|
Suburban Electrification Of The London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) was involved in the development of railway electrification of Britain. Like the LNER and the SR the LMS took over several schemes that had been developed by its constituent companies and also completed some of its own. All were suburban lines, in London, Liverpool and Manchester, and were usually steam lines converted to electric traction. Each service is listed below, showing dates of opening and the railway responsible for its conversion. London District Fourth rail, route length in 1927 was 40.2 miles (64.3 km). * Whitechapel - Upminster, used by District Railway and opened in sections as follows: ** 1905 Whitechapel - East Ham ** 1908 East Ham - Barking ** 1932 Barking - Upminster * 1914 Willesden Junction - Earl's Court * 1916 Broad Street - Kew Bridge - Richmond * Euston / Broad Street - Watford Junction, opened in sections as follows: ** 1917 Willesden Junction - Watford Junction: London and North Western Railway ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Electric Multiple Unit Motor-coach (CJ Allen, Steel Highway, 1928)
LMS may refer to: Science and technology * Labeled magnitude scale, a scaling technique * Learning management system, education software * Least mean squares filter, producing least mean square error * Leiomyosarcoma, a rare form of cancer * Lenz microphthalmia syndrome * Computerised Library management system * Licentiate in Medicine and Surgery, a degree in India * LMS color space * Laboratory information management system (but usually LIMS) Organisations * Latin Mass Society of England and Wales * List of Marjan Šarec, a Slovenian political party * London Mathematical Society * London, Midland and Scottish Railway * London Missionary Society * ''League of Legends'' Master Series * Loving Municipal Schools Entertainment * Last man standing (gaming), a type of video game * LMS, family band of Denroy Morgan Other uses * Leamington Spa railway station code, England * Local Mitigation Strategy * Local Management of Schools, in the Education Reform Act 1988 *Loïc Mbe Soh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croxley Green Railway Station
Croxley Green railway station is a disused terminus between Rickmansworth and Watford on the A412 road at the end of a short branch line. History The station was opened in 1912 by the London and North Western Railway as the terminus of the branch line of the Watford-Rickmansworth line. The original wooden station building was burned in the early hours of 10 March 1913 by a group of Suffragette A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right to vote in public elections in the United Kingdom. The term refers in particular to members ...s. A goods yard opened just to the east of the station shortly after, which by 1939 it was expanded and a loop constructed from the southern to the northern siding. The London Midland Region of British Railways, and later Network SouthEast after sectorisation, continued to run services until 1996. Not far from the terminus, a depot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Kirby Railway Station
West Kirby railway station serves the town of West Kirby in Merseyside, England. The station is the terminus of the West Kirby branch line, which is one of the two branches of the Wirral Line, part of the Merseyrail network,. There is a central island platform between two terminus tracks, and two parallel sidings for out-of-use electric trains. A second station, terminal to a rail link to Hooton, lay to the east of the Wirral Line station, but closed in 1962. History Wirral line In 1873, the Hoylake and Birkenhead Railway was authorised to construct two extensions to its lines. One was a short connecting section near to Birkenhead docks, and the other was the extension from Hoylake to West Kirby. The station and the extension were opened on 1 April 1878 as the terminus of the Wirral Railway's route from Birkenhead Park station. The station's original signal box was built in 1886, to a London and North Western Railway (LNWR) design. This signal box was removed and replac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkenhead Park Railway Station
Birkenhead Park railway station is a station serving the town of Birkenhead, in Merseyside, England. It lies on the Wirral Line of the Merseyrail network. History The name of the station comes from nearby Birkenhead Park, one of the UK's first Victorian municipal parks. In 1850 its layout - created by Joseph Paxton - had a profound influence on visiting American landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted. Eight years later he took inspiration from Birkenhead Park (and other green spaces like Derby Arboretum) to win a competition to design New York's new city park. The station was opened on 2 January 1888, as a joint interchange station between the Seacombe, Hoylake and Deeside Railway and the Mersey Railway. The station replaced the Wirral Railway's original terminus at Wallasey Bridge Road, which was close to the present-day Birkenhead North station. The station was an interchange between the Wirral Railway's line to West Kirby and the Mersey Railway's new line to Live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
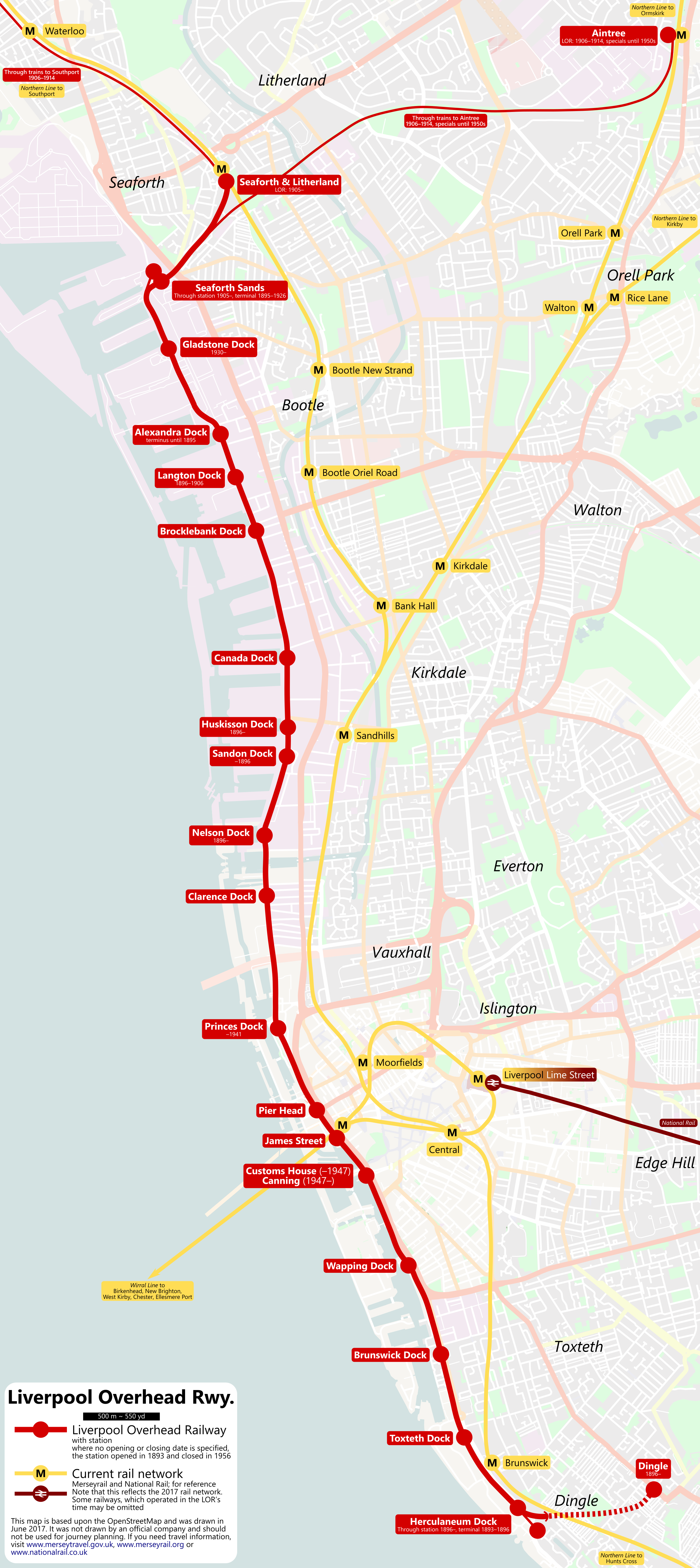
Liverpool Overhead Railway
The Liverpool Overhead Railway (known locally as the Dockers' Umbrella or Ovee) was an overhead railway in Liverpool which operated along the Liverpool Docks and opened in 1893 with lightweight electric multiple units. The railway had a number of world firsts: it was the first electric elevated railway, the first to use automatic signalling, electric colour light signals and electric multiple units, and was home to one of the first passenger escalators at a railway station. It was the second oldest electric metro in the world, being preceded by the 1890 City and South London Railway. Originally spanning from Alexandra Dock to Herculaneum Dock, the railway was extended at both ends over the years of operation, as far south as Dingle and north to Seaforth & Litherland. A number of stations opened and closed during the railway's operation owing to relative popularity and damage, including air bombing during World War II. At its peak almost 20 million people used the railway eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aintree Railway Station
Aintree railway station is a railway station that serves the village of Aintree, Merseyside, England. It is on the Ormskirk branch of the Merseyrail network's Northern Line. Until 1968 it was known as Aintree Sefton Arms after a nearby public house. The station's design reflects that it is the closest station to Aintree Racecourse, where the annual Grand National horse race takes place. History Opened by the East Lancashire Railway in April 1849, then taken over by the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway ten years later, it became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway during the Grouping of 1923. The line then passed on to the London Midland Region of British Railways on nationalisation in 1948. The L&YR electrified both routes from in 1906 (two years after a successful trial of the system on the neighbouring line to ), extending it subsequently as far as by 1913. The western end of the North Mersey Branch from Gladstone Dock & Bootle (which had opened in 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire And Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major British railway company before the 1923 Grouping. It was incorporated in 1847 from an amalgamation of several existing railways. It was the third-largest railway system based in northern England (after the Midland and North Eastern Railways). The intensity of its service was reflected in the 1,650 locomotives it owned – it was by far the most densely-trafficked system in the British Isles with more locomotives per mile than any other company – and that one third of its 738 signal boxes controlled junctions averaging one every . No two adjacent stations were more than apart and its 1,904 passenger services occupied 57 pages in '' Bradshaw'', a number exceeded only by the Great Western Railway, the London and North Western Railway, and the Midland Railway. It was the first mainline railway to introduce electrification of some of its lines, and it also ran steamboat services across the Irish Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ormskirk Railway Station
Ormskirk railway station in Ormskirk, Lancashire, England, is a cross-platform interchange between Merseyrail services from Liverpool Central and Northern Trains services from Preston on the Ormskirk branch line, northeast of Liverpool. The station building and three arch road bridge are both Grade II listed structures. History The station was built by the East Lancashire Railway's Liverpool, Ormskirk and Preston Junction section, and opened on 2 April 1849. From 13 May 1859, the station was owned by the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway. From 1 January 1923 the station was owned by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. British Railways nationalised all railways on 1 January 1948 and the station became part of the London Midland Region. A branch line to via was opened by the ELR in March 1858 shortly before it was absorbed by the L&YR – this left the main line to Preston just to the north of the station. The line from Liverpool was subsequently electrified in 1913 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossens Railway Station
Crossens railway station was a railway station serving Crossens, a suburb of Southport, Sefton, Merseyside, England. History Located on the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway main line between and , it was opened to passengers by the West Lancashire Railwayin 1878. In April 1904 it became the last electrified station on the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway's suburban lines from Liverpool Exchange railway station Liverpool Exchange railway station was a railway station located in the city centre of Liverpool, England. Of the four terminal stations in Liverpool's city centre, Exchange station was the only station not accessed via a tunnel. The station w ..., forming a terminus of the Southport - Crossens electric branch. Services ended on 6 September 1964 with the closure of the Southport to Preston line.Cadwallader, Jonathan and Jenkins, Martin (2010) ''Merseyside Electrics'', Ian Allan Publishing, (p34 has colour photo of Crossens station looking north, with electric tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southport Railway Station
Southport railway station serves the town of Southport, Merseyside, England. The station is the terminal of the Southport branch of the Northern Line of the electric Merseyrail network and the diesel-operated Manchester-Southport Line. It is the fourth busiest station on the Merseyrail network. The station and services to Liverpool and are operated by Merseyrail, with Manchester services operated by Northern Trains. History The Liverpool line was originally built in 1848 by the Liverpool, Crosby and Southport Railway to a temporary station at Eastbank Street, about half a mile short of the current terminus. The current station opened as Southport Chapel Street on 22 August 1851 and became the terminus for all trains in 1857, when passenger services were transferred from the adjacent . From 1882 the West Lancashire Railway to Preston Fishergate Hill operated from Southport Derby Road (later known as Southport Central) outside Chapel Street Station. In 1884, another lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool Exchange Railway Station
Liverpool Exchange railway station was a railway station located in the city centre of Liverpool, England. Of the four terminal stations in Liverpool's city centre, Exchange station was the only station not accessed via a tunnel. The station was badly damaged during World War II and lost a large proportion of the trainshed roof, which was never rebuilt, remaining an iron frame. The station's long-distance services were switched to in the 1960s, and, as a terminus, the station became redundant in the late 1970s, when its remaining local services switched to the newly opened Merseyrail tunnels under Liverpool city centre. It was closed in 1977, being replaced by the new underground station nearby. Station construction and opening The grandly-appointed station opened on 13 May 1850, replacing an earlier temporary station at Liverpool Great Howard Street railway station, Great Howard Street further north up the track. The station was designed by John Hawkshaw. The station had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)