|
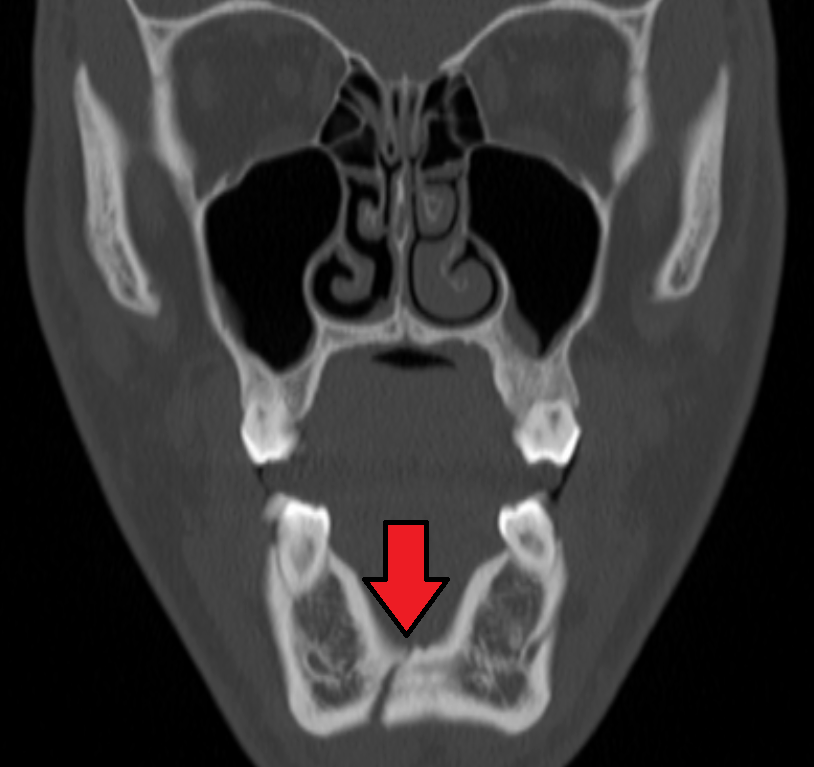
Submental Space
The submental space is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space located between the mylohyoid muscle superiorly, the platysma muscle inferiorly, under the chin in the midline. The space coincides with the anatomic region termed the submental triangle, part of the anterior triangle of the neck. Location and structure Anatomic boundaries The boundaries of the submental space are: * the mylohyoid muscle superiorly * the investing layer of deep cervical fascia (and this in turn is covered by the platysma muscle) inferiorly * the inferior border of the mandible anteriorly * the hyoid bone posteriorly * the anterior bellies of the digastric muscles laterally. Communications The communications of the submental space are: * the submandibular spaces posterolaterally. * the sublingual space superiorly (via erosion through the mylohyoid). Contents Its contents are submental lymph nodes, areolar connective tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascial Spaces Of The Head And Neck
Fascial spaces (also termed fascial tissue spaces or tissue spaces) are potential spaces that exist between the fasciae and underlying organs and other tissues. In health, these spaces do not exist; they are only created by pathology, e.g. the spread of pus or cellulitis in an infection. The fascial spaces can also be opened during the dissection of a cadaver. The fascial spaces are different from the fasciae themselves, which are bands of connective tissue that surround structures, e.g. muscles. The opening of fascial spaces may be facilitated by pathogenic bacterial release of enzymes which cause tissue lysis (e.g. hyaluronidase and collagenase). The spaces filled with loose areolar connective tissue may also be termed clefts. Other contents such as salivary glands, blood vessels, nerves and lymph nodes are dependent upon the location of the space. Those containing neurovascular tissue (nerves and blood vessels) may also be termed compartments. Generally, the spread of infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on the outside by the lips and inside by the pharynx. In tetrapods, it contains the tongue and, except for some like birds, teeth. This cavity is also known as the buccal cavity, from the Latin ''bucca'' ("cheek"). Some animal phyla, including arthropods, molluscs and chordates, have a complete digestive system, with a mouth at one end and an anus at the other. Which end forms first in ontogeny is a criterion used to classify bilaterian animals into protostomes and deuterostomes. Development In the first multicellular animals, there was probably no mouth or gut and food particles were engulfed by the cells on the exterior surface by a process known as endocytosis. The particles became enclosed in vacuoles into which enzymes were secr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascial Spaces Of The Head And Neck
Fascial spaces (also termed fascial tissue spaces or tissue spaces) are potential spaces that exist between the fasciae and underlying organs and other tissues. In health, these spaces do not exist; they are only created by pathology, e.g. the spread of pus or cellulitis in an infection. The fascial spaces can also be opened during the dissection of a cadaver. The fascial spaces are different from the fasciae themselves, which are bands of connective tissue that surround structures, e.g. muscles. The opening of fascial spaces may be facilitated by pathogenic bacterial release of enzymes which cause tissue lysis (e.g. hyaluronidase and collagenase). The spaces filled with loose areolar connective tissue may also be termed clefts. Other contents such as salivary glands, blood vessels, nerves and lymph nodes are dependent upon the location of the space. Those containing neurovascular tissue (nerves and blood vessels) may also be termed compartments. Generally, the spread of infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyspnoea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, interstitial lung disease, congestive heart failure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful. Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired. The legs and face are the most common sites involved, although cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The leg is typically affected following a break in the skin. Other risk factors include obesity, leg swelling, and old age. For facial infections, a break in the skin beforehand is not usually the case. The bacteria most commonly involved are streptococci and '' Staphylococcus aureus''. In contrast to cellulitis, erysipelas is a bacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig's Angina
Ludwig's angina (lat.: Angina ludovici) is a type of severe cellulitis involving the floor of the mouth and is often caused by bacterial sources. Early in the infection, floor of the mouth raises due to swelling, leading to difficulty swallowing saliva. As a result, patients may present with difficulty speaking and drooling. As the condition worsens, the airway may be compromised and hardening of the spaces on both sides of the tongue may develop. Overall, this condition has a rapid onset over a few hours. The majority of cases follow a dental infection. Other causes include a parapharyngeal abscess, mandibular fracture, cut or piercing inside the mouth, or submandibular salivary stones. The infection spreads through the connective tissue of the floor of the mouth and is normally caused by infectious and invasive organisms such as ''Streptococcus'', ''Staphylococcus'', and ''Bacteroides''. Prevention is by appropriate dental care including management of dental infections. Init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incision And Drainage
Incision and drainage (I&D), also known as clinical lancing, are minor surgical procedures to release pus or pressure built up under the skin, such as from an abscess, boil, or infected paranasal sinus. It is performed by treating the area with an antiseptic, such as iodine-based solution, and then making a small incision to puncture the skin using a sterile instrument such as a sharp needle or a pointed scalpel. This allows the pus fluid to escape by draining out through the incision. Good medical practice for large abdominal abscesses requires insertion of a drainage tube, preceded by insertion of a PICC line to enable readiness of treatment for possible septic shock. Adjunct antibiotics Uncomplicated cutaneous abscesses do not need antibiotics after successful drainage. In incisional abscesses For incisional abscesses, it is recommended that incision and drainage is followed by covering the area with a thin layer of gauze followed by sterile dressing. The dressing should be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a disease#Terminology, condition in its own right. It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liquids from the mouth to the stomach, a lack of Pharynx, pharyngeal sensation or various other inadequacies of the swallowing mechanism. Dysphagia is distinguished from other symptoms including odynophagia, which is defined as painful swallowing, and Globus Pharyngis, globus, which is the sensation of a lump in the throat. A person can have dysphagia without odynophagia (dysfunction without pain), odynophagia without dysphagia (pain without dysfunction) or both together. A psychogenic disease, psychogenic dysphagia is known as phagophobia. Classification Dysphagia is classified into the following major types: # Oropharyngeal dysphagia # Esophageal dysphagia, Esophageal and obstructive dysphagia # Neuromuscular symptom comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In many areas of the world, the most common bacteria present is ''methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus''. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world. Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it looks like and is confirmed by cutting it open. Ultrasound imaging may be useful in cases in which the diagnosis is not clear. In abscesses around the anus, computer tomography (CT) may be important to look for deeper infection. Standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Fracture
Mandibular fracture, also known as fracture of the jaw, is a break through the mandibular bone. In about 60% of cases the break occurs in two places. It may result in a decreased ability to fully open the mouth. Often the teeth will not feel properly aligned or there may be bleeding of the gums. Mandibular fractures occur most commonly among males in their 30s. Mandibular fractures are typically the result of trauma. This can include a fall onto the chin or a hit from the side. Rarely they may be due to osteonecrosis or tumors in the bone. The most common area of fracture is at the condyle (36%), body (21%), angle (20%) and symphysis (14%). While a diagnosis can occasionally be made with plain X-ray, modern CT scans are more accurate. Immediate surgery is not necessarily required. Occasionally people may go home and follow up for surgery in the next few days. A number of surgical techniques may be used including maxillomandibular fixation and open reduction internal fixati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontogenic Infection
An odontogenic infection is an infection that originates within a tooth or in the closely surrounding tissues. The term is derived from '' odonto-'' (Ancient Greek: , – 'tooth') and '' -genic'' (Ancient Greek: , ; – 'birth'). The most common causes for odontogenic infection to be established are dental caries, deep fillings, failed root canal treatments, periodontal disease, and pericoronitis. Odontogenic infection starts as localised infection and may remain localised to the region where it started, or spread into adjacent or distant areas. It is estimated that 90-95% of all orofacial infections originate from the teeth or their supporting structures and are the most common infections in the oral and maxilofacial region. Odontogenic infections can be severe if not treated and are associated with mortality rate of 10 to 40%. Furthermore, about 70% of odontogenic infections occur as periapical inflammation, i.e. acute periapical periodontitis or a periapical abscess. The next m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)