|
Skaergaard Intrusion
The Skaergaard intrusion is a layered igneous intrusion in the Kangerlussuaq area, East Greenland. It comprises various rock types including gabbro, ferro diorite, anorthosite and granophyre. Discovered by Lawrence Wager in 1931 during the British Arctic Air Route Expedition led by Gino Watkins, the intrusion has been important to the development of key concepts in igneous petrology, including magma differentiation and fractional crystallisation and the development of layering. The Skaergaard intrusion formed when tholeiitic magma was emplaced about 55 million years ago,Brooks, CK, Gleadow, AJW (1977) ''A fission-track age for the Skaergaard intrusion and the age of the East Greenland basalts''. Geology, v. 5, p. 539-540. during the initial opening of the North Atlantic Ocean. The body represents essentially a single pulse of magma, which crystallized from the bottom upward and the top downward. The intrusion is characterized by exceptionally well-developed cumulate layering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Layered Intrusion
A layered intrusion is a large sill-like body of igneous rock which exhibits vertical layering or differences in composition and texture. These intrusions can be many kilometres in area covering from around to over and several hundred metres to over in thickness.Blatt, Harvey and Tracy, Robert J. (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic,'' 2nd ed., pp. 123–132 & 194–197, Freeman, While most layered intrusions are Archean to Proterozoic in age (for example, the Paleoproterozoic Bushveld complex), they may be any age such as the Cenozoic Skaergaard intrusion of east Greenland or the Rum layered intrusion in Scotland. Although most are ultramafic to mafic in composition, the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of Greenland is an alkalic intrusion. Layered intrusions are typically found in ancient cratons and are rare but worldwide in distribution. The intrusive complexes exhibit evidence of fractional crystallization and crystal segregation by settling or floating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Malcolm Brown
Sir George Malcolm Brown, FRS (5 October 1925 – 27 March 1997) was one of the most respected geologists of the second half of the twentieth century. His formidable reputation as an igneous petrologist enabled him to become one of the few scientists invited by NASA to work on the Moon rock samples recovered from the Apollo 11 lunar mission. Early life Brown was born in Redcar and was educated at Coatham School. Following a period in the RAF, he entered the geology department of Durham University in 1947, graduating with First Class Honours in 1950. The Professor of Geology, Lawrence Wager, recognised Brown's abilities, and took him with him as a research student following his move to the Chair in Geology at Oxford University. Brown's research centred on the ultrabasic complex of Rhum, Scotland and built upon earlier work undertaken by W.A. Deer and L.R. Wager. He received his D.Phil in 1954. Academic career Expeditions to Greenland to research the Skaergaard intrusio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Research
Arctic studies may include: * Arctic ecology *Geology *Meteorology *Pedology *Oceanography See also * List of Arctic research programs * List of research stations in the Arctic A number of governments maintain permanent research stations in the Arctic. Also known as Arctic bases, polar stations or ice stations, these bases are widely distributed across the northern polar region of Earth. Historically few research st ... References Earth sciences Arctic research {{arctic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Greenland
Greenland is the largest island on Earth. Only one-fifth of its surface area is exposed bedrock, the rest being covered by ice. The exposed surface is approximately 410,000 km2. The geology of Greenland is dominated by crystalline rocks of the Precambrian Shield."Greenland Geology." ''Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland''. 20 June 2003 (retrieved 26 Dec 2010) The crystalline rocks of the Nuuk/Qeqertarsuatsiaat area comprise some of the oldest bedrock in Greenland which covers most of western Greenland. The surface has been altered several times and has an appearance as though it were shaped billions of years ago. This is one of the reasons why the Nuuk area is extraordinary and also because the particular climate zone for the area limits the vegetation which makes it poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skaergaardite
Skaergaardite is an intermetallic platinum group mineral with the general chemical formula Pd Cu. The mineral is named after its discovery location: the Skaergaard intrusion, Kangerdlugssuaq area, East Greenland. The mineral name was approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 2003. The mineral has also been reported in the Duluth intrusion in Minnesota and the Rum layered intrusion in Scotland. Occurrence Skaergaardite is associated with igneous intrusions containing well-preserved, oxide-rich, tholeiitic gabbro. It is found as inclusions in titanian magnetite, ilmenite, pyroxenes, and plagioclase. Skaergaardite can occur as an inclusion by itself, but is more commonly found in composite microglobule inclusions of copper iron sulfide minerals and other precious metal bearing minerals. Crystallography and symmetry The crystallography of skaergaardite was determined using x-ray powder diffraction data. It has an isometric (cubic) crystal system an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
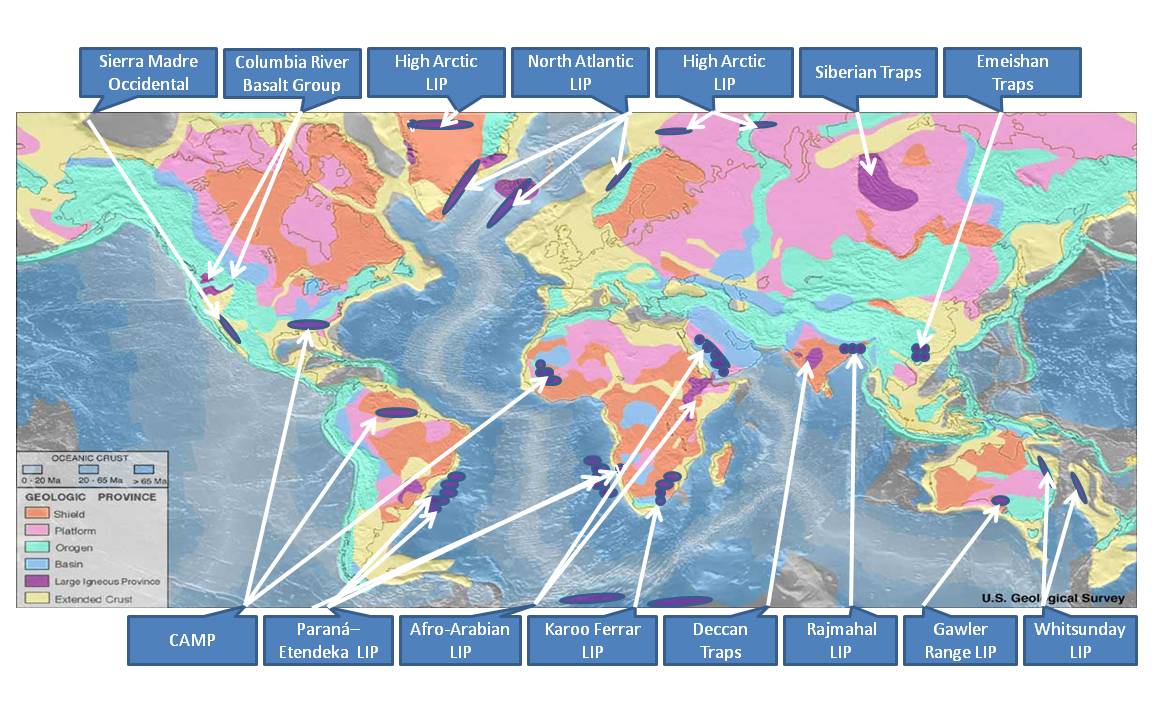
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reaching the surface of the earth via a mantle plume. Flood basalt provinces such as the Deccan Traps of India are often called '' traps'', after the Swedish word ''trappa'' (meaning "staircase"), due to the characteristic stairstep geomorphology of many associated landscapes. Michael R. Rampino and Richard Stothers (1988) cited eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurring in the past 250 million years, creating large igneous provinces, lava plateaus, and mountain ranges. However, more have been recognized such as the large Ontong Java Plateau, and the Chilcotin Group, though the latter may be linked to the Columbia River Basalt Group. Large igneous provinces have been connected to five mass extinction events, and may be associated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With the exception of extremely rare native iron deposits, it is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring minerals on Earth. Naturally magnetized pieces of magnetite, called lodestone, will attract small pieces of iron, which is how ancient peoples first discovered the property of magnetism. Magnetite is black or brownish-black with a metallic luster, has a Mohs hardness of 5–6 and leaves a black streak. Small grains of magnetite are very common in igneous and metamorphic rocks. The chemical IUPAC name is iron(II,III) oxide and the common chemical name is ''ferrous-ferric oxide''. Properties In addition to igneous rocks, magnetite also occurs in sedimentary rocks, including banded iron formations and in lake and marine sediment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite to anorthite endmembers (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium and calcium atoms can substitute for each other in the mineral's crystal lattice structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or 'record-groove' effect. Plagioclase is a major constituent mineral in the Earth's crust, and is consequently an important diagnostic tool in petrology for identifying the composition, origin and evolution of igneous rocks. Plagioclase is also a major constituent of rock in the hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) or magnesium (Mg) and more rarely zinc, manganese or lithium, and Y represents ions of smaller size, such as chromium (Cr), aluminium (Al), magnesium (Mg), cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V) or even iron (Fe II) or (Fe III). Although aluminium substitutes extensively for silicon in silicates such as feldspars and amphiboles, the substitution occurs only to a limited extent in most pyroxenes. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra. Pyroxenes that crystallize in the monoclinic system are known as clinopyroxenes and those that crystallize in the orthorhombic system are known as orthopyroxenes. The name ''pyroxene'' is derived from the Ancient Greek words for 'f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. For this reason, olivine has been proposed as a good candidate for accelerated weathering to sequester carbon dioxide from the Earth's oceans and atmosphere, as part of climate change mitigation. Olivine also has many other historical uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulate Rock
Cumulate rocks are igneous rocks formed by the accumulation of crystals from a magma either by settling or floating. Cumulate rocks are named according to their texture; cumulate texture is diagnostic of the conditions of formation of this group of igneous rocks. Cumulates can be deposited on top of other older cumulates of different composition and colour, typically giving the cumulate rock a layered or banded appearance. Formation Cumulate rocks are the typical product of precipitation of solid crystals from a fractionating magma chamber. These accumulations typically occur on the floor of the magma chamber, although they are possible on the roofs if anorthite plagioclase is able to float free of a denser mafic melt. Cumulates are typically found in ultramafic intrusions, in the base of large ultramafic lava tubes in komatiite and magnesium rich basalt flows and also in some granitic intrusions. Terminology Cumulates are named according to their dominant mineralogy and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_Stillwater_Mine_MT.jpg)