|
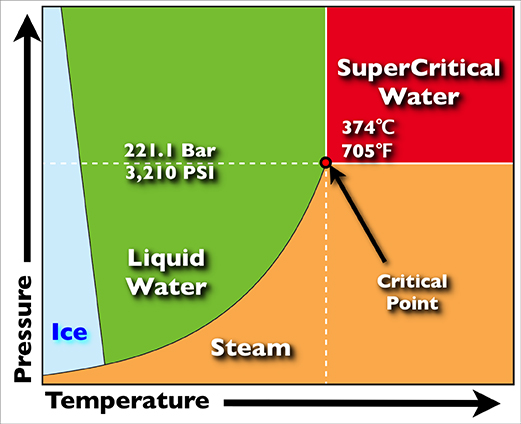
Supercritical Fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is a substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCFs are superior to gases in their ability to dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned". Supercritical fluids occur in the atmospheres of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn, the terrestrial planet Venus, and probably in those of the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. Supercritical water is found on Earth, such as the water issuing from black smokers, a type of hydrothermal vent. SCFs are used as a substitute for organic solvents in a range of industrial and laborato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth. Compared to Uranus, its neighbouring ice giant, Neptune is slightly smaller, but more massive and denser. Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined solid surface. Neptune orbits the Sun once every 164.8 julian year (astronomy), years at an orbital distance of . It is named after Neptune (mythology), the Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol representing Trident of Poseidon, Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System that was not initially observed by direct empirical observation. Rather, unexpected changes in the orbit of Uranus led Alexis Bouvard to hypothesise that its orbit was subject to gravitational Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as Pa. It is sometimes used as a ''reference pressure'' or ''standard pressure''. It is approximately equal to Earth's average atmospheric pressure at sea level. History The standard atmosphere was originally defined as the pressure exerted by a 760 mm column of mercury at and standard gravity (''g''n = ). It was used as a reference condition for physical and chemical properties, and the definition of the centigrade temperature scale set 100 °C as the boiling point of water at this pressure. In 1954, the 10th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) adopted ''standard atmosphere'' for general use and affirmed its definition of being precisely equal to dynes per square centimetre (). This defined pressure in a way that is independent of the properties of any particular substance. In addition, the CGPM noted that there had been some misapprehension that the previous definition (from the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pascal (unit)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is an SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m2). It is also equivalent to 10 barye (10 Ba) in the CGS system. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. The unit of measurement called '' standard atmosphere (atm)'' is defined as . Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phase Transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic State of matter, states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma (physics), plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical property, physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition States of matter Phase transitions commonly refer to when a substance tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Supercritical Steam Generator
A supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure and temperature, frequently used in the production of electric power. In contrast to a subcritical boiler in which steam bubbles form, a supercritical steam generator operates above the critical pressure and temperature . Under these conditions, the liquid water density decreases smoothly with no phase change, becoming indistinguishable from steam. The water temperature drops below the critical point as it does work in a high pressure turbine and enters the generator's condenser, resulting in slightly less fuel use. The efficiency of power plants with supercritical steam generators is higher than with subcritical steam because thermodynamic efficiency is directly related to the magnitude of their temperature drop. At supercritical pressure the higher temperature steam is converted more efficiently to mechanical energy in the turbine (as given by Carnot's theorem). Technically, the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Decaffeination
Decaffeination is the removal of caffeine from coffee beans, cocoa, tea leaves, and other caffeine-containing materials. Decaffeinated products are commonly termed by the abbreviation decaf. To ensure product quality, manufacturers are required to test the newly decaffeinated coffee beans to make sure that caffeine concentration is relatively low. A caffeine content reduction of at least 97% is required under United States FDA standards. A 2006 study found decaffeinated drinks to contain typically 1–2% of the original caffeine content, but sometimes as much as 20%. Decaffeinated coffee Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge performed the first isolation of caffeine from coffee beans in 1820, after the German poet Goethe heard about his work on belladonna extract, and requested he perform an analysis on coffee beans. Though Runge was able to isolate the compound, he did not learn much about the chemistry of caffeine itself, nor did he seek to use the process commercially to produce decaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Supercritical carbon dioxide (s) is a fluid state of carbon dioxide where it is held at or above its critical temperature and critical pressure. Carbon dioxide usually behaves as a gas in air at standard temperature and pressure (STP), or as a solid called dry ice when cooled and/or pressurised sufficiently. If the temperature and pressure are both increased from STP to be at or above the critical point for carbon dioxide, it can adopt properties midway between a gas and a liquid. More specifically, it behaves as a supercritical fluid above its critical temperature () and critical pressure (), expanding to fill its container like a gas but with a density like that of a liquid. Supercritical is becoming an important commercial and industrial solvent due to its role in chemical extraction, in addition to its relatively low toxicity and environmental impact. The relatively low temperature of the process and the stability of also allows compounds to be extracted with little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solvents
A solvent (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syntheses and purification processes Some petrochemical solvents are highly toxic and emit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |