|
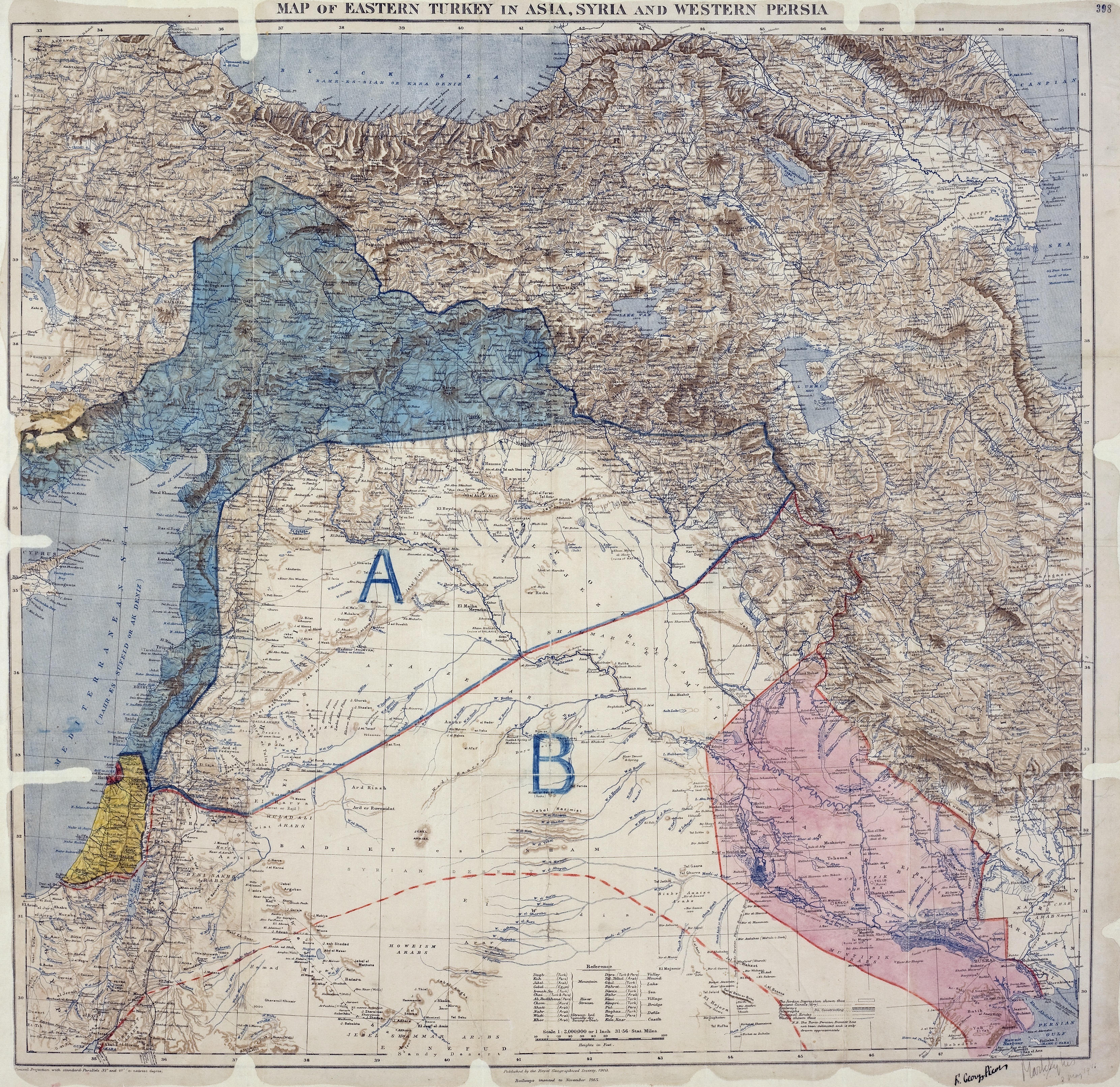
Syria-Cilicia Commemorative Medal
The Syria-Cilicia Medal () was a French decoration awarded to military personnel engaged in the hostilities that erupted in the Middle East in the immediate aftermath of World War I. Instituted in 1922, this campaign medal was awarded by the French Government for military service in the interwar period, to those serving on its behalf, since 1918, against ''de facto'' powers in The Levant. The Levant Campaign began in January 1920 when the Arab Kingdom of Syria engaged French armed forces in what would become called the Franco-Syrian War. This campaign ended on 24 July 1920, when French troops entered Damascus abolishing the Arab Kingdom of Syria. Turkey took advantage of the situation by also engaging France in what is now called the Franco-Turkish War pitting the French Colonial Forces and French Armenian Legion against the Turkish forces known as the Kuva-yi Milliye. This campaign, running from May 1920 to October 1921 resulted in French partial occupation of Turkish te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious". , motto = , image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg , image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg , seal_type = Seal , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Arab world#Asia , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Damascus within Syria , pushpin_relief = 1 , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_name1 = Damascus Governorate, Capital City , government_footnotes = , government_type = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Mohammad Tariq Kreishati , parts_type = Municipalities , parts = 16 , established_title = , established_date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noël Édouard, Vicomte De Curières De Castelnau
Noël Édouard, vicomte de Curières de Castelnau (24 December 1851 – 19 March 1944) was a French army general, army group commander and Chief of Staff of the Armed Forces during the First World War. Elected deputy in 1919 and president of the Army Commission in the legislature, he then took the head of a confessional political movement, the ''Fédération Nationale Catholique''. During the Second World War, he opposed Marshal Pétain and the Vichy regime and supported the French Resistance. For a long time controversial because of a Catholicism that was considered outrageous by his opponents, historians have moderated that portrait by emphasising his great loyalty to republican institutions and disputed in particular that he could have been reactionary or anti-Semitic. Early life The son of Michel de Castelnau, mayor of Saint-Affrique, Noël Édouard Marie Joseph de Curières de Castelnau was born in Saint-Affrique, into an aristocratic family of the Rouergue. He is the third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Assembly (France)
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known as (), meaning "delegate" or "envoy" in English; etymologically, it is a cognate of the English word ''deputy'', which is the standard term for legislators in many parliamentary systems). There are 577 , each elected by a single-member constituency (at least one per department) through a two-round system; thus, 289 seats are required for a majority. The president of the National Assembly, Yaël Braun-Pivet, presides over the body. The officeholder is usually a member of the largest party represented, assisted by vice presidents from across the represented political spectrum. The National Assembly's term is five years; however, the President of France may dissolve the Assembly, thereby calling for new elections, unless it has been dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée De La Légion D'Honneur
The Musée national de la Légion d'honneur et des ordres de chevalerie (French language, French for "National museum of the Legion of Honour and of orders of chivalry") is a French national museum of orders of merit and orders of chivalry. It is located in the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur beside the Musée d'Orsay at 2, rue de la Légion-d'Honneur, in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, 7th arrondissement of Paris, France. It is open daily except Monday and Tuesday; admission is free. The nearest métro and RER stations are Musée d'Orsay (Paris RER), Musée d'Orsay, Solférino (Paris Métro), Solférino, and Assemblée Nationale (Paris Métro), Assemblée Nationale. History The museum is housed within the Hôtel de Salm, built in 1782 by architect Pierre Rousseau for Frederick III, Prince of Salm-Kyrburg. The building burned in 1871 during the Paris Commune, and it subsequently was restored by a subscription of medallists. Since 1804, this building has been called the Palais de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordonnance
In French politics, an ''ordonnance'' (, "order") is a statutory instrument issued by the Council of Ministers in an area of law normally reserved for primary legislation enacted by the French Parliament. They function as temporary statutes pending ratification by the Parliament; failing ratification they function as mere executive regulations. ''Ordonnances'' should not be confused with '' décrets'' issued by the prime minister (an order-in-council) or president, or with ministerial orders (''arrêtés''); these are issued either in matters where the Constitution allows primary legislation from the Council or as secondary legislation implementing a statute. In the French justice system, the word can also refer to a summary ruling made by a single judge for simple cases. Current usage Motivations Article 34 of the Constitution of France restricts certain legal matters to primary legislation to be enacted by Parliament. All other areas of law fall within the domain of delegate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Syrian Revolt
The Great Syrian Revolt ( ar, الثورة السورية الكبرى) or Revolt of 1925 was a general uprising across the State of Syria and Greater Lebanon during the period of 1925 to 1927. The leading rebel forces comprised fighters of the Jabal Druze State in southern Syria, joined by Sunni, Druze, Alawite, and Christian factions. The common goal was to end French rule in the newly mandated regions, passed from Turkish to French administration following World War I. This revolution came in response to the repressive policies pursued by the French authorities under the Mandate for Syria and Lebanon, in dividing Syria into several occupied territories. The new French administration was perceived as being prejudiced against the dominant Arab culture and of intending to change the existing character of the country. In addition resentment was caused by the refusal of the French authorities to set a timetable for the independence of Syria. This revolution was an extension of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Pasha Al-Atrash
Sultan al-Atrash, (March 5, 1891 – March 26, 1982) ( ar, سلطان الأطرش), commonly known as Sultan Pasha al-Atrash ( ar, سلطان باشا الأطرش, links=no) was a prominent Arab Druze leader, Syrian nationalist and Commander General of the Syrian Revolution (1925–27). He fought against the French. One of the most influential figures in Syrian and Druze history, he played a major role in deciding the destiny of Jabal al-Druze and of Syria in general. Early life and career Sultan al-Atrash was born in al-Qrayya, a village 20 km south of Suwayda known for the famous Druze family of Al-Atrash, which had nominally governed the region since 1879. His father Zuqan led a fierce battle against the Ottomans near Al-Kefr in 1910, where he faced the forces of Sami Pasha al-Farouqi. He was captured and later executed in 1911. Sultan al-Atrash was an Ottoman army conscript, serving in the Balkans prior to the outbreak of World War I. Role in the Arab revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Agreement
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surrender, in which an army agrees to give up arms; or a ceasefire or truce, in which the parties may agree to temporarily or permanently stop fighting. The art of negotiating a peace treaty in the modern era has been referred to by legal scholar Christine Bell as the , with a peace treaty potentially contributing to the legal framework governing the post conflict period, or . Elements of treaties The content of a treaty usually depends on the nature of the conflict being concluded. In the case of large conflicts between numerous parties, international treaty covering all issues or separate treaties signed between each party. There are many possible issues that may be included in a peace treaty such as the following: * Formal designation of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuva-yi Milliye
The Kuva-yi Milliye ( ota, قواى مليه; 'National Forces' or 'Nationalist Forces') were irregular Turkish militia forces active in the early period of the Turkish War of Independence. These irregular forces emerged after the occupation of the parts of Turkey by the Allied forces in accordance with the Armistice of Mudros. Later, ''Kuva-yi Milliye'' were integrated to the regular army (''Kuva-yi Nizamiye'') of the Grand National Assembly. Some historians call this period (1918–20) of the Turkish War of Independence the "Kuva-yi Milliye phase".. Yılı Özel Sayısı. History In the Armistice of Mudros, Ottoman Empire was divided between the Allies, where the Greeks occupied the west, the British occupied the capital and southeast, and the Italians and the French occupied the south of the country. The ''Kuva-yi Milliye'' were the first armed groups to defend the Turks and muslims' rights in Anatolia and Rumelia. The ''Kuva-yi Milliye'' consisted of deserted Ottoman arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Armenian Legion
The Armenian Legion (french: Légion arménienne) was a volunteer unit that was raised by the Allied Powers to serve in the Middle East Theatre during World War I. Trained and led by French army commanders, the Légion d'Orient (The Eastern Legion), as the unit was originally known, was created in 1916, its ranks chiefly drawn from Levantine and Armenian exiles and refugees from the Ottoman Empire. In 1919, it was renamed the "Légion Arménienne" (The Armenian Legion). Background The establishment of an Armenian fighting force was first proposed by Boghos Nubar, the head of the Armenian National Delegation in Paris, during the landing of Allied forces to Alexandretta in 1914, to British military planners. The British government rejected the plan, on the basis that such a plan would lead to the massacres of local Armenians. However, appeals by the Armenian National Defense Committee continued into 1915. French authorities also rejected the plan at the end of 1915. In 1916, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |