British Columbia, Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, the third-largest metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowichan Peoples
Cowichan may refer either to: *the Cowichan Tribes First Nation located in and around Duncan, British Columbia *the Cowichan Valley, a region on Vancouver Island centred on Duncan, British Columbia, which contains: ** Cowichan Valley Regional District, British Columbia, Cowichan Valley Regional District, a supra-municipal regional government **Cowichan Lake, a 30 km long body of water **the town of Lake Cowichan **Cowichan River **Cowichan Bay, British Columbia, a bay and community. *the Cowichan sweater, a heavy-wool knit animal and geometric patterns made by the women of the Cowichan people. ;British Columbia provincial electoral districts: *Cowichan (electoral district), Cowichan 1871–1920 *Cowichan-Alberni 1894 *Cowichan-Newcastle 1920–1963 *Cowichan-Malahat 1966–1986 *Cowichan-Ladysmith 1991–2005 *Nanaimo-North Cowichan 2009–2020 *Cowichan Valley (electoral district), Cowichan Valley 2009–present ;Canadian federal electoral districts: *Cowichan—Malahat— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BC Hydro
The British Columbia Hydro and Power Authority, trade name, operating as BC Hydro, is a Canadian electric utility in the province of British Columbia. It is the main electricity distributor, serving more than 4 million customers in most areas, with the exception of the City of New Westminster, where the city runs its own electrical department and portions of the Kootenays, West Kootenay, Okanagan, the Boundary Country and Similkameen Country, Similkameen regions, where FortisBC, a subsidiary of Fortis Inc. directly provides electric service to 213,000 customers and supplies municipally owned utilities in the same area. As a provincial Crown corporation, BC Hydro reports to the BC Ministry of Energy, Mines and Low Carbon Innovation, and is regulated by the British Columbia Utilities Commission (BCUC). Its mandate is to generate, purchase, distribute and sell electricity. BC Hydro operates 32 hydroelectric facilities and two natural gas-fueled thermal power plants. As of 2014, 95 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
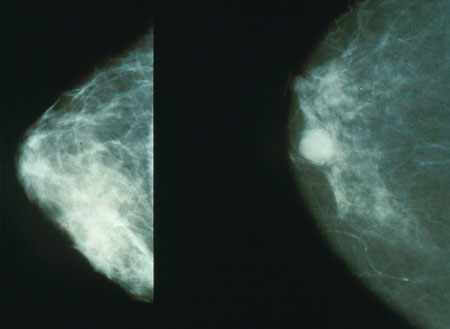
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses, microcalcifications, asymmetries, and distortions. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Health
Island Health, also known as the Vancouver Island Health Authority, is the publicly funded health care provider in the southwestern portion of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It was established as one of five geographically based health authorities in 2001 by the Government of British Columbia. Island Health provides health care to over 850,000 people over a geographic area of 56,000 sq km. In the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in British Columbia, Island Health had 96 intensive care unit (ICU) beds and 140 ventilators available, including 22 transport ventilators. Communities The region includes the communities of: * Vancouver Island * Gulf Islands * Johnstone Strait * Central Coast (part of) The largest population center is Greater Victoria on the southern tip of Vancouver Island as the majority constituent of the Capital Regional District (CRD; population 383,360 as of the Canada 2016 Census), which also includes some of the southern Gulf Islands. Outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' () is a Canadian Act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still in force with amendments, it is the primary document that defines how the Government of Canada interacts with the 614 First Nation bands in Canada and their members. Throughout its long history, the act has been a subject of controversy and has been interpreted in different ways by both Indigenous Canadians and non-Indigenous Canadians. The legislation has been amended many times, including "over five major changes" made in 2002. The act is very wide-ranging in scope, covering governance, land use, healthcare, education, and more on Indian reserves. Notably, the original ''Indian Act'' defines two elements that affect all Indigenous Canadians: * It says how reserves and bands can operate. The act sets out rules for governing Indian reserves, defines how bands can be created, and defines the powers of "ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Fuca Electoral Area
The Capital Regional District (CRD) is a local government administrative district encompassing the southern tip of Vancouver Island and the southern Gulf Islands in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The CRD is one of several regional districts in British Columbia and had an official population of 415,451 as of the Canada 2021 Census. The CRD encompasses the thirteen municipalities of Greater Victoria and three unincorporated areas: Juan de Fuca Electoral Area on Vancouver Island, Salt Spring Island Electoral Area, and Southern Gulf Islands Electoral Area. The CRD also acts as the local government for most purposes in the Electoral Areas. CRD headquarters is in the City of Victoria, although there are many office and operational facilities throughout the region. The total land area is . The CRD was formed in 1966 as a federation of seven municipalities and five electoral areas to provide coordination of regional issues and local government in rural areas in the Greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broom Hill, Greater Victoria
Broom Hill is a hill and eponymous rural neighbourhood in Sooke, British Columbia. Its residential subdivisions surround Broom Hill proper, which is composed of gabbro which rises to an elevation of 283 metres (928 feet). Above the subdivisions, most of the terrain has a forest cover dominated by Douglas-fir The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is the tallest tree in the Pinaceae family. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Or .... Trails At the top of Broom Hill is a swing looking out over Sooke Harbour and the Juan de Fuca Strait. There are three access points to the trail Blanchard Rd, Mountain Heights Dr and Denfield RdMap Hikers and bikers regularly travel the trails, but they are not marked, and cell phone service is weak. Where Broom Hill Got Its Name In the 1850's Captain Walter Colquhoun Grant was scouting for new lumber markets in Hawaii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
''First Nations'' () is a term used to identify Indigenous peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized List of First Nations band governments, First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group", along with women, Visible minority, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Many of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te'mexw Treaty Association
The Te'mexw Treaty Association (from Halkomelem 'land, earth') handles Treaty negotiations in the BC Treaty Process for a number of First Nations located in the northern Strait of Georgia of British Columbia. The members of the association are former signatories of the Douglas Treaties, a group of treaties signed in the 1850s. Treaty Process The Treaty group has reached Stage 5 in the BC Treaty Process. Membership See also *List of tribal councils in British Columbia The following is a List of tribal councils in British Columbia. Treaty Council organizations are not listed. List of tribal councils Defunct: * Fraser Canyon Indian Administration ( Nlaka'pamux) * In-SHUCK-ch Nation * Tsimshian Tribal Coun ... References First Nations organizations in British Columbia Southern Vancouver Island {{Treaty-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Canada
The Constitution of Canada () is the supreme law in Canada. It outlines Canada's system of government and the civil and human rights of those who are citizens of Canada and non-citizens in Canada. Its contents are an amalgamation of various codified acts, treaties between the Crown and Indigenous Peoples (both historical and modern), uncodified traditions and conventions. Canada is one of the oldest constitutional monarchies in the world. The Constitution of Canada comprises core written documents and provisions that are constitutionally entrenched, take precedence over all other laws and place substantive limits on government action; these include the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly the ''British North America Act, 1867)'' and the ''Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.''Monahan, Patrick J.; Shaw, Byron; Ryan, Padraic (2017). ''Constitutional Law'' (5th ed.). Toronto, ON: Irwin Law Inc. pp.3-9. The ''Constitution Act'', ''1867'' provides for a constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |