|
Subglottic Stenosis
Subglottic stenosis is a congenital or acquired narrowing of the subglottic airway. It can be congenital, acquired, iatrogenic, or very rarely, idiopathic. It is defined as the narrowing of the portion of the airway that lies between the vocal cords and the lower part of the cricoid cartilage. In a normal infant, the subglottic airway is 4.5-5.5 millimeters wide, while in a premature infant, the normal width is 3.5 millimeters. Subglottic stenosis is defined as a diameter of under 4 millimeters in an infant. Acquired cases are more common than congenital cases due to prolonged intubation being introduced in the 1960s. It is most frequently caused by certain medical procedures or external trauma, although infections and systemic or autoimmune diseases can also cause it. Signs and symptoms Symptoms may range from stridor during exercise to complete obstruction of the airway. In idiopathic cases, symptoms may be mistaken for asthma. In congenital cases, symptoms occur soon after bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weight loss, shortness of breath, palpitations, and Orthostatic hypotension, feeling faint with standing. In AL amyloidosis, specific indicators can include enlargement of the tongue and periorbital purpura. In wild-type ATTR amyloidosis, non-cardiac symptoms include: bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, lumbar spinal stenosis, biceps tendon rupture, Small fiber peripheral neuropathy, small fiber neuropathy, and autonomic dysfunction. There are about 36 different types of amyloidosis, each due to a specific Proteopathy, protein misfolding. Within these 36 proteins, 19 are grouped into Organ-limited amyloidosis, localized forms, 14 are grouped as Systemic disease, systemic forms, and three proteins can identify as either. These proteins can become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloon Catheter
A balloon catheter is a type of "soft" catheter with an inflatable "balloon" at its tip which is used during a catheterization procedure to enlarge a narrow opening or passage within the Human body, body. The deflated balloon catheter is positioned, then inflated to perform the necessary procedure, and deflated again in order to be removed. Some common uses include: *angioplasty or balloon septostomy, via cardiac catheterization (heart cath) *tuboplasty via uterus, uterine catheterization *pyeloplasty using a detachable inflatable balloon stent positioned via a cystoscopy, cystoscopic transvesicular approach. Angioplasty balloon catheters Balloon catheters used in angioplasty are either of Over-the-Wire (OTW) or Rapid Exchange (Rx) design. Rx catheters nowadays are about 90% of the Coronary Intervention market. While OTW Catheters may still be useful in highly tortuous vascular pathways, they sacrifice deflation time and pushability. When a balloon catheter is used to compress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin T
Robin most commonly refers to several species of passerine birds. Robin may also refer to: Animals * Australasian robins, red-breasted songbirds of the family Petroicidae * Many members of the subfamily Saxicolinae (Old World chats), including: **European robin (''Erithacus rubecula'') ** Bush-robin **Forest robin **Magpie-robin **Scrub robin ** Robin-chat ** Bagobo robin **White-starred robin **White-throated robin ** Blue-fronted robin **Larvivora (6 species) **Myiomela (3 species) * Some red-breasted New-World true thrushes (''Turdus'') of the family Turdidae, including: ** American robin (''T. migratorius'') (so named by 1703) ** Rufous-backed thrush (''T. rufopalliatus'') ** Rufous-collared thrush (''T. rufitorques'') ** Formerly other American thrushes, such as the clay-colored thrush (''T. grayi'') * Pekin robin or Japanese (hill) robin, archaic names for the red-billed leiothrix (''Leiothrix lutea''), red-breasted songbirds * Sea robin, a fish with small "legs" (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FEV1
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time. Spirometry generates pneumotachographs, which are charts that plot the volume and flow of air coming in and out of the lungs from one inhalation and one exhalation. Testing Spirometer The spirometry test is performed using a device called a spirometer, which comes in several different varieties. Most spirometers display the following graphs, called spirograms: * a ''volume-time curve'', showing volume (litres) along the Y-axis and time (seconds) along the X-axis * a ''flow-volume loop'', which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
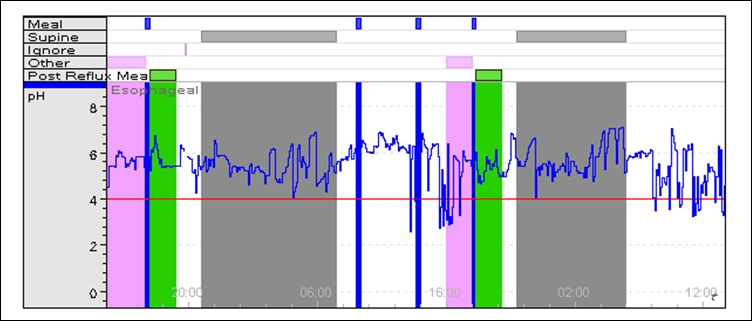
Esophageal PH Monitoring
In gastroenterology, esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document reflux disease, assess the severity of the disease and monitor the response of the disease to medical or surgical treatment. It can also be used in diagnosing laryngopharyngeal reflux. Background The importance of refluxed gastric contents in the pathogenesis of GERD was emphasized by Winkelstein who introduced the term " peptic esophagitis" and by Bernstein and Baker who reported the symptom of heartburn following instillation of hydrochloric acid in the distal esophagus in what then became known as the acid perfusion test. Formal measurement of acid in the esophagus was first described in 1960 by Tuttle. He used a glass pH probe to map the gastroesophageal pH gradient, and demonstrated a sharp gradient in normal subjects and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Disease
An occupational disease or industrial disease is any chronic ailment that occurs as a result of work or occupational activity. It is an aspect of occupational safety and health. An occupational disease is typically identified when it is shown that it is more prevalent in a given body of workers than in the general population, or in other worker populations. The first such disease to be recognised, squamous-cell carcinoma of the scrotum, was identified in chimney sweep boys by Sir Percival Pott in 1775. Occupational hazards that are of a traumatic nature (such as falls by roofers) are not considered to be occupational diseases. Under the law of workers' compensation in many jurisdictions, there is a presumption that specific diseases are caused by the worker being in the work environment and the burden is on the employer or insurer to show that the disease came about from another cause. Diseases compensated by national workers compensation authorities are often termed occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ionizing radiation (such as sunburn, caused by ultraviolet radiation). Most burns are due to heat from hot fluids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainly in the home or the workplace. In the home, risks are associated with domestic kitchens, including stoves, flames, and hot liquids. In the workplace, risks are associated with fire and chemical and electric burns. Alcoholism and smoking are other risk factors. Burns can also occur as a result of self-harm or violence between people (assault). Burns that affect only the superficial skin layers are known as superficial or first-degree burns. They appear red without blisters, and pain typically lasts around three days. When the injury extends into some of the underlying skin layer, it is a partial-thickness or second-degree burn. Blisters are frequently present and they are often very painful. Healing can re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of solid or liquid material such as pharyngeal secretions, food, drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the trachea and lungs. When pulmonary aspiration occurs during eating and drinking, the aspirated material is often colloquially referred to as "going down the wrong pipe". Consequences of pulmonary aspiration include no injury at all, chemical pneumonitis, pneumonia, or even death from asphyxiation. These consequences depend on the volume, chemical composition, particle size, and presence of infectious agents in the aspirated material, and on the underlying health status of the person. In healthy people, aspiration of small quantities of material is common and rarely results in disease or injury. People with significant underlying disease or injury are at greater risk for developing respiratory complications following pulmonary aspiration, especially hospitalized patients, because of certain factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyarthritis
Polyarthritis is any type of arthritis that involves 5 or more joints simultaneously. It can be associated with autoimmune conditions; it may be experienced at any age and is not sex specific. Causes Polyarthritis is often caused by an auto-immune disorder such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus erythematosus, or other inflammatory rheumatic diseases, like crystal arthropathies. It can also be caused by cancer or various medications. Another cause of polyarthritis is infection, which may be viral or bacterial. Viruses that cause polyarthritis include alphaviruses, such as chikungunya virus, Sindbis virus and Ross River virus. Arthritis caused by bacterial infection of the joint is termed septic arthritis and does not commonly affect multiple joints. It may notably be caused by ''gonococcus''. Bacteria can also cause polyarthritis not by directly infecting the joints; instead, infection located elsewhere in the body can cause immune reaction, which become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relapsing Polychondritis
Relapsing polychondritis is a systemic disease characterized by repeated episodes of inflammation and in some cases deterioration of cartilage. The disease can be life-threatening if the respiratory tract, heart valves, or blood vessels are affected. The exact mechanism is poorly understood. The diagnosis is reached on the basis of the symptoms and supported by investigations such as blood tests and sometimes other investigations. Treatment may involve symptomatic treatment with painkillers or anti-inflammatory medications, and more severe cases may require suppression of the immune system. Signs and symptoms Though any cartilage in the body may be affected in persons with relapsing polychondritis, in many cases the disease affects several areas while sparing others. The disease may be variable in its signs and symptoms, resulting in a difficult diagnosis which may leads to delayed recognition for several months, years or decades. Associated diseases There are several other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |