|
Syriac Studies
Syriac studies is the study of the Syriac language and Syriac Christianity. A specialist in Syriac studies is known as a Syriacist. Specifically, British, French, and German scholars of the 18th and 19th centuries who were involved in the study of Syriac/Aramaic language and literature were commonly known by this designation, at a time when the Syriac language was little understood outside Assyrian, Syriac Christian and Maronite Christian communities. In Germany the field of study is distinguished between ''Aramaistik'' (Aramaic studies) and ''Neuaramaistik'' (Neo-Aramaic (Syriac) studies). At universities Syriac studies are mostly incorporated into a more 'general' field of studies, such as Eastern Christianity at the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, Aramaic studies at the University of Oxford and University of Leiden, Eastern Christianity at Duke University, or Semitic studies at the Freie Universität Berlin. Most students learn the Syriac langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syriac Language
The Syriac language (; syc, / '), also known as Syriac Aramaic (''Syrian Aramaic'', ''Syro-Aramaic'') and Classical Syriac ܠܫܢܐ ܥܬܝܩܐ (in its literary and liturgical form), is an Aramaic language, Aramaic dialect that emerged during the first century AD from a local Aramaic dialect that was spoken by Arameans in the ancient Aramean kingdom of Osroene, centered in the city of Edessa. During the Early Christian period, it became the main literary language of various Aramaic-speaking Christian communities in the historical region of Syria (region), Ancient Syria and throughout the Near East. As a liturgical language of Syriac Christianity, it gained a prominent role among Eastern Christian communities that used both Eastern Syriac Rite, Eastern Syriac and Western Syriac Rite, Western Syriac rites. Following the spread of Syriac Christianity, it also became a liturgical language of eastern Christian communities as far as India (East Syriac ecclesiastical province), India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syriaca
This list of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names is intended to help those unfamiliar with classical languages to understand and remember the scientific names of organisms. The binomial nomenclature used for animals and plants is largely derived from Latin and Greek words, as are some of the names used for higher taxa, such as orders and above. At the time when biologist Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) published the books that are now accepted as the starting point of binomial nomenclature, Latin was used in Western Europe as the common language of science, and scientific names were in Latin or Greek: Linnaeus continued this practice. Although Latin is now largely unused except by classical scholars, or for certain purposes in botany, medicine and the Roman Catholic Church, it can still be found in scientific names. It is helpful to be able to understand the source of scientific names. Although the Latin names do not always correspond to the current English common n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maronite Church
The Maronite Church is an Eastern Catholic ''sui iuris'' particular church in full communion with the pope and the worldwide Catholic Church, with self-governance under the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches. The current head of the Maronite Church is Patriarch Bechara Boutros al-Rahi, who was elected in March 2011 following the resignation of Patriarch Nasrallah Boutros Sfeir. The current seat of the Maronite Patriarchate is in Bkerke, northeast of Beirut, Lebanon. Officially known as the Antiochene Syriac Maronite Church, it is part of Syriac Christianity by liturgy and heritage. The early development of the Maronite Church can be divided into three periods, from the 4th to the 7th centuries. A congregation movement, with Saint Maron from the Taurus Mountains as an inspirational leader and patron saint, marked the first period. The second began with the establishment of the Monastery of Saint Maroun on the Orontes, built after the Council of Chalcedon to defend the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Church Of The East
The Ancient Church of the East is an Eastern Christian denomination. It branched from the Assyrian Church of the East in 1964, under the leadership of Mar Thoma Darmo (d. 1969). It is one of three Assyrian Churches that claim continuity with the historical Church of the East (the ancient Patriarchal Province of Seleucia-Ctesiphon), the others being the Assyrian Church of the East and the Chaldean Catholic Church. The Ancient Church of the East is headquartered in Baghdad, Iraq. From 1972 until his death in February 2022, the Church was headed by Catholicos-Patriarch Mar Addai II Giwargis. History The Ancient Church of the East began when in 1968 some members of the Assyrian Church of the East, then led by Shimun XXIII Eshai, left it and consecrated their own patriarch, Thoma Darmo. Darmo was strongly opposed to the system of hereditary succession of the position of patriarch of the Assyrian Church of the East, as well as its adoption of the Gregorian calendar "and other moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nestorian Church
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian Church, was an Eastern Christian church of the East Syriac Rite, based in Mesopotamia. It was one of three major branches of Eastern Christianity that arose from the Christological controversies of the 5th and 6th centuries, alongside the Oriental Orthodox Churches and the Chalcedonian Church. During the early modern period, a series of schisms gave rise to rival patriarchates, sometimes two, sometimes three. Since the latter half of the 20th century, three churches in Iraq claim the heritage of the Church of the East. Meanwhile, the East Syriac churches in India claim the heritage of the Church of the East in India. The Church of the East organized itself in 410 as the national church of the Sasanian Empire through the Council of Seleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaldean Catholic Church
, native_name_lang = syc , image = Assyrian Church.png , imagewidth = 200px , alt = , caption = Cathedral of Our Lady of Sorrows Baghdad, Iraq , abbreviation = , type = , main_classification = Eastern Catholic , orientation = Syriac Christianity (Eastern) , scripture = Peshitta , theology = Catholic theology , polity = , governance = Holy Synod of the Chaldean Church , structure = , leader_title = Pope , leader_name = Francis , leader_title1 = Patriarch , leader_name1 = Louis Raphaël I Sako , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = , leader_title3 = , leader_name3 = , fellowships_type = , fellowships = , fellowships_type1 = , fellowships1 = , division_type = , division = , division_type1 = , division1 = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syriac Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = syc , image = St_George_Syriac_orthodox_church_in_Damascus.jpg , imagewidth = 250 , alt = Cathedral of Saint George , caption = Cathedral of Saint George, Damascus, Syria , type = Church of Antioch, Antiochian , main_classification = Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian , orientation = Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox , scripture = Peshitta , theology = Miaphysitism , polity = Episcopal polity, Episcopal , structure = Koinonia, Communion , leader_title = Patriarch , leader_name = Ignatius Aphrem II Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch and All the East, Patriarch , fellowships_type = Catholicos of India, Catholicate of India , fellowships = Malankara Syriac Orthodox Church , associations = World Council of Churches , area = Middle East, India, and Assyrian–Chaldean� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Church Of The East
The Assyrian Church of the East,, ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية sometimes called Church of the East, officially the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East,; ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية الرسولية الجاثلقية المقدسة is an Eastern Christian church that follows the traditional Christology and ecclesiology of the historical Church of the East. It belongs to the eastern branch of Syriac Christianity, and employs the Divine Liturgy of Saints Addai and Mari belonging to the East Syriac Rite. Its main liturgical language is Classical Syriac, a dialect of Eastern Aramaic, and the majority of its adherents are ethnic Assyrians. The church also has an archdiocese located in India, known as the Chaldean Syrian Church of India. The Assyrian Church of the East is officially headquartered in the city of Erbil, in northern Iraq; its original area also spread into southeastern Turkey, northeastern Syria and northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicianism
Phoenicianism is a form of Lebanese nationalism adopted by many Lebanese people, at the time of the creation of Greater Lebanon. It constitutes identification of the Lebanese people with the ancient Phoenicians. Position Proponents claim that the land of Lebanon has been inhabited uninterruptedly since Phoenician times, and that the current population descends from the original population, with some admixture due to immigration over the centuries. They argue that Arabization merely represented a shift to the Arabic language as the vernacular of the Lebanese people, and that, according to them, no actual shift of ethnic identity, much less ancestral origins, occurred. In light of this "old controversy about identity", some Lebanese prefer to see Lebanon, Lebanese culture and themselves as part of "Mediterranean" and "Canaanite" civilization, in a concession to Lebanon's various layers of heritage, both indigenous, foreign non-Arab, and Arab. Some consider addressing all Lebanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
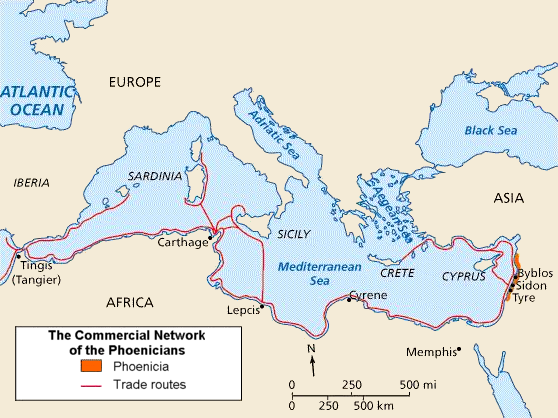
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arameanism
Terms for Syriac Christians are endonymic (native) and exonymic (foreign) terms, that are used as designations for ''Syriac Christians'', as adherents of Syriac Christianity. In its widest scope, Syriac Christianity encompass all Christian denominations that follow East Syriac Rite or West Syriac Rite, and thus use Classical Syriac as their main liturgical language. Traditional divisions among Syriac Christians along denominational lines are reflected in the use of various theological and ecclesiological designations, both historical and modern. Specific terms such as: Jacobites, Saint Thomas Syrian Christians, Maronites, Melkites, Nasranis, and Nestorians have been used in reference to distinctive groups and branches of Eastern Christianity, including those of Syriac liturgical and linguistic traditions. Some of those terms are polysemic, and their uses (both historical and modern) have been a subject of terminological disputes between different communities, and also among sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |