|
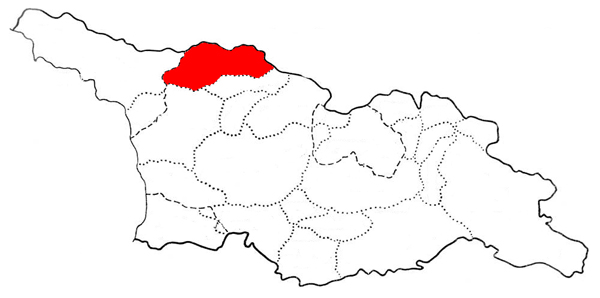
Svan Language
Svan ( ''lušnu nin''; ka, სვანური ენა, tr) is a Kartvelian languages, Kartvelian language spoken in the western Georgia (country), Georgian region of Svaneti primarily by the Svans, Svan people. With its speakers variously estimated to be between 30,000 and 80,000, the UNESCO designates Svan as a "definitely endangered language". It is of particular interest because it has retained many features that have been lost in the other Kartvelian languages. Features Familial features Like all languages of the Caucasian language family, Svan has a large number of consonants. It has agreement between subject and object, and a split ergativity, split-ergative Morphosyntactic alignment, morphosyntactic system. Verbs are marked for grammatical aspect, aspect, evidentiality and Kartvelian languages#Verb, "version". Distinguishing features Svan retains the voiceless uvular plosive, voiceless aspirated uvular plosive, , and the glides and . It has a larger vowel inventor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region on the coast of the Black Sea. It is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia, and is today generally regarded as part of Europe. It is bordered to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. Georgia covers an area of . It has a Demographics of Georgia (country), population of 3.7 million, of which over a third live in the capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city, Tbilisi. Ethnic Georgians, who are native to the region, constitute a majority of the country's population and are its titular nation. Georgia has been inhabited since prehistory, hosting the world's earliest known sites of winemaking, gold mining, and textiles. The Classical antiquity, classical era saw the emergence of several kingdoms, such as Colchis and Kingdom of Iberia, Iberia, that formed the nucleus of the modern Georgian state. In the early fourth centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lentekhi
Lentekhi ( ka, ლენტეხი, ) is a small town and Lentekhi District's ( Raion) capital in Georgia's western region of Racha-Lechkhumi and Kvemo Svaneti, 323 km northwest to the nation's capital Tbilisi. Situated on the southern slope of the Central Caucasus, the district is a site of alpinism. History Lentekhi ethnographically belongs to a historic Georgian province of Lower, or Kvemo Svaneti. Cultural heritage of the area includes several monuments, particularly St George's Church of Jgëræg (the 10th century), the Archangel Church of Thargizel (the 9–10th centuries), Tekal Church (the 10–11th centuries), Lentekhi Castle of the Dadiani, and the famous Svanetian towers in the village of Leksuri. There is a river that goes through the town and its inhabitants survive largely off of farming and lumber, though in recent years government restrictions have slowed this latter industry. Like in much of Georgia, tourism is seen as the future source of income ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Consonant
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as , . In some languages, dentals are distinguished from other groups, such as alveolar consonants, in which the tongue contacts the gum ridge. Dental consonants share acoustic similarity and in the Latin script are generally written with consistent symbols (e.g. ''t'', ''d'', ''n''). In the International Phonetic Alphabet, the diacritic for dental consonant is . When there is no room under the letter, it may be placed above, using the character , such as in / p͆/. Cross-linguistically Languages, such as Albanian, Irish and Russian, velarization is generally associated with more dental articulations of coronal consonants. Thus, velarized consonants, such as Albanian , tend to be dental or denti-alveolar, and non-velarized consonants tend to be retracted to an alveolar position. Sanskrit, Hindustani and all other Indo-Aryan languages have an entire set of dental stops that occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, both of which are present in English. A third labial articulation is dentolabials, articulated with the upper lip against the lower teeth (the reverse of labiodental), normally only found in pathological speech. Generally precluded are linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue contacts the posterior side of the upper lip, making them coronals, though sometimes, they behave as labial consonants. The most common distribution between bilabials and labiodentals is the English one, in which the nasal and the stops, , , and , are bilabial and the fricatives, , and , are labiodental. The voiceless bilabial fricative, voiced bilabial fricative, and the bilabial approximant do not exist as the primary realizations of any sounds in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Georgian
Old Georgian (ႤႬႠჂ ႵႠႰႧႭჃႪႨ, ''enay kartuli'') is a literary language of the Georgian monarchies attested from the 5th century. The language remains in use as the liturgical language of the Georgian Orthodox Church and for the most part is still intelligible. Spoken Old Georgian gave way to what is classified as Middle Georgian in the 11th century, which in turn developed into the modern Georgian language in the 18th century. Periodization Two periods are distinguished within Old Georgian: Early Old Georgian (5th to 8th centuries) and Classical Old Georgian (9th to 11th centuries). Two different dialects are represented in Early Old Georgian, known as Khanmet’i (ხანმეტი, 5th to 7th c.) and Haemet’i (ჰაემეტი, 7th and 8th c.). They are so named after the presence of a second-person subject prefix and a third-person object prefix ''kh-'' or ''h-'' in the verbal morphology where Classical Old Georgian has ''h-'', ''s-'' or zero. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ushguli
Ushguli ( ka, უშგული ) is a community of five medieval villages located at the head of the Enguri gorge in Svaneti, Georgia. Ushguli is one of the highest continuously inhabited settlements in Europe. Compared to somewhat more developed towns like Mestia, Ushguli is not in an accessible location, which has preserved many of the villages' medieval characteristics, including unique defensive tower houses called Svan towers. Anthony Bourdain: Parts Unknown9 reasons to visit Georgia now CNN, 17 May 2016 Because of their preservation and traditional architecture, Ushguli, Mestia, and the surrounding area was recognized as the ''Upper Svaneti'' UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. Location and features Ushguli is located at an altitude of near the foot of Shkhara, one of the highest summits of the Greater Caucasus mountains. About 70 families (about 200 people) live in the area, enough to support a small school. The area is snow-covered for 6 months of the year, and oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian National Museum
The Georgian National Museum ( ka, საქართველოს ეროვნული მუზეუმი, tr) unifies several leading museums in Georgia. The museum was established within the framework of structural, institutional, and legal reforms aimed at modernizing the management of the institutions united within this network, and at coordinating research and educational activities. Since its formation on December 30, 2004, the Museum has been directed by professor David Lordkipanidze. The Georgian National Museum integrates the management of the following museums: * Simon Janashia Museum of Georgia, Tbilisi * Samtskhe-Javakheti History Museum, Akhaltsikhe * Open Air Museum of Ethnography, Tbilisi * Art Museum of Georgia, Tbilisi, and its branches * Museum of the Soviet Occupation, Tbilisi *Dmanisi Museum-Reserve of History and Archaeology, Dmanisi Dmanisi ( ka, დმანისი, tr, , ) is a town and archaeological site in the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evdokia Kozhevnikova
Evdokia Kozhevnikova-Gugushvili ( ka, ევდოკია კოჟევნიკოვა-გუგუშვილი; ; 28 December 1905 – 1975) was a Soviet ethnographer who did extensive fieldwork in the province of Svaneti in the Republic of Georgia. During the course of her fieldwork, she acquired considerable fluency in Svan, and produced some 1200 handwritten pages in the language between 1927 and 1936. She never completed her dissertation, and her unpublished work remained almost entirely unknown to the academic world until her records were rediscovered in the 2010s. Since then, researchers at the Georgian National Museum as well as some foreign anthropologists have begun to catalog, translate, and analyse several hundred pages from Kozhevnikova's archives. In 2023, the Georgian National Museum published a compilation of papers about Kozhevnikova and her work, entitled ''Dina Kozhevnikova: Ethnographical Records.'' Early life and education Kozhevnikova was born o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zan Languages
The Zan languages, or Zanuri ( ka, ზანური ენები) or Colchidian, are a branch of the Kartvelian languages constituted by the Mingrelian and Laz languages. The grouping is disputed as some Georgian linguists consider the two to form a dialect continuum of one Zan language. This is often challenged on the most commonly applied criteria of mutual intelligibility when determining borders between languages, as Mingrelian and Laz are only partially mutually intelligible, though speakers of one language can recognize a sizable amount of vocabulary of the other, primarily due to semantic loans, lexical loans and other areal features resulting from geographical proximity and historical close contact common for dialect continuums. The term ''Zan'' comes from the Greco-Roman name of one of the chief Colchian tribes, which is almost identical to the name given to the Mingrelians by the Svans ( ''mə-zän''). Georgian linguist Akaki Shanidze proposed the name "Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Millennium BC
File:2nd millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: Hammurabi, Babylonian king, best known for his Code of Hammurabi, code of laws; The gold Mask of Tutankhamun, funerary mask of Tutankhamun has become a symbol of ancient Egyptian civilization and its enduring legacy; Nebra sky disc is considered the oldest concrete representation of astronomical phenomena, such as the sun, moon, and stars; Mask of Agamemnon; Hieroglyphs from the tomb of Seti I; The Lion Gate of Hattusa is a testament to the architectural and artistic skills of the Hittites (Background: Bull-Leaping Fresco ca. 1450-1400 BC). rect 23 27 345 383 Hammurabi rect 433 16 775 443 Tutankhamun rect 869 18 1264 338 Nebra sky disc rect 103 408 375 680 Mask of Agamemnon rect 466 470 833 705 Egyptian hieroglyphs rect 870 392 1262 656 Hittites rect 1 1 1279 719 Minoan civilization The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC. In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Language
Georgian (, ) is the most widely spoken Kartvelian language, Kartvelian language family. It is the official language of Georgia (country), Georgia and the native or primary language of 88% of its population. It also serves as the literary language or lingua franca for speakers of related languages. Its speakers today amount to approximately 3.8 million. Georgian is written with its own unique Georgian scripts, alphabet, alphabetical systems of unclear origin. Georgian is most closely related to the Zan languages (Megrelian and Laz language, Laz) and more distantly to Svan language, Svan. Georgian has various dialects, with standard Georgian based on the Kartlian dialect, and all dialects are mutually intelligible. The history of Georgian spans from Early Old Georgian in the 5th century, to Modern Georgian today. Its development as a written language began with the Christianization of Georgia in the 4th century. Georgian phonology features a rich consonant system, including aspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodori Valley
, , photo = , photo_caption = , map = Caucasus mountains#Georgia#Georgia Abkhazia , map_image = , map_caption = , location = , country_type = Internationally recognised country , country = Georgia , region_type = Partially recognised state , region = Abkhazia , state = , district = , city = , relief = 1 , label = , label_position = , coordinates = , coordinates_ref = , elevation = , elevation_m = , elevation_ft = , elevation_ref = , length = , length_mi = , length_km = , length_orientation = , length_note = , width = , width_mi = , width_km = , width_orientation = , width_note = , area = , area_mi2 = , area_km2 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |