|
Styphelia Rigida
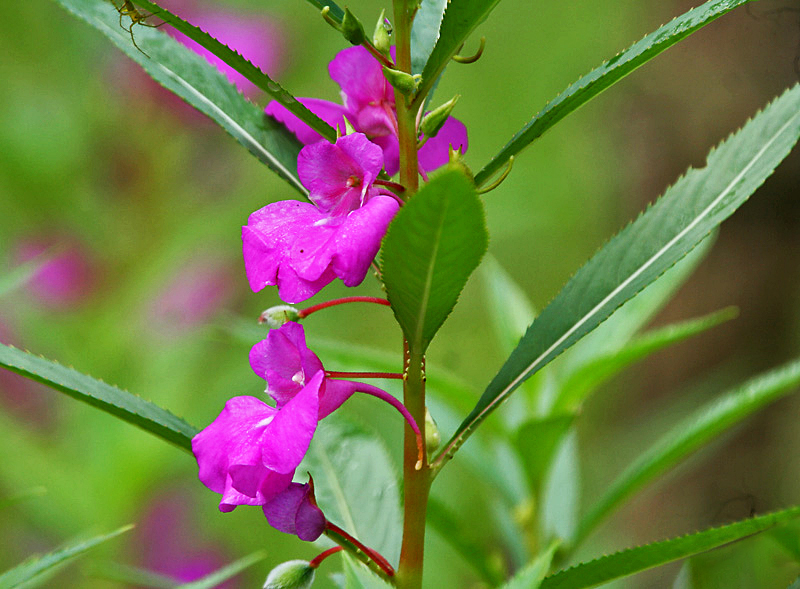
''Styphelia rigida'' is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south of Western Australia. It was first formally described in 1839 by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle who gave it the name ''Leucopogon rigidus'' in his '' Prodromus Systematis Naturalis Regni Vegetabilis'' from an unpublished description by Allan Cunningham. In 2020, Michael Hislop, Darren Crayn and Caroline Puente-Lelievre transferred the species to ''Styphelia'' as ''S. rigida'' in ''Australian Systematic Botany''. The specific epithet (''rigida'') means "hard" or "stiff", probably referring to the branchlets. ''Styphelia rigida'' is found in the Esperance Plains bioregion of southern Western Australia and is listed as "not threatened" by the Western Australian Government Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions The Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) is the Government of Western Australia, Western Australian government depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Clyde Hislop
Michael Clyde Hislop (born 1955) is an Australian botanist based in Perth at the Western Australian Herbarium. Career Hislop specialises in the curation, identification and taxonomy of plants, particularly the genus '' Styphelia'' which he recircumscribed with two other researchers. He has also helped to identify and name numerous species found in the Pilbara The Pilbara () is a large, dry, sparsely populated regions of Western Australia, region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Indigenous Australians, Aboriginal people; wealth disparity; its ancient landscapes; the prevailing r ..., Goldfields and South-West of Western Australia. '' Grevillea hislopii'' was named in his honour. References Living people Botany in Western Australia Scientists from Perth, Western Australia 1955 births {{WesternAustralia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styphelia
''Styphelia'' is a genus of shrubs in the family Ericaceae, native from Mainland Southeast Asia, Indo-China through the Pacific to Australia. Most have minute or small leaves with a sharp tip, single, tube-shaped flowers arranged in leaf wikt:axil, axils and with the ends of the petals rolled back with hairs in the inside of the tube. Description Plants in the genus ''Styphelia'' are usually erect or spreading shrubs that have egg-shaped, elliptical or oblong, more or less Sessility (botany), sessile leaves with many fine, almost parallel veins and a sharp point on the tip. The flowers are usually arranged singly in leaf axils with small bracts grading to larger Bract#Bracteole, bracteoles at the base and five, usually coloured sepals. The petals are fused to form a cylindrical tube with their tips rolled back. The inside of the petal tube is hairy and the five stamens and thread-like Style (botany), style extend beyond the end of the tube. The fruit is a drupe with a dry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Western Australia
The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,842 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,030 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genus, genera from 211 Family (biology), families; there are also 1,335 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority. History Indigenous Australians have a long history with the flora of Western Australia. They have for over 50,000 years obtained detailed information on most plants. The information includes its uses as sources for food, shelter, tools and medicine. As Indigenous Australians passed the knowledge along orally or by example, most of this information has been lost, along many of the names they gave the flora. It was not until Europeans started to explore Western Australia that systematic written de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericales Of Australia
The Ericales are a large and diverse order of flowering plants in the asterid group of the eudicots. Well-known and economically important members of this order include tea and ornamental camellias, persimmon, ebony, blueberry, cranberry, lingonberry, huckleberry, kiwifruit, Brazil nut, argan, sapote, azaleas and rhododendrons, heather, heath, impatiens, phlox, Jacob's ladder, primroses, cyclamens, shea, sapodilla, pouterias, and trumpet pitchers. The order includes 22 families, according to the APG IV system of classification. The Ericales include trees, bushes, lianas, and herbaceous plants. Together with ordinary autophytic plants, they include chlorophyll-deficient mycoheterotrophic plants (e.g., '' Sarcodes sanguinea'') and carnivorous plants (e.g., genus '' Sarracenia''). Mycorrhizal associations are quite common among the order representatives, and three kinds of mycorrhiza are found exclusively among Ericales (namely, ericoid, arbutoid and monotropoid myco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Biodiversity, Conservation And Attractions (Western Australia)
The Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) is the Government of Western Australia, Western Australian government department responsible for managing lands and waters described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'', the ''Rottnest Island Authority Act 1987'', the ''Swan and Canning Rivers Management Act 2006'', the ''Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority Act 1998'', and the ''Zoological Parks Authority Act 2001'', and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The Department reports to the Minister for Environment and the Minister for Tourism. DBCA was formed on 1 July 2017 by the merger of the Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW), the Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority, the Zoological Parks Authority and the Rottnest Island Authority. The former DPaW became the Parks and Wildlife Service. Status Parks and Wildlife Service The Formerly Department of Parks and Wildlife. the Parks and Wildlife Servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperance Plains
Esperance Plains, also known as Eyre Botanical District, is a biogeography, biogeographic region in southern Western Australia on the South_coast_of_Western_Australia , south coast between the Avon Wheatbelt and Hampton bioregions, and bordered to the north by the Mallee (biogeographic region), Mallee region. It is a plain punctuated by granite and quartz outcrops and ranges, with a semi-arid Mediterranean climate and vegetation consisting mostly of mallee-heath and Proteaceae, proteaceous scrub. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a bioregion under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Esperance Plains may be roughly approximated as the land within of the coast between Albany, Western Australia, Albany and Point Culver on the south coast of Western Australia. It has an area of about , making it about 9% of the Southwest Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Systematic Botany
''Australian Systematic Botany'' is an international peer-reviewed scientific journal published by CSIRO Publishing. It is devoted to publishing original research, and sometimes review articles, on topics related to systematic botany, such as biogeography, taxonomy and evolution. The journal is broad in scope, covering all plant, algal and fungal groups, including fossils. First published in 1978 as ''Brunonia'', the journal adopted its current name in 1988. The current editor-in-chief is Daniel Murphy ( Royal Botanic Gardens Melbourne). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in BIOSIS, CAB Abstracts, Current Contents (Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences), Elsevier BIOBASE, Kew Index, Science Citation Index and Scopus. Impact factor According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2015 impact factor of 0.648. References External links * Australian Systematic Botanyat SCImago Journal Rank Australian Systematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Cunningham (botanist)
Allan Cunningham (13 July 1791 – 27 June 1839) was an English botany, botanist and List of explorers, explorer, primarily known for his expeditions into uncolonised areas of eastern Australia to collect plants and report on the suitability of the land for grazing purposes. Early life Cunningham was born in Wimbledon, London, England, the son of Allan Cunningham (head gardener at Wimbledon Park House), who came from Renfrewshire, Scotland, and his English wife Sarah (née Juson/Jewson née Dicken). Allan Cunningham was educated at a Putney private school, Reverend John Adams (educational writer), John Adams Academy and then went into a solicitor's office (a Lincoln's Inn Conveyancer). He afterwards obtained a position with William Townsend Aiton superintendent of Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Kew Gardens, and this brought him in touch with Robert Brown (Scottish botanist from Montrose), Robert Brown and Joseph Banks. Brazil On Banks' recommendation, Cunningham went to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darren M
Darren is a masculine given name of uncertain etymological origins. Some theories state that it originated from an Anglicisation of the Irish first name Darragh or Dáire, meaning "oak tree". According to other sources, it is thought to come from the Gaelic surname meaning "great", but is also linked to a Welsh mountain named Moel Darren. It is also believed to be a variant of Darrell, which originated from the French surname ''D'Airelle'', meaning "of Airelle". The common spelling of Darren is found in the Welsh language, meaning "edge": Black Darren and Red Darren are found on the eastern side of the Hatterrall Ridge, west of Long Town. In New Zealand, the Darran Mountains are in the south of the country. The name increased in use for boys after American author Zane Grey used the name Daren Lane for the hero of his 1922 novel ''The Beast''; a number of American parents used the full name of the character, Daren Lane, as first and middle names for their sons. While the name i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustin Pyramus De Candolle
Augustin Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (, , ; 4 February 17789 September 1841) was a Swiss people, Swiss botany, botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at a herbarium. Within a couple of years de Candolle had established a new genus, and he went on to document hundreds of plant families and create a new natural plant classification system. Although de Candolle's main focus was botany, he also contributed to related fields such as phytogeography, agronomy, paleontology, medical botany, and economic botany. De Candolle originated the idea of "Nature's war", which influenced Charles Darwin and the principle of natural selection. De Candolle recognized that multiple species may develop similar characteristics that did not appear in a common evolutionary ancestor; a phenomenon now known as convergent evolution. During his work with plants, de Candolle noticed that plant leaf movements follow a near-24-hour cycle in constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |