|
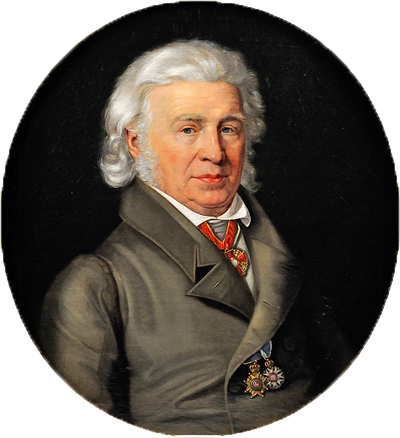
Samuel Thomas Von Sömmerring
Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring (28 January 1755 – 2 March 1830) was a German physician, anatomist, anthropologist, paleontologist and inventor. Sömmerring discovered the macula in the retina of the human eye. His investigations on the brain and the nervous system, on the sensory organs, on the embryo and its malformations, on the structure of the lungs, etc., made him one of the most important German anatomists. Career Sömmerring was born in Thorn (Toruń), Royal Prussia (a province of the Crown of Poland) as the ninth child of the physician Johann Thomas Sömmerring. In 1774 he completed his education in Thorn and began to study medicine at the University of Göttingen. He visited Petrus Camper lecturing at the University in Franeker. He became a professor of anatomy at the Collegium Carolinum (housed in the Ottoneum, now a Natural History Museum) in Kassel and, beginning in 1784, at the University of Mainz. There he was for five years the dean of the medical faculty. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wendelin Moosbrugger
Wendelin Moosbrugger, or Mosbrugger (20 October 1760 in Au, Vorarlberg – 20 August 1849 in Aarau) was an Austrian portrait painter and Portrait miniature, miniaturist. He came from a family that had a widespread reputation as builders, plasterers and painters. Life and work As a child, he showed a special talent for drawing and painting. He received his first training in Konstanz and worked as a decorative painter. He attracted the attention of Elector Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Baden, Charles Frederick, while painting at the Electoral residence in Mannheim, and was enrolled at the recently established University of Mannheim, Palatine Academy. Family article Although he lived in Konstanz after 1794, he was also active in Karlsruhe and Vienna, as well as at the court in Stuttgart. He also did portraits of the nobility in Cologne. Following the example of Napoleon, German princes flocked to have themselves immortalized in paint. He did, in fact, do a portrait of Napoleon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Organ
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system receives signals from the senses which continuously receive information from the environment, interprets these signals, and causes the body to respond, either chemically or physically.) Although traditionally five human senses were identified as such (namely sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing), it is now recognized that there are many more. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought. In organisms, a sensory organ consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's adaptive immunity, they help prevent sickness from an infectious disease. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Herd immunity protects those who may be immunocompromised and cannot get a vaccine because even a weakened version would harm them. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. However, some diseases, such as measles outbreaks in America, have seen rising cases due to relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Mainz on the left bank, and Wiesbaden, the capital of the neighbouring state Hesse, on the right bank. Mainz is an independent city with a population of 218,578 (as of 2019) and forms part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region. Mainz was founded by the Romans in the 1st century BC as a military fortress on the northernmost frontier of the empire and provincial capital of Germania Superior. Mainz became an important city in the 8th century AD as part of the Holy Roman Empire, capital of the Electorate of Mainz and seat of the Archbishop-Elector of Mainz, the Primate of Germany. Mainz is famous as the birthplace of Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of a movable-type printing press, who in the early 1450s manufactured his first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Directory
The Directory (also called Directorate, ) was the governing five-member committee in the French First Republic from 2 November 1795 until 9 November 1799, when it was overthrown by Napoleon Bonaparte in the Coup of 18 Brumaire and replaced by the Consulate. ''Directoire'' is the name of the final four years of the French Revolution. Mainstream historiography also uses the term in reference to the period from the dissolution of the National Convention on 26 October 1795 (4 Brumaire) to Napoleon's coup d’état. The Directory was continually at war with foreign coalitions, including Britain, Austria, Prussia, the Kingdom of Naples, Russia and the Ottoman Empire. It annexed Belgium and the left bank of the Rhine, while Bonaparte conquered a large part of Italy. The Directory established 196 short-lived sister republics in Italy, Switzerland and the Netherlands. The conquered cities and states were required to send France huge amounts of money, as well as art treasures, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Mainz
The Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (german: Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz) is a public research university in Mainz, Rhineland Palatinate, Germany, named after the printer Johannes Gutenberg since 1946. With approximately 32,000 students (2018) in about 100 schools and clinics, it is among the largest universities in Germany. Starting on 1 January 2005 the university was reorganized into 11 faculties of study. The university is a member of the German U15, a coalition of fifteen major research-intensive and leading medical universities in Germany. The Johannes Gutenberg University is considered one of the most prestigious universities in Germany. The university is part of the IT-Cluster Rhine-Main-Neckar. The Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, the Goethe University Frankfurt and the Technische Universität Darmstadt together form the Rhine-Main-Universities (RMU). History The first University of Mainz goes back to the Archbishop of Mainz, Prince-elector and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassel
Kassel (; in Germany, spelled Cassel until 1926) is a city on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel and the district of the same name and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020. The former capital of the state of Hesse-Kassel has many palaces and parks, including the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Kassel is also known for the ''documenta'' exhibitions of contemporary art. Kassel has a public university with 25,000 students (2018) and a multicultural population (39% of the citizens in 2017 had a migration background). History Kassel was first mentioned in 913 AD, as the place where two deeds were signed by King Conrad I. The place was called ''Chasella'' or ''Chassalla'' and was a fortification at a bridge crossing the Fulda river. There are several yet unproven assumptions of the name's origin. It could be derived from the ancient ''Castellum Cattorum'', a castle of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoneum
The Ottoneum in Kassel, Germany was the first theater building built in Germany and is now a museum of natural history. History The Ottoneum was built between 1603-1606 under Landgrave Moritz by the architect William Vernukken. The name 'Ottoneum' comes from Landgrave Motiz's favourite son Otto. With the beginning of the Thirty Years' War (1618-1648) the Ottoneum's heyday as a cultural centre came to an end and the building was put to other uses. It was not until 1696 when the court architect Johann Conrad Giesler converted the building to house the Landgrave art and natural history collection. The work was ordered by Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel (Landgrave Karl), and was undertaken by Master Builder Paul du Ry. In 1709 Karl founded the Collegium Carolinum, a scientific research centre with famous scholars Georg Forster and Samuel Thomas von Soemmerring at its core. It was during this time that the Ottoneum also housed an anatomical theatre and an observatory. By 1779 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collegium Carolinum (Kassel)
The Collegium Carolinum (also known as ) was a scientific institution in Kassel, Germany. It was founded in 1709 by Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel and closed after the 1785 death of Frederick II, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel. The Ottoneum housed most of its activities. However, a new anatomical theatre, the first in Germany, was used by Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring. The Collegium Carolinum was founded as a "new kind of university", where mathematics, the sciences, anatomy and geography should be more important compared to the classical humanist subjects taught at the nearby University of Marburg. In 1766, it was reorganised into a polytechnic by Frederick II and concentrated more on the arts and applicable sciences. Notable professors *Georg Forster, naturalist *Johannes von Müller, historian * Johann August Nahl, sculptor *Simon Louis du Ry, architect *Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring (28 January 1755 – 2 March 1830) was a German physici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franeker
Franeker (; fry, Frjentsjer) is one of the eleven historical cities of Friesland and capital of the municipality of Waadhoeke. It is located north of the Van Harinxmakanaal and about 20 km west of Leeuwarden. As of 1 January 2014, it had 12,781 inhabitants. The Eise Eisinga Planetarium, established in 1781, is located in the city. History Franeker was founded around 800 as a Carolingian stronghold. The name probably derives from ''Froon-acker'', meaning "land of the lord/king"; the oldest street in the city is still called Froonacker. Beginning around the 11th century, Franeker developed into the administrative center Westergoa. Franeker received city rights in 1374. In the 15th century, Albert, Duke of Saxony established himself in Franeker. The city appeared for a time to be growing into the primary city of Friesland, but was eventually overshadowed in this role by Leeuwarden. During the period of the Dutch Revolt, the town sided early on with William I. From 1585 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrus Camper
Petrus Camper FRS (11 May 1722 – 7 April 1789), was a Dutch physician, anatomist, physiologist, midwife, zoologist, anthropologist, palaeontologist and a naturalist in the Age of Enlightenment. He was one of the first to take an interest in comparative anatomy, palaeontology, and the facial angle. He was among the first to mark out an "anthropology," which he distinguished from natural history. He studied the orangutan, the Javan rhinoceros, and the skull of a mosasaur, which he believed was a whale. Camper was a celebrity in Europe and became a member of the Royal Society (1750), the Göttingen (1779), and Russian Academy of Sciences (1778), the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1783), the French (1786) and the Prussian Academy of Sciences (1788). He designed and constructed tools for his patients, and for surgeries. He was an amateur drawer, a sculptor, a patron of art and a conservative, royalist politician. Camper published some lectures containing an account of his craniome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, including the Kingdom of Poland proper. The Polish Crown was at the helm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1795. Major political events The Kingdom of Poland has been traditionally dated back to c. 966, when Mieszko I and his pagan Slavic realm joined Christian Europe ( Baptism of Poland), establishing the state of Poland, a process started by his Polan Piast dynasty ancestors. His oldest son and successor, Prince Bolesław I Chrobry, Duke of Poland, became the first crowned King of Poland in 1025. Union of Krewo The Union of Krewo was a set of prenuptial agreements made in the Kreva Castle on August 13, 1385. Once Jogaila confirmed the prenuptial agreements on August 14, 1385, Poland and Lithuania formed a personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

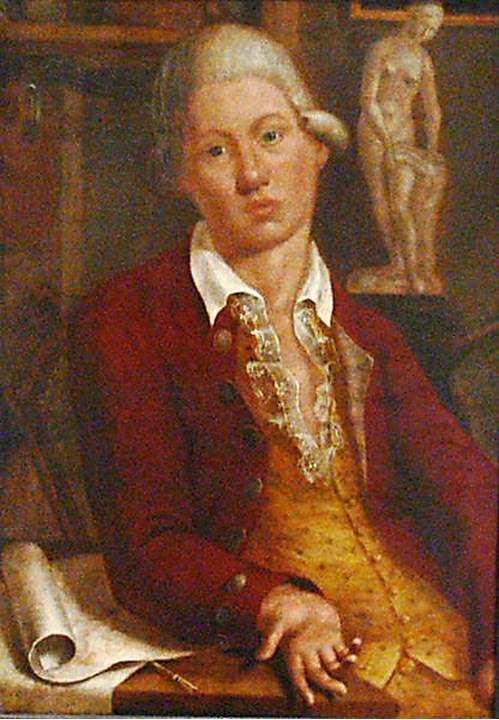




_1572.jpg)


