|
Savings Identity
The saving identity or the saving-investment identity is a concept in national income accounting stating that the amount saved in an economy will be the amount invested in new physical machinery, new inventories, and the like. More specifically, in an open economy (an economy with foreign trade and capital flows), private saving plus governmental saving (the government budget surplus or the negative of the deficit) plus foreign investment domestically (capital inflows from abroad) must equal private physical investment. In other words, the flow variable investment must be financed by some combination of private domestic saving, government saving (surplus), and foreign saving (foreign capital inflows). This is an "identity", meaning it is true by definition. This identity only holds true because investment here is defined as including inventory accumulation, both deliberate and unintended. Thus, should consumers decide to save more and spend less, the fall in demand would lead to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Income Accounting
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income (NNI adjusted for natural resource depletion – also called as NNI at factor cost). All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by ''imputing'' monetary values to them. National accounts Arriving at a figure for the total production of goods and services in a large region like a country entails a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saving-investment Balance
In economics, saving-investment balance or I-S balance is a balance of national savings and national investment, which is equal to current account. This relationship is obtained from the national income identity. Description This is the national income identity: :Y=C+I+G+(EX-IM) where *Y: GDP, *C: national consumption, *I: national investment, *G: government spending, *EX: export, *IM: import, *EX-IM: current account. The national income identity can be rewritten as following:Christiano, 2003Rough Notes on National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments Northwestern University, p.3. :(Y-T-C)+(T-G)-I=EX-IM where T is defined as tax. (Y-T-C) is savings of private sector and (T-G) is savings of government. Here, we define S as National savings (= savings of private sector + savings of government) and rewrite the identity as following: :S-I=EX-IM This identity implies that the difference of national savings and national investment is equal to current account.Tejvan Pettinger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Equilibrium
In economics, general equilibrium theory attempts to explain the behavior of supply, demand, and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting markets, by seeking to prove that the interaction of demand and supply will result in an overall general equilibrium. General equilibrium theory contrasts to the theory of ''partial'' equilibrium, which analyzes a specific part of an economy while its other factors are held constant. In general equilibrium, constant influences are considered to be noneconomic, therefore, resulting beyond the natural scope of economic analysis. The noneconomic influences is possible to be non-constant when the economic variables change, and the prediction accuracy may depend on the independence of the economic factors. General equilibrium theory both studies economies using the model of equilibrium pricing and seeks to determine in which circumstances the assumptions of general equilibrium will hold. The theory dates to the 1870s, particularly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Wealth Of Nations
''An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'', generally referred to by its shortened title ''The Wealth of Nations'', is the ''magnum opus'' of the Scottish economist and moral philosopher Adam Smith. First published in 1776, the book offers one of the world's first collected descriptions of what builds nations' wealth, and is today a fundamental work in classical economics. By reflecting upon the economics at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the book touches upon such broad topics as the division of labour, productivity, and free markets. History ''The Wealth of Nations'' was published in two volumes on 9 March 1776 (with books I–III included in the first volume and books IV and V included in the second), during the Scottish Enlightenment and the Scottish Agricultural Revolution. It influenced several authors and economists, such as Karl Marx, as well as governments and organizations, setting the terms for economic debate and discussion fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— or "The Father of Capitalism",———— he wrote two classic works, ''The Theory of Moral Sentiments'' (1759) and ''The Wealth of Nations, An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations'' (1776). The latter, often abbreviated as ''The Wealth of Nations'', is considered his ''magnum opus'' and the first modern work that treats economics as a comprehensive system and as an academic discipline. Smith refuses to explain the distribution of wealth and power in terms of God's will, God’s will and instead appeals to natural, political, social, economic and technological factors and the interactions between them. Among other economic theories, the work introduced Smith's idea of absolute advantage. Smith studied social philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
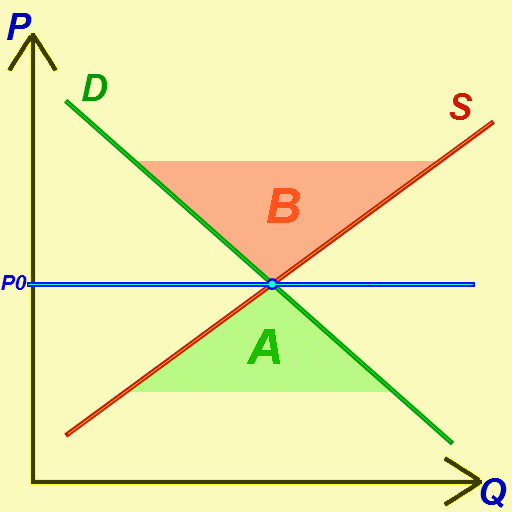
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the ( equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of ''equilibrium'' in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium. Understanding economic equilibriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exogenous Variable
In an economic model, an exogenous variable is one whose measure is determined outside the model and is imposed on the model, and an exogenous change is a change in an exogenous variable.Mankiw, N. Gregory. ''Macroeconomics'', third edition, 1997.Varian, Hal R., ''Microeconomic Analysis'', third edition, 1992.Chiang, Alpha C. ''Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics'', third edition, 1984. In contrast, an endogenous variable is a variable whose measure is determined by the model. An endogenous change is a change in an endogenous variable in response to an exogenous change that is imposed upon the model. The term endogeneity in econometrics has a related but distinct meaning. An endogenous random variable is correlated with the error term in the econometric model, while an exogenous variable is not. Examples In the LM model of interest rate determination, the supply of and demand for money determine the interest rate contingent on the level of the money supply, so the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity (mathematics)
In mathematics, an identity is an equality relating one mathematical expression ''A'' to another mathematical expression ''B'', such that ''A'' and ''B'' (which might contain some variables) produce the same value for all values of the variables within a certain range of validity. In other words, ''A'' = ''B'' is an identity if ''A'' and ''B'' define the same functions, and an identity is an equality between functions that are differently defined. For example, (a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2 and \cos^2\theta + \sin^2\theta =1 are identities. Identities are sometimes indicated by the triple bar symbol instead of , the equals sign. Common identities Algebraic identities Certain identities, such as a+0=a and a+(-a)=0, form the basis of algebra, while other identities, such as (a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab +b^2 and a^2 - b^2 = (a+b)(a-b), can be useful in simplifying algebraic expressions and expanding them. Trigonometric identities Geometrically, trigonometric ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Of Trade
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance of trade for goods versus one for services. The balance of trade measures a flow of exports and imports over a given period of time. The notion of the balance of trade does not mean that exports and imports are "in balance" with each other. If a country exports a greater value than it imports, it has a trade surplus or positive trade balance, and conversely, if a country imports a greater value than it exports, it has a trade deficit or negative trade balance. As of 2016, about 60 out of 200 countries have a trade surplus. The notion that bilateral trade deficits are bad in and of themselves is overwhelmingly rejected by trade experts and economists. Explanation The balance of trade forms part of the current account, which includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
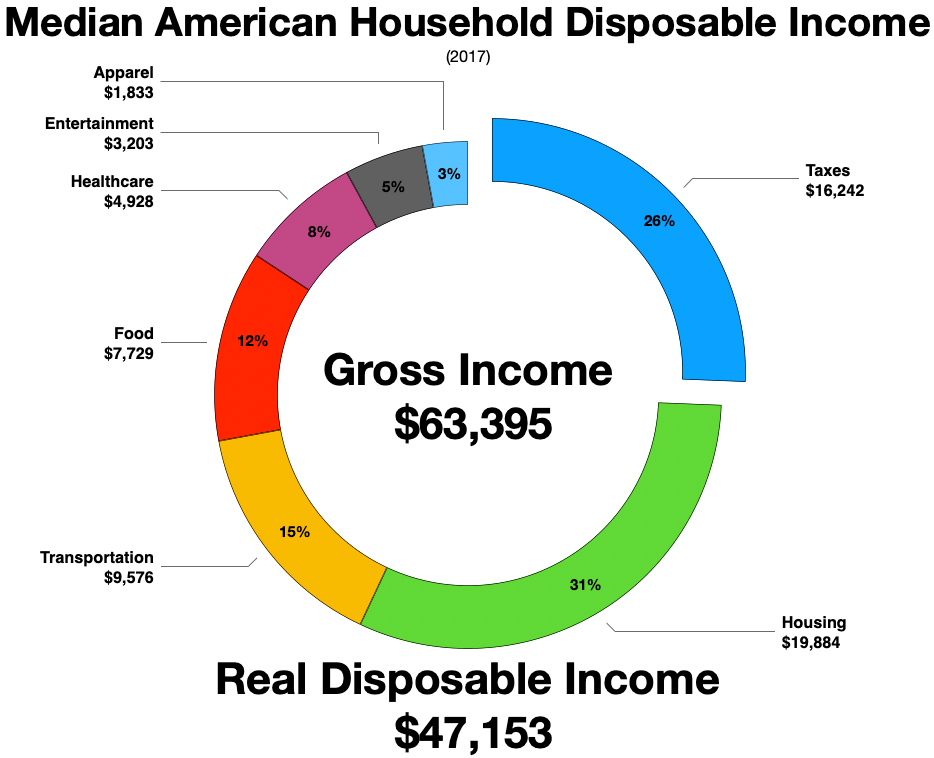
Disposable Income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current income taxes. In national accounts definitions, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major category of personal r privateconsumption expenditure) yields personal (or, private) savings, hence the income left after paying away all the taxes is referred to as disposable income. Restated, consumption expenditure plus savings equals disposable income after accounting for transfers such as payments to children in school or elderly parents’ living and care arrangements. The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the fraction of a change in disposable income that is consumed. For example, if disposable income rises by $100, and $65 of that $100 is consumed, the MPC is 65%. Restated, the marginal propensity to save is 35%. For the purposes of calculating the amount of income subject to garnishments, United States' federal law defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saving (economics)
Saving is income not spent, or deferred consumption. Methods of saving include putting money aside in, for example, a deposit account, a pension account, an investment fund, or as cash. Saving also involves reducing expenditures, such as recurring costs. In terms of personal finance, saving generally specifies low-risk preservation of money, as in a deposit account, versus investment, wherein risk is a lot higher; in economics more broadly, it refers to any income not used for immediate consumption. Saving does not automatically include interest. ''Saving'' differs from ''savings''. The former refers to the act of not consuming one's assets, whereas the latter refers to either multiple opportunities to reduce costs; or one's assets in the form of cash. Saving refers to an activity occurring over time, a flow variable, whereas savings refers to something that exists at any one time, a stock variable. This distinction is often misunderstood, and even professional economists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Economy
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems. Autarky as an ideal or method has been embraced by a wide range of political ideologies and movements, especially left-wing ideologies like African socialism, mutualism, war communism, communalism, swadeshi, syndicalism (especially anarcho-syndicalism), and left-wing populism, generally in an effort to build alternative economic structures or to control resources against structures a particular movement views as hostile. Conservative, centrist and nationalist movements have also adopted autarky in an attempt to preserve part of an existing social order or to develop a particular industry. Proponents of autarky have argued for national self-sufficiency to reduce foreign economic, political and cultural influences, as well as to promote international peace. Economists are generally supportive of free trade. There is a broad consensus among economists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |