|
Swedish Overseas Colonies
Swedish overseas colonies () consisted of the overseas colonies controlled by Sweden. Sweden possessed overseas colonies from 1638 to 1663, in 1733 and from 1784 to 1878. Sweden possessed five colonies, four of which were short lived. The colonies spanned three continents: Africa, Asia and North America. List The former Swedish colonies in Africa were: * Swedish Gold Coast (1650–1663; lost to Denmark and the Dutch) Including the Cape Coast (1649–1663) consisting of the following settlements: *: Fort Apollonia, presently Beyin: 1655–1657. *:Fort Christiansborg/ Fort Frederiksborg, which became the capital, presently Osu: 1652–1658 *: Fort Batenstein, presently Butri: 1649–1656. *: Fort Witsen, presently Takoradi: 1653–1658. *: Carolusborg: April 1650 – January/February 1658, 10 December 1660 – 22 April 1663 The former Swedish colonies in the Americas: *New Sweden (1638–1655; lost to the Dutch) * Sankt Barthélemy (1784–1878; sold to France, modern Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, spoken predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, making it the Germanic_languages#Statistics, fourth most spoken Germanic language, and the first among its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other North Germanic languages, Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian language, Norwegian and Danish language, Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century, and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional Variety ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
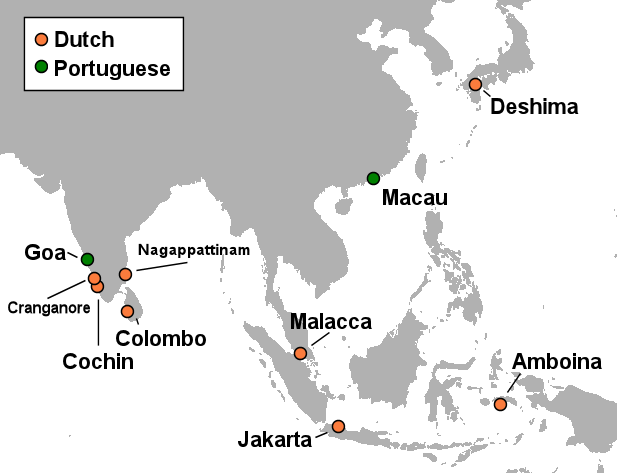
Dutch Empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Dutch East India Company (1602–1799) and Dutch West India Company (1621–1792)—and subsequently governed by the Dutch Republic (1581–1795) and modern Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1975). Following the ''de facto'' independence of the Dutch Republic from the Spanish Empire in the late 16th century, various trading companies known as '' voorcompagnie'' led maritime expeditions overseas in search of commercial opportunities. By 1600, Dutch traders and mariners had penetrated the lucrative Asian spice trade but lacked the capital or manpower to secure or expand their ventures; this prompted the States General in 1602 to consolidate several trading enterprises into the semi-state-owned Dutch East India Company (, VOC), which was g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Swedish Colony Of Saint Barthélemy
The Swedish colony of Saint Barthélemy existed for nearly a century. In 1784, one of French king Louis XVI's ministers ceded Saint Barthélemy to Sweden in exchange for trading rights in the Swedish port of Gothenburg. Swedish rule lasted until 1878 when the French repurchased the island. Background Following problems experienced by early French settlers, Saint Barthélemy was successfully colonized by French mariners in 1763. Attracted by the island's prosperity during the American Revolutionary War, Gustav III of Sweden agreed to exchange French trading rights in Gothenburg against Swedish colonization of the island. In addition to its fresh water sources, the island produced moderate amounts of cotton, sugar, cocoa, tobacco and fruits while it promised substantial revenue from trade through its natural harbour on the island's west coast. On 1 July 1784, the island became a Swedish possession. The king informed Sweden's privy council of the acquisition on 23 August. On 1 S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New Sweden
New Sweden () was a colony of the Swedish Empire between 1638 and 1655 along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. Established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a great power, New Sweden formed part of the Swedish efforts to Swedish colonization of the Americas, colonize the Americas. Settlements were established on both sides of the Delaware River. Fort Christina, located in what is now Wilmington, Delaware, was the first settlement, named after Christina, Queen of Sweden. The settlers were Swedes, Finns, and a number of Dutch people, Dutch. New Sweden was conquered by the Dutch Republic in 1655 and incorporated into the Dutch colony of New Netherland. History By the middle of the 17th century, Sweden had reached its greatest territorial extent and was one of the great powers of Europe; it was the ''Swedish Empire, stormaktstiden'' ("age of greatness" or "great power period"). Sweden then include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cape Castle
Cape Coast Castle () is one of about forty "slave castles", or large commercial forts, built on the Gold Coast of West Africa (now Ghana) by European traders. It was originally a Portuguese "feitoria" or trading post, established in 1555, which was named ''Cabo Corso''. In 1653, a timber fort was constructed by the Swedish Africa Company. It originally was a centre for timber and gold trade, and then was later used in the Atlantic slave trade. Other Ghanaian slave castles include Elmina Castle and Fort Christiansborg. They were used to harbour enslaved Africans before they were loaded onto ships and sold in the Americas, especially the Caribbean. This "gate of no return" was the last stop before crossing the Atlantic Ocean. Cape Coast Castle, along with other forts and castles in Ghana, are included on the UNESCO World Heritage List because of their testimony to the Atlantic gold and slave trades. Trade history The large quantity of gold dust found in Ghana was what primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Takoradi
Sekondi-Takoradi ( ) is a city in Ghana comprising the twin cities of Sekondi and Takoradi. It is the capital of Sekondi-Takoradi Metropolitan District and the Western Region of Ghana. Sekondi-Takoradi is the region's largest city as well as an industrial and commercial center with a population of 245,382 people, according to the 2021 census. Since 2021 the mayor of the city and the metropolitan area has been Abdul-Mumin Issah. Kwabena Okyere Darko-Mensah is the current member of parliament for Takoradi and Armah Blay Nyameke for Sekondi. Both cities grew from Dutch and English forts built around the 17th century. After a railway and a deepwater seaport was built in Sekondi and Takoradi in 1903 and 1928, both cities became important economic sectors in Ghana. They merged in 1946. Leading industries in the city are timber, cocoa processing, plywood, shipbuilding, its harbour and railway repair, and recently, sweet crude oil and crude oil. The most common occupation in Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fort Witsen
Fort Witsen, also Fort Tacaray, was a fort on the Dutch Gold Coast, established in 1665 near Takoradi. This fort was destroyed after a few years, and in 1684 the site was abandoned. A map from 1791 shows, however, that the Dutch had renewed their presence in the fort again.Nationaal Archief, Dutch National Archives, object number: VEL0759. SourceAtlas of Mutual Heritage The fort was handed over to United Kingdom, Britain, along with the entire Dutch Gold Coast, on 6 April 1872, owing to the provisions of the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870-1871. References {{Authority control Buildings and structures completed in 1656 Castles in Ghana Dutch Gold Coast 1665 establishments in the Dutch Empire Forts in Ghana, Witsen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Butri
Butre is a village in the Ahanta West district, district in the Western Region of Ghana. Butre contains the Fort Batenstein Fort Batenstein was a fort and trading post established by the Dutch on the Gold Coast in 1656. It was situated near Butre (old spelling: ''Boutry''). The fort was ceded with the entire Dutch Gold Coast to Britain in 1872. At this fort, the Tre ... Castle.Touring Ghana - Western Region References Populated places in Ahanta West Municipal District {{WesternRegionGH-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fort Batenstein
Fort Batenstein was a fort and trading post established by the Dutch on the Gold Coast in 1656. It was situated near Butre (old spelling: ''Boutry''). The fort was ceded with the entire Dutch Gold Coast to Britain in 1872. At this fort, the Treaty of Butre was signed on 27 August 1656 between the Dutch and the Ahanta. In 1979, the fort was designated a World Heritage Site (along with several other castles and forts in Ghana) because of its historical importance in European trade and exploitation in West Africa. Name ''Batenstein'' literally translates to "profit fort," which historian Albert van Dantzig sees as evidence of a cynical sense of humour on the part of the directors of the Dutch West India Company: the fort at Komenda, which was the site of the fierce Komenda Wars with the British, was named '' Vredenburgh'' (literally "peace borough"), the commercially unsuccessful fort at Senya Beraku was named '' Goede Hoop'' ("Good Hope"), and the fort at Apam, which took fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Osu, Accra
Osu is a neighbourhood in central Accra, Accra, Ghana, West Africa. It is located about east of the central business district, and is locally known as the "West End" of Accra. Bounded to the south by the Gulf of Guinea, Osu's western boundary is the Independence Avenue. Osu is separated from the northern district of Labone, Accra, Labone by Ring Road. Due to its establishment as a settlement in the 17th century, Osu has a mix of houses dating from the early 20th century and modern office towers. Economy The head office of Starbow was in Osu. ." Starbow. Retrieved on 6 May 2013. "832 First Street Adjacent to the Salvation Army Territorial Headquarters Osu, Accra"  Lan ...
|
Fort Frederiksborg
Fort Frederiksborg, later Fort Royal, was a Danish-Norwegian and later English fort on the Gold Coast in contemporary Ghana. It was built in 1661, with the approval of the King of Fetu, a few hundred yards from Cape Coast Castle, which was at that time in Swedish hands, on Amanfro Hill. Along with several other castles and forts nearby, Fort Frederiksborg was inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1979 because of its testimony to European economic influence on West Africa and the Atlantic slave trade. History Frederiksborg was a small fort from which Cape Coast Castle could easily be bombarded. It functioned for a short time as the headquarters of the Danish West India Company on the Danish Gold Coast, before it was moved to Christiansborg Castle in Osu. In 1665 the English Royal African Company took over Cape Coast Castle Cape Coast Castle () is one of about forty slave fort, "slave castles", or large commercial forts, built on the Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Osu Castle
Osu Castle (also known as Fort Christiansborg or the Castle) is a castle located in Osu, Ghana, on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea in Africa. A substantial fort was built by Denmark-Norway in the 1660s; thereafter, the fort changed ownership between Denmark-Norway, Portugal, the Akwamu, Britain, and finally post-Independence Ghana. Under Denmark–Norway control it was the capital of the Danish Gold Coast, and held and dispatched enslaved people overseas. In 1902, Osu Castle became the seat of government in Ghana but this has now moved to Jubilee House. Because of its testimony to European colonial influence in West Africa and the Atlantic slave trade, the castle was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979 along with several other castles and forts in Ghana. History The area was first occupied in 1550 by the Portuguese, though in the 17th century Portuguese influence diminished. The area came under the control of Sweden in the late 1640s, led by the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |