|
Suspensory Ligament Of The Penis
The suspensory ligament of the penis is attached to the pubic symphysis, which holds the penis close to the pubic bone and supports it when erect. The ligament does not directly connect to the Corpus cavernosum penis, but may still play a role in erectile dysfunction. The ligament can be surgically lengthened in a procedure known as ligamentolysis, which is a form of penis enlargement. Gallery File:Slide4Nemo.JPG, Anterior abdominal wall. Intermediate dissection. Anterior view. File:Spermatic cord.jpg, Suspensory ligament of penis. See also * Suspensory ligament of clitoris * fundiform ligament The fundiform ligament or fundiform ligament of the penis is a specialization or thickening of the superficial ( Scarpa's) fascia extending from the linea alba of the lower abdominal wall. It runs from the level of the pubic bone, laterally aroun ... of penis References External links * The Mayo Clinic -Penis enlargement: Fulfillment or fallacy?* {{Authority control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
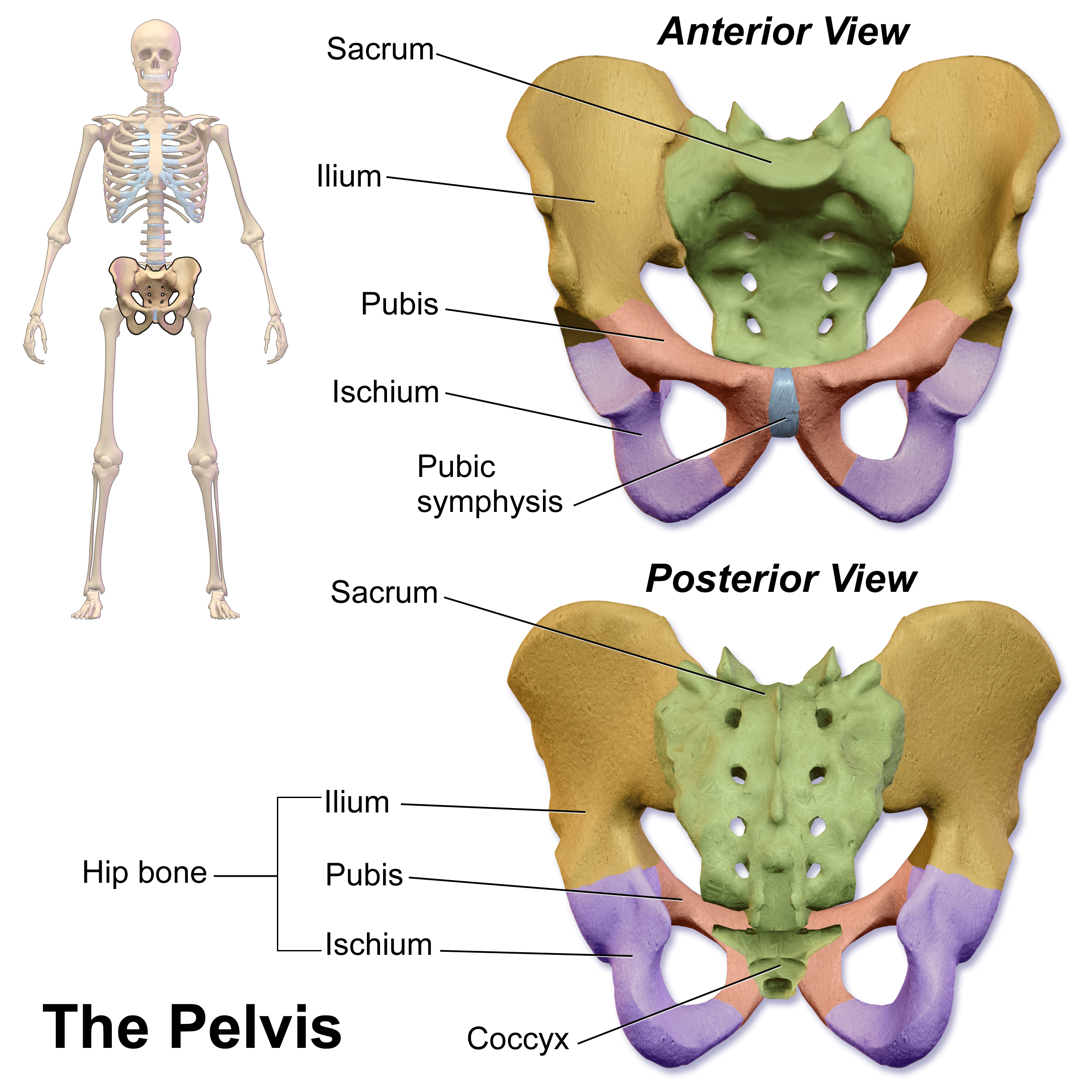
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do not bear a penis in every animal species, and in those species in which the male does bear a so-called penis, the penises in the various species are not necessarily homologous. The term ''penis'' applies to many intromittent organs, but not to all. As an example, the intromittent organ of most cephalopoda is the hectocotylus, a specialized arm, and male spiders use their pedipalps. Even within the Vertebrata there are morphological variants with specific terminology, such as Hemipenis, hemipenes. In most species of animals in which there is an organ that might reasonably be described as a penis, it has no major function other than intromission, or at least conveying the sperm to the female, but in the Eutheria, placental mammals the peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal or sexual attraction, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection varies considerably between humans. Physiologically, an erection is required for a male to effect vaginal penetration or sexual intercourse and is triggered by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, causing the levels of nitric oxide (a vasodilator) to rise in the trabecular arteries and smooth muscle of the penis. The arteries dilate causing the corpora cavernosa of the penis (and to a lesser extent the corpus spongiosum) to fill with blood; simultaneously the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles compress the veins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Cavernosum Penis
A corpus cavernosum penis (singular) (literally "cave-like body" of the penis, plural corpora cavernosa) is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue, which contain most of the blood in the penis during an erection. Such a corpus is homologous to the corpus cavernosum clitoridis in the female; the body of the clitoris that contains erectile tissue in a pair of corpora cavernosa with a recognisably similar structure. Anatomy The two corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum (also known as the ''corpus cavernosum urethrae'' in older texts and in the adjacent diagram) are three expandable erectile tissues along the length of the penis, which fill with blood during penile erection. The two corpora cavernosa lie along the penis shaft, from the pubic bones to the head of the penis, where they join. These formations are made of a sponge-like tissue containing trabeculae, irregular blood-filled spaces lined by endothelium and separated by septum of the penis. The male ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men.Cunningham GR, Rosen RC. Overview of male sexual dysfunction. In: UpToDate, Martin KA (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA, 2018. Through its connection to self-image and to problems in sexual relationships, erectile dysfunction can cause psychological harm. In about 80% of cases, physical causes can be identified. These include cardiovascular disease; diabetes mellitus; neurological problems, such as those following prostatectomy; hypogonadism; and drug side effects. About 10% of cases are psychological impotence, caused by thoughts or feelings; here, there is a strong response to placebo treatment. The term ''erectile dysfunction'' is not used for other disorders of erection, such as priapism. Treatment involves addressing the underlying causes, lifestyle modifications, and addres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penis Enlargement
Penis enlargement, or male enhancement, is any technique aimed to increase the size of a human penis. Some methods aim to increase total length, others the shaft's girth, and yet others the glans size. Techniques include surgery, supplements, ointments, patches, and physical methods like pumping, jelqing, and traction. Surgical penis enlargement methods can be effective; however, such methods carry risks of complications and are not medically indicated except in cases involving a micropenis. Noninvasive methods have received little scientific study, and most lack scientific evidence of effectiveness. However, limited scientific evidence supports some elongation by prolonged traction. Some quack products may improve penis erection, mistaken by consumers for penis enlargement. Surgical methods There are several surgical penis enlargement treatments, most of which carry a risk of significant complications. Procedures by unlicensed surgeons can lead to serious complications. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspensory Ligament Of Clitoris
The suspensory ligament of the clitoris is a fibrous band at the deep fascial level that extends from the pubic symphysis to the deep fascia of the clitoris, anchoring the clitoris to the pubic symphysis. By virtue of this connection, the pubic symphysis supports the clitoris. The suspensory ligament of the clitoris consistently displays two components: a superficial fibro-fatty structure extending from a broad base within the mons pubis to converge on the body of the clitoris and extending into the labia majora, and a deep component with a narrow origin on the symphysis pubis extending to the body and the bulbs of the clitoris. Its form and position differ from those of the suspensory ligament of the penis. During sexual arousal, the ligament shortens and swells. This pulls the clitoral shaft in such a way that the clitoral glans appears to retract beneath the clitoral hood. See also * Suspensory ligament of penis The suspensory ligament of the penis is attached to the pubic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundiform Ligament
The fundiform ligament or fundiform ligament of the penis is a specialization or thickening of the superficial ( Scarpa's) fascia extending from the linea alba of the lower abdominal wall. It runs from the level of the pubic bone, laterally around the sides of the penis like a sling, and then unites at the base of the penis before going to the septum of the scrotum. It is just superficial to the suspensory ligament A suspensory ligament is a ligament that supports a body part, especially an organ. Types include: * Suspensory ligament of axilla, also known as Gerdy's ligament * Cooper's ligaments, also known as the suspensory ligaments of Cooper or Suspensory .... Although rarely mentioned, this ligament is also found in females. External links * - "Anterior Abdominal Wall: Layers of the Superficial Fascia" * - "The Male Perineum and the Penis: The Fundiform Ligament" * Mammal male reproductive system Ligaments Sexual anatomy {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal Male Reproductive System
Most mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypuses and the echidnas, lay eggs. The monotremes have a sex determination system different from that of most other mammals. In particular, the sex chromosomes of a platypus are more like those of a chicken than those of a therian mammal. The mammary glands of mammals are specialized to produce milk, a liquid used by newborns as their primary source of nutrition. The monotremes branched early from other mammals and do not have the teats seen in most mammals, but they do have mammary glands. The young lick the milk from a mammary patch on the mother's belly. Viviparous mammals are in the subclass Theria; those living today are in the Marsupialia and Placentalia infraclasses. A marsupial has a short gestation period, typically shorter than its estrous cycle, and gives birth to an underdeveloped (altricial) newborn that then undergoes further development; in many species, this ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligaments
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



