|
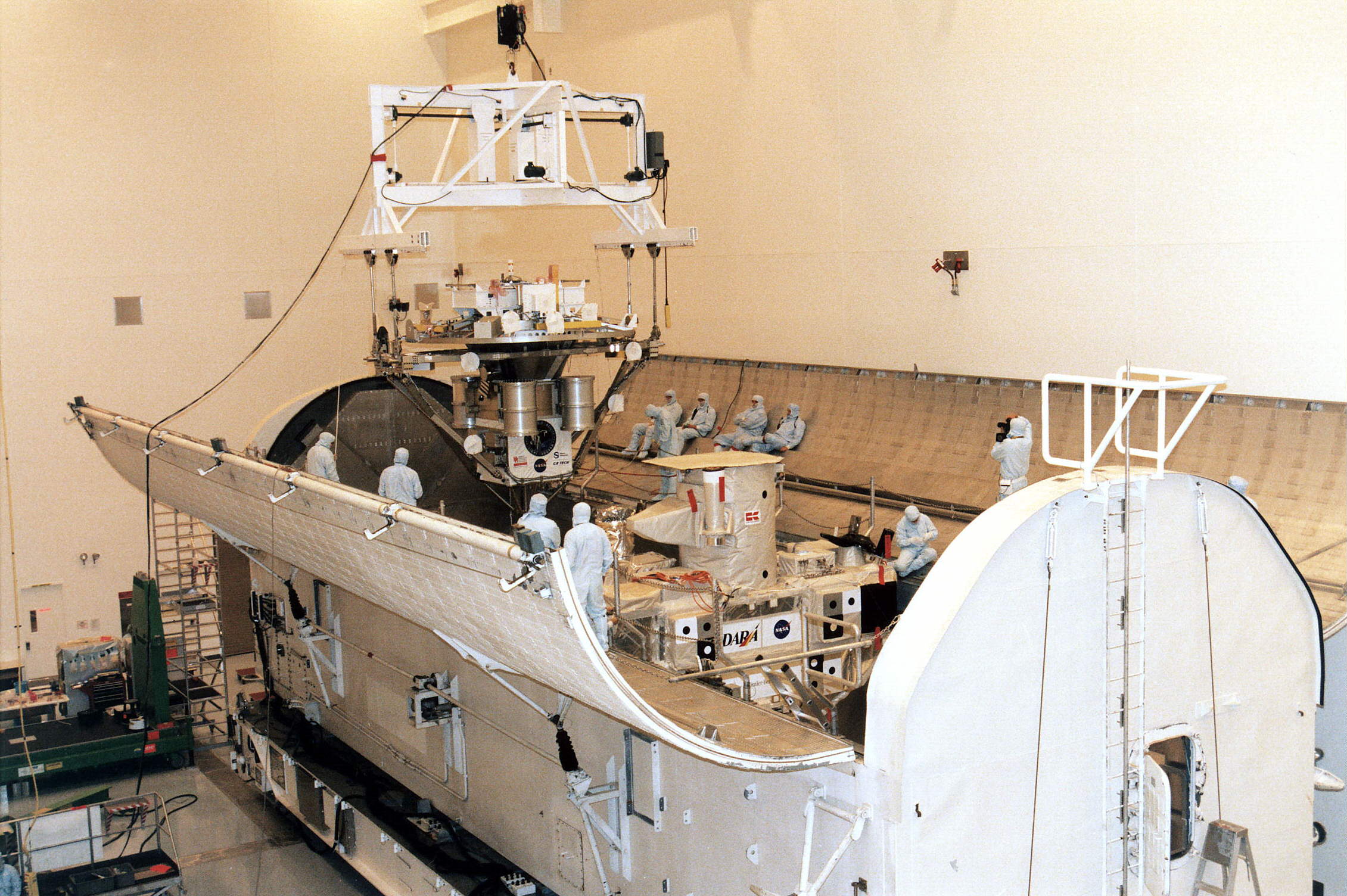
Shuttle Pallet Satellite
The shuttle pallet satellite was a satellite bus designed to be deployed and then retrieved for return to Earth on NASA's Space Shuttle. It carried a variety of payloads both scientific and military in nature. It was made by Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm and first flew in 1983. It was carried for the first time during the STS-7 mission and called SPAS-01 carrying 10 payloads. It flew again on the STS-39 mission in 1991 called IBSS-SPAS (Infrared Background Signature Survey – Shuttle Palette Satellite) for the DOD testing various ballistic missile detection sensors. SPAS flew for the third time with the STS-51 mission in 1991 called ORFEUS-SPAS (Orbiting & Retrievable Far & Extreme UV Spectrometer – Shuttle Palette Satellite) with ultraviolet instruments. ORFEUS-SPAS was flown again on the STS-80 mission. SPAS was flown for the second to last time with the CRISTA-SPAS (Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers & Telescopes for the Atmosphere – Shuttle Palette Satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
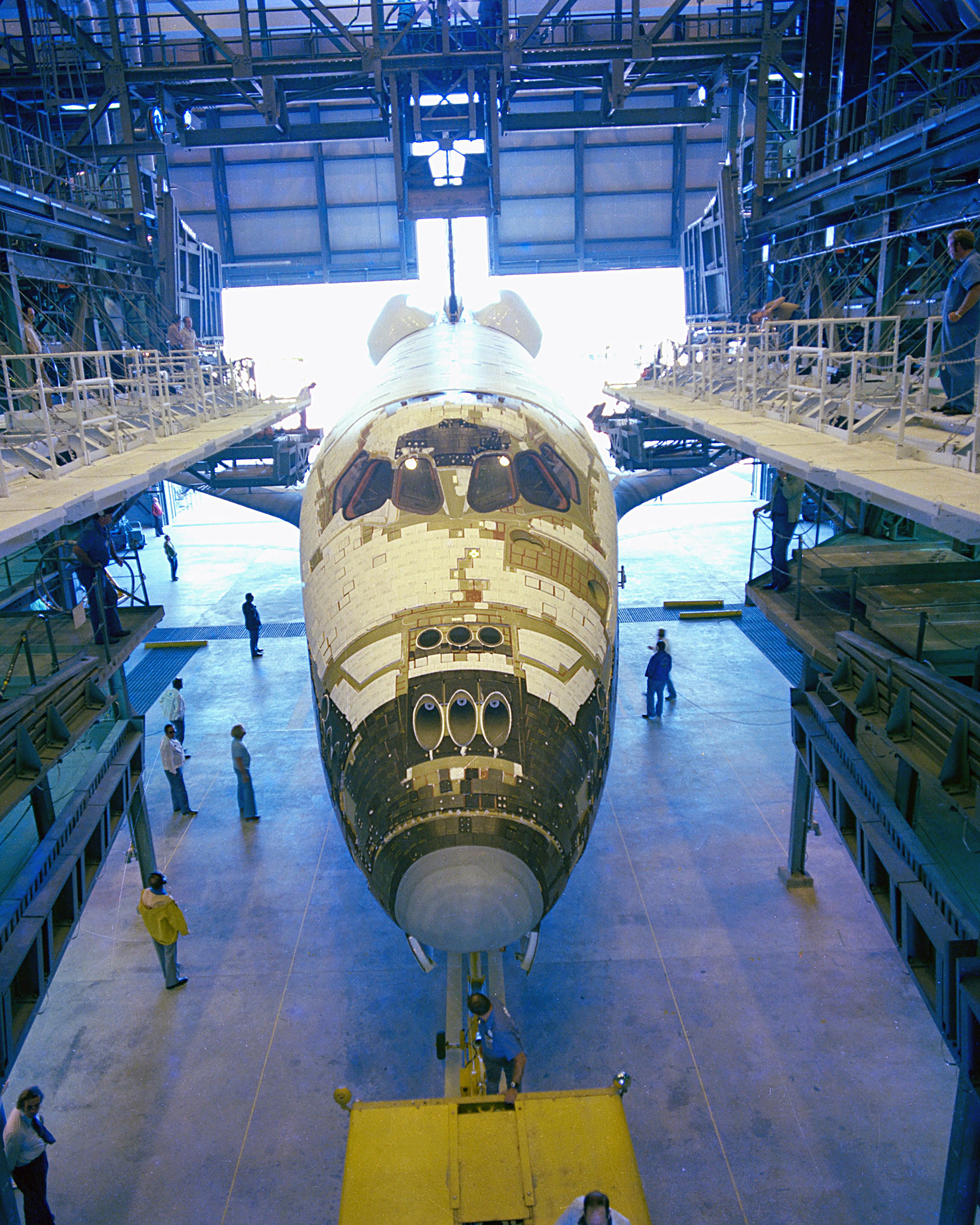
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) was a West German aerospace manufacturer. It was formed during the late 1960s as the result of efforts to consolidate the West German aerospace industry; aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt AG merged with the civil engineering and aviation firm Bölkow during 1968, while rival aircraft manufacturer Hamburger Flugzeugbau was acquired by the company in the following year. The company was responsible for the development and manufacture of various aircraft during its existence. Among its best-known products was the MBB Bo 105 light twin-engine helicopter and its enlarged derivative, the MBB/Kawasaki BK 117. MBB was also a key early partner on the Airbus A300, a wide-body twin-jet airliner; the company's involvement in the A300's development and production led to it forming a key component of the multinational Airbus consortium. It was also involved in numerous experimental aircraft programmes, such as the MBB Lampyridae, an aborted stealth aircraft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-7
STS-7 was NASA's seventh Space Shuttle mission, and the second mission for the Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. During the mission, ''Challenger'' deployed several satellites into orbit. The shuttle launched from Kennedy Space Center on June 18, 1983, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base on June 24, 1983. STS-7 carried Sally Ride, America's first female astronaut. Crew Support crew * John E. Blaha * Roy D. Bridges Jr. (ascent CAPCOM) * Guy Gardner * Terry Hart * Jon McBride * Bryan D. O'Connor (entry CAPCOM) Crew seat assignments Mission summary STS-7 began on June 18, 1983, with an on-time liftoff at 07:33:00 a.m. EDT. It was the first spaceflight of an American woman (Ride), the largest crew to fly in a single spacecraft up to that time (five people), and the first flight that included members of NASA's Group 8 astronaut class, which had been selected in 1978 to fly the Space Shuttle. President Ronald Reagan also sent his personal favorite Jelly Belly jelly bean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-39
STS-39 was the twelfth mission of the NASA Space Shuttle ''Discovery'', and the 40th orbital shuttle mission overall. The primary purpose of the mission was to conduct a variety of payload experiments for the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). Crew Crew seating arrangements Mission highlights Launch was originally scheduled for March 9, 1991, but during processing work at Pad LC-39A, significant cracks were found on all four lug hinges on the two external tank umbilical door drive mechanisms. NASA managers opted to roll back the vehicle to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on March 7, 1991, and then to Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) for repair. The faulty hinges were replaced with units taken from orbiter ''Columbia'', and reinforced. ''Discovery'' was returned to the pad on April 1, 1991, and the launch was rescheduled for April 23. The mission was again postponed when, during prelaunch external tank loading, a transducer on high-pressure oxidizer turbopump f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-51
STS-51 was a NASA Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' mission that launched the Advanced Communications Technology Satellite (ACTS) in September 1993. The flight also featured the deployment and retrieval of the SPAS-ORFEUS satellite and its IMAX camera, which captured spectacular footage of ''Discovery'' in space. A spacewalk was also performed during the mission to evaluate tools and techniques for the STS-61 Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission later that year. STS-51 was the first shuttle mission to fly a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver, a Trimble TANS Quadrex. It was mounted in an overhead window where limited field of view (FoV) and signal attenuation from the glass severely impacted receiver performance. Full triple-redundant 3-string GPS would not happen until 14 years later with STS-118 in 2007. Crew Launch Preparations STS-51 was notable for having been scrubbed three times on the launchpad, each time after the crew had boarded the spacecraft: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-80
STS-80 was a Space Shuttle mission flown by Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. The launch was originally scheduled for 31 October 1996, but was delayed to 19 November for several reasons. Likewise, the landing, which was originally scheduled for 5 December, was pushed back to 7 December after bad weather prevented landing for two days. It was the longest Shuttle mission ever flown at 17 days, 15 hours, and 53 minutes. Although two spacewalks were planned for the mission, they were both canceled after problems with the airlock hatch prevented astronauts Tom Jones and Tammy Jernigan from exiting the orbiter. Crew Crew seating arrangements *During landing, Musgrave remained on the flight deck in order to film the spacecraft's reentry through the overhead windows. Mission highlights * The mission deployed two satellites and successfully recovered them after they had performed their tasks. * Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-66
STS-66 was a Space Shuttle program mission that was flown by the Space Shuttle ''Atlantis''. STS-66 launched on 3 November 1994 at 11:59:43.060 am EDT from Launch Pad 39-B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. ''Atlantis'' landed at Edwards Air Force Base on 14 November 1994 at 10:33:45 am EST. Crew Mission highlights The Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Sciences – 3 (ATLAS-03) was the primary payload aboard STS-66. It continued the series of Spacelab flights to study the energy of the sun and how it affects the Earth's climate and environment. The ATLAS-03 mission made the first detailed measurements from the Shuttle of the Northern Hemisphere's middle atmosphere in late fall. The timing of the flight, when the Antarctic ozone hole is diminishing, allowed scientists to study possible effects of the ozone hole on mid-latitudes, the way Antarctic air recovers, and how the northern atmosphere changes as the winter season approaches. In addition to the ATLAS-03 inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-85
STS-85 was a Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' mission to perform multiple space science packages. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on 7 August 1997. A major experiment was the CRISTA-SPAS free-flyer which had various telescopes on board. Crew Mission highlights The deployment and retrieval of a satellite designed to study Earth's middle atmosphere along with a test of potential International Space Station hardware highlighted NASA's sixth Shuttle mission of 1997. The prime payload for the flight, the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-Shuttle Pallet Satellite-2 ( CRISTA-SPAS-2) made its second flight on the Space Shuttle (previous flight STS-66 in 1994) and was the fourth mission in a cooperative venture between the German Space Agency (DARA) and NASA. During the flight, Davis used ''Discoverys robot arm to deploy the CRISTA-SPAS payload for about 9 days of free-flight. CRISTA-SPAS consists of three telescopes and four spectrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |