|
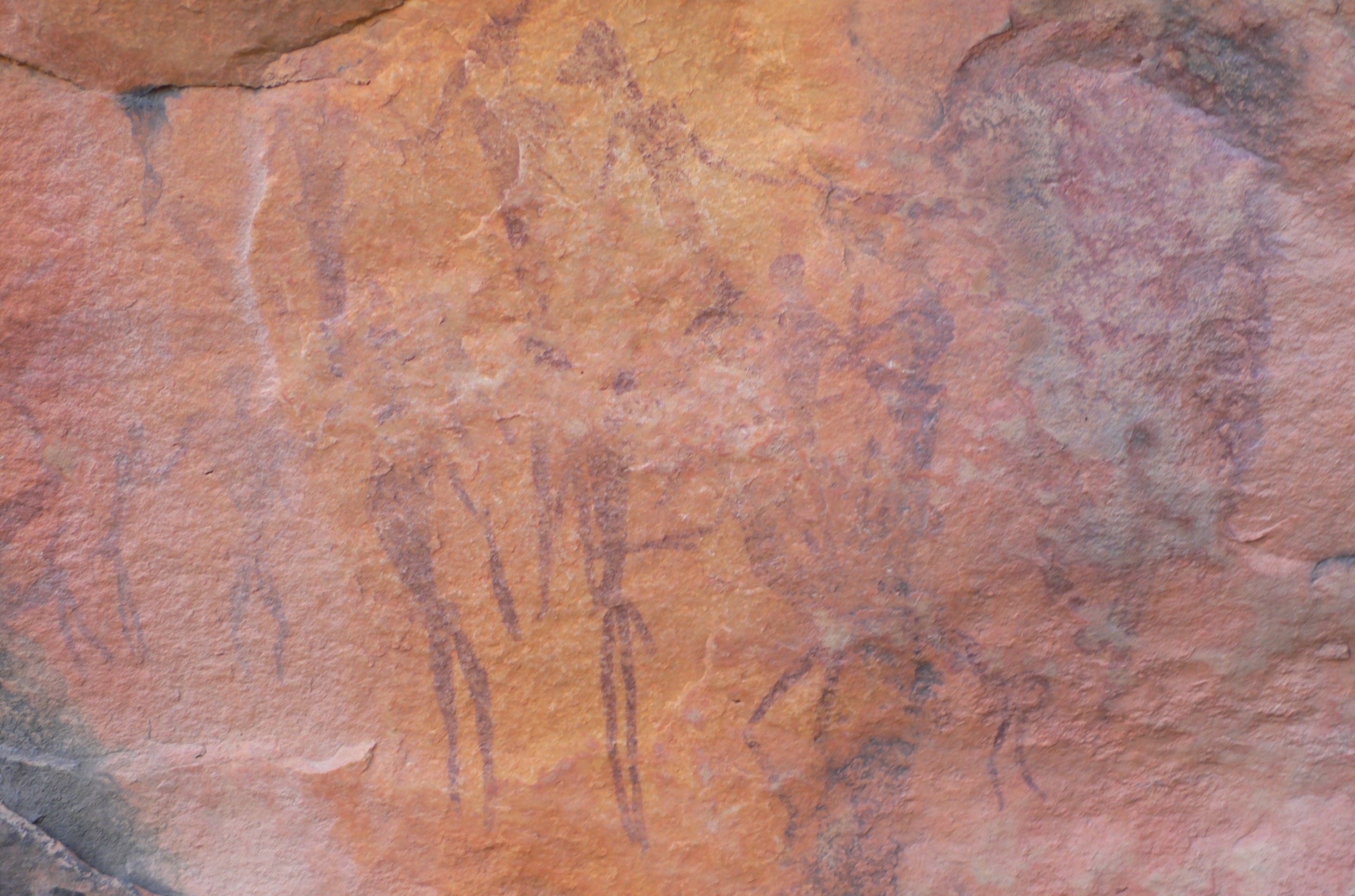
San Rock Art
The San, or Bushmen, are indigenous people in Southern Africa particularly in what is now South Africa and Botswana. Their ancient rock paintings and carvings (collectively called rock art) are found in caves and on rock shelters. The artwork depicts non-human beings, hunters, and half-human half-animal hybrids. The half-human hybrids are believed to be medicine men or healers involved in a healing dance.”Gall, Sandy. "The Bushmen of the Kalahari." Ecologist 33.7 (2003): 28-31. A painting discovered at Blombos Cave is thought to be the oldest known instance of human art, dating to around 73,000 years ago. Gall writes, “The Laurens van der Post panel at Tsodilo is one of the most famous rock paintings.” High on this rock face in Botswana is the image of a “magnificent red eland bull” painted, according to Van der Post, “only as a Bushman who had a deep identification with the eland could have painted him.” Also on this rock face is a female giraffe that is motionl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ǀXam Language
ǀXam pronounced , in English ) is considered an extinct language of South Africa formerly spoken by the ǀXam-ka ǃʼē of South Africa. It is part of the ǃUi branch of the Tuu languages and closely related to the moribund Nǁng language. Much of the scholarly work on ǀXam was performed by Wilhelm Bleek, a German linguist of the 19th century, who studied a variety of ǀXam spoken at Achterveld, and (with Lucy Lloyd) another spoken at Strandberg and Katkop while working with ǁKábbo, Diaǃkwāin, ǀAǃkúṅta, ǃKwéite̥n ta ǁKēn, ǀHaṅǂkassʼō and other speakers. The surviving corpus of ǀXam comes from the stories told by and vocabulary recorded from these individuals in the Bleek and Lloyd Collection. Name The pipe at the beginning of the name "ǀXam" represents a dental click, like the English interjection ''tsk, tsk!'' used to express pity or shame. The denotes a voiceless velar fricative click accompaniment. Compared to other Khoisan languages, there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
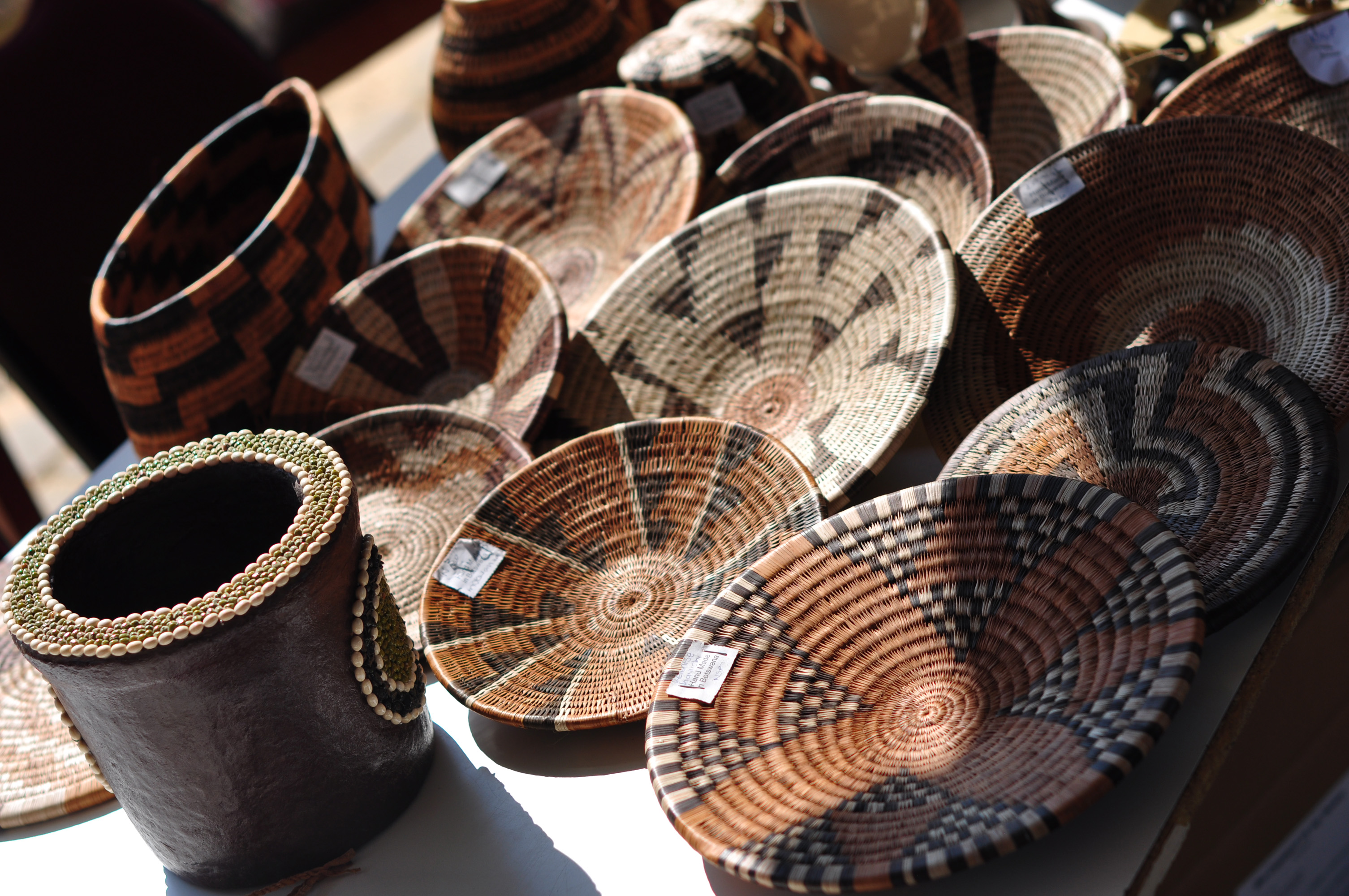
Botswana Culture
Besides referring to the language of the dominant people groups in Botswana, ''Setswana'' is the adjective used to describe the rich cultural traditions of the Batswana - whether construed as members of the Setswana ethnic groups or of all citizens of Botswana. the Batswana believe in the rich culture of Botho-Ubuntu, ‘‘People are not individuals, living in a state of independence, but part of a community, living in relationships and interdependence.’ Batswana believe in working together and in being united. The name Batswana is used as a nationality for the people of Botswana and as an ethnicity for people who practice the same culture and speak the same language in neighbouring South Africa.There are different ethnic groups in the country Botswana among them are the Tswana(Barolong, Bakwena, Bangwato,Batlokwa,Bakgatla, Baphuthing, Bataung, Bangwaketse, Batawana, Bahurutshe,Balete);BaKalanga(BaLilima,Baperi,BaWumbe ,BaNambya);Ovaherero(Baherero,Ovambanderu);Wayei, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildebeest Kuil Rock Art Centre
Wildebeest Kuil Rock Art Centre is a rock engraving site with visitor centre on land owned by the !Xun and Khwe San situated about 16 km from Kimberley, Northern Cape, South Africa. It is a declared Provincial Heritage Site managed by the Northern Cape Rock Art Trust in association with the McGregor Museum. The engravings exemplify one of the forms often referred to as ‘ Bushman rock art' – or Khoe-San rock art – with the rock paintings of the Drakensberg, Cederberg and other regions of South Africa being generally better known occurrences. Differing in technique, the engravings have many features in common with rock paintings. A greater emphasis on large mammals such as elephant, rhino and hippo, in addition to eland, and an often reduced concern with depicting the human form set the engravings apart from the paintings of the sub-continent. Rock Art and Other Archaeological Traces Background South Africa's rich heritage of rock art occurs in the form of engravings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twyfelfontein
Twyfelfontein (Afrikaans: ''uncertain spring''), officially known as ǀUi-ǁAis ( Damara/Nama: ''jumping waterhole''), is a site of ancient rock engravings in the Kunene Region of north-western Namibia. It consists of a spring in a valley flanked by the slopes of a sandstone table mountain that receives very little rainfall and has a wide range of diurnal temperatures. The site has been inhabited for 6,000 years, first by hunter-gatherers and later by Khoikhoi herders. Both ethnic groups used it as a place of worship and a site to conduct shamanist rituals. In the process of these rituals at least 2,500 items of rock carvings have been created, as well as a few rock paintings. Displaying one of the largest concentrations of rock petroglyphs in Africa, UNESCO approved Twyfelfontein as Namibia's first World Heritage Site in 2007. History Twyfelfontein valley has been inhabited by Stone-age hunter-gatherers of the Wilton stone age culture group since approximately 6,000 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
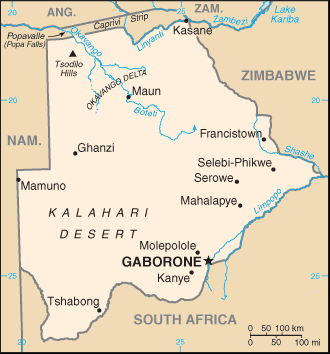
Tsodilo Hills
The Tsodilo Hills are a UNESCO World Heritage Site (WHS), consisting of rock art, rock shelters, depressions, and caves in southern Africa. It gained its WHS listing in 2001 because of its unique religious and spiritual significance to local peoples, as well as its unique record of human settlement over many millennia. UNESCO estimates there are over 4500 rock paintings at the site. The site consists of a few main hills known as the Child Hill, Female Hill, and Male Hill. Geography There are four chief hills. The highest is 1,400 metres AMSL, one of the highest points in Botswana. The four hills are commonly described as the "Male" (the highest), "Female", "Child", plus an unnamed knoll. They are about 40 km from Shakawe and can be reached via a good graded dirt road. There is a managed campsite between the two largest hills, with showers and toilets. It is near the most famous of the San paintings at the site, the Laurens van der Post panel, after the South-African write ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 11 Cave
The Apollo 11 Cave is an archeological site in the ǁKaras Region of south-western Namibia, approximately southwest of Keetmanshoop. The name given to the surrounding area and presumably the cave by the Nama people was "Goachanas".John Mason, "Apollo 11 Cave in Southwest Namibia: Some Observations on the Site and Its Rock Art" The South African Archaeological Bulletin, Vol. 61, No. 183 (Jun., 2006), pp. 76-89 However, the cave was given its name by German archaeologist Wolfgang Erich Wendt in reference to Apollo 11's then recent return to Earth.Wiebke Schmidt''Auf den Spuren der ältesten Kunst.'' Allgemeine Zeitung, ''May 2, 2008'' Overview The cave contained some of the oldest pieces of mobile art ever discovered in southern Africa, associated with charcoal that was radiocarbon dated from 27,500 to 25,500 BP. The art slabs found in this cave are referred to as the Apollo 11 Stones. In total, seven grey-brown quartzite slabs were excavated from the cave. Besides the slab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The White Lady (Namibia)
The White Lady is a rock painting, located on a panel, also depicting other art work, on a small rock overhang, deep within Brandberg Mountain. The giant granite monolith located in Damaraland and called 'The Brandberg' is Namibia's highest mountain. The painting's German name is ''Weiße Dame''. The painting has long been an archaeological dilemma, and several different hypotheses have been put forth on its origins, authorship and dating. It is now usually accepted to be a bushmen painting, dating back at least 2000 years ago. Location and description The "White Lady" archaeological site is located close to the road from Khorixas to Hentie's Bay, in the area of Uis, on the Brandberg Massif. The Brandberg itself hosts over 1.000 bushmen paintings, scattered around in rock shelters and caves.Namibia 1 on 1 The "White Lady Group" is found in a cave known as "Maack Shelter" and portrays several human figures as well as oryxes, on a rock panel measuring about 5.5 m x 1.5 m. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driekops Eiland
Driekops Eiland (also called Driekopseiland) is a rock engraving or petroglyph site in the bed of the Riet River close to the town of Plooysburg, near Kimberley, Northern Cape, South Africa. The engravings There are more than 3500 individual engravings at this site, predominantly pecked geometric images, occur on glaciated basement rock exposed in the bed of the river and are submerged when the river rises. Archaeologists and geomorphologists have estimated that the engravings may have been made in two episodes – before about 2500 years ago and after about 1000 years ago. Debates The site has been at the centre of a number of debates about South African rock engravings. Sensational claims about the site and makers of the engravings are advanced by Brenda Sullivan, Cyril Hromnik and others in books such as ''Spirit of the rocks''. The ideas set out by these authors, often involving ancient visitors from foreign lands, and alleged links between the engravings and Ogham inscrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Religion
The San religion is the traditional religion and mythology of the San people. It is poorly attested due to their interactions with Christianity. Gods and mythical figures ;ǀXam The ǀXam prayed to the Sun and Moon. Many myths are ascribed to various stars. * ǀKágge̥n (sometimes corrupted to "Cagn") is Mantis, a demiurge and hero in ǀXam folklore. He is a trickster god who can shape-shift. He and his wife ǀHúnntuǃattǃatte̥n. * ǀHúnntuǃattǃatte̥n (also known as or corrupted to "Coti"), the Dassie, adopted !Xo, Porcupine, as their daughter. * !Xo, Porcupine, as their parents ǀKágge̥n and ǀHúnntuǃattǃatte̥n, married Ichneumon, son was the Ichneumon. * /Kwammang-a, a dangerous stranger carnivore, married !Xo, son was the Ichneumon. * Ichneumon, a small, furry carnivore, mongoose. * ǂKá̦gára and ǃHãunu are brothers-in-law who fought with lightning, causing massive storms in the east. ;Other ǃXu is the Khoikhoi word ''ǃKhub'' 'rich man, master ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Healing Practices
In the culture of the San (also known as Ju/'oansi, !Kung, or Bushmen), an indigenous people of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa, and Angola, healers administer a wide range of practices, from oral remedies containing plant and animal material, making cuts on the body and rubbing in 'potent' substances, inhaling smoke of smouldering organic matter like certain twigs or animal dung, wearing parts of animals or 'jewellery' that 'makes them strong.' Anecdotal records reveal that the Khoikhoi and San people have used ''Sceletium tortuosum'' since ancient times as an essential part of the indigenous culture and materia mediac. The trance dance is one of the most distinctive features of San culture. Trance dance The San heal whilst in an altered state of consciousness in what is known as a 'trance dance' or 'healing dance'. Trance dance rituals take place over an entire night. Participants will sometimes tie offerings to animal spirits to the trees, and will use drums in order to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Price Institute For Palaeontological Research
The Evolutionary Studies Institute (ESI) is a paleontological, paleoanthropological and archeological research institute operated through the Faculty of Science of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa. Previously known as the Bernard Price Institute for Palaeontological Research (BPI) it was renamed the Evolutionary Studies Institute in 2013 to better showcase the scope of its research. History The Evolutionary Studies Institute was first named the Bernard Price Institute after Bernard Price, an engineer and general manager of the Victoria Falls and Transvaal Power Company who provided steady research funding. The institute was set up in 1937 as an institute for geophysical research, but since has become known for its paleontological research. The institute's first director was Basil Schonland. When World War II began in 1939, the South African Defense Force ordered the BPI to contribute to the war effort. Schonland led the development of South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |