|
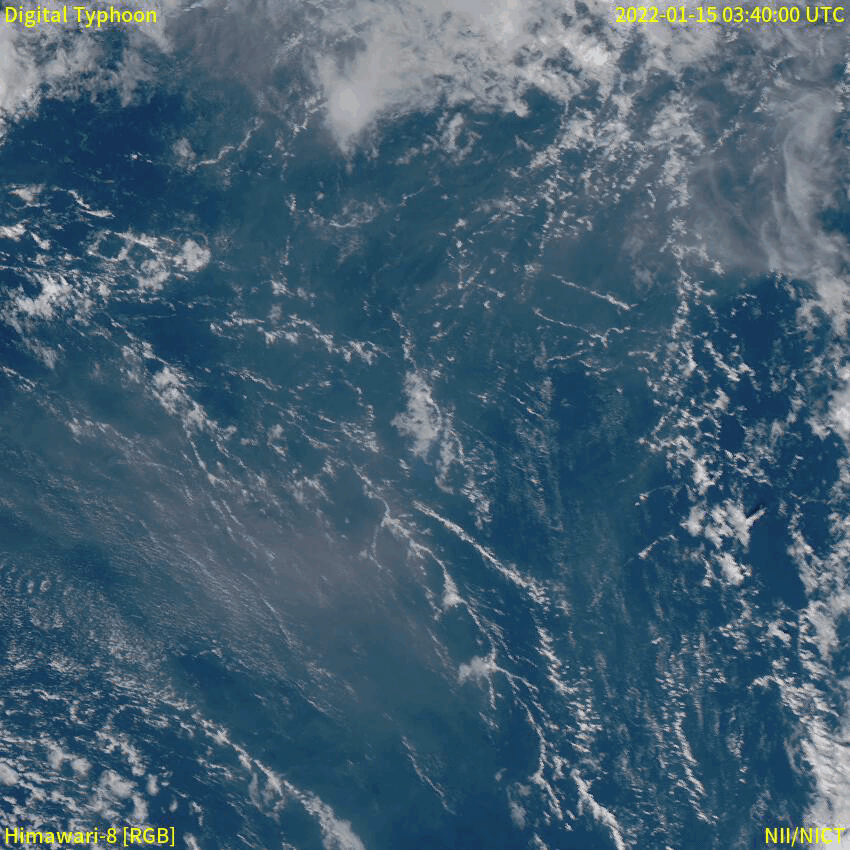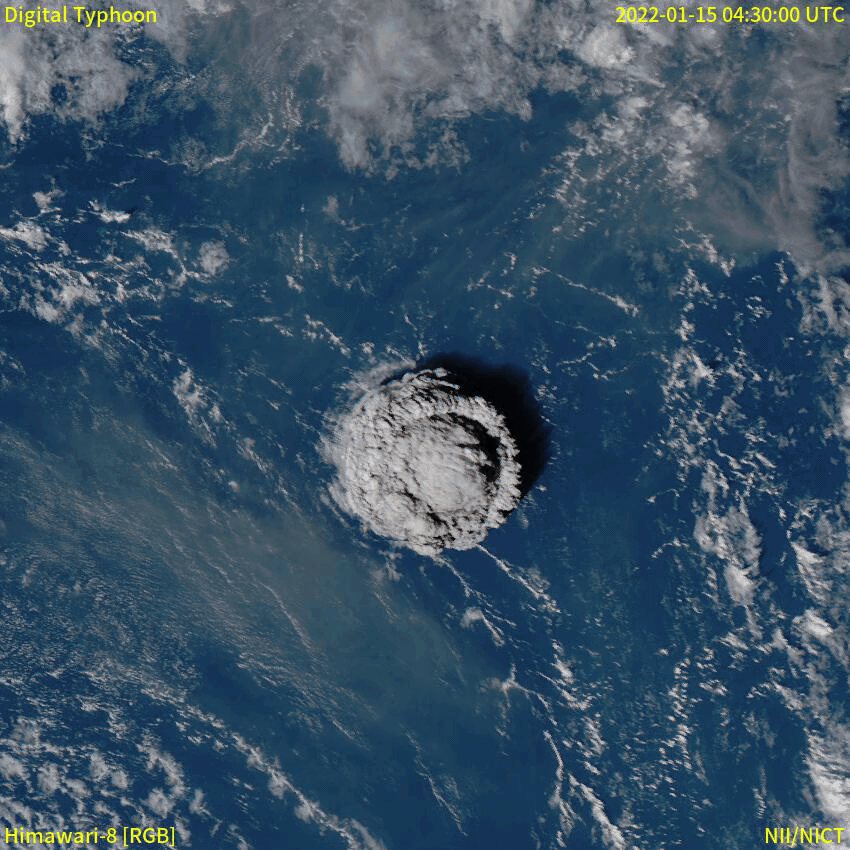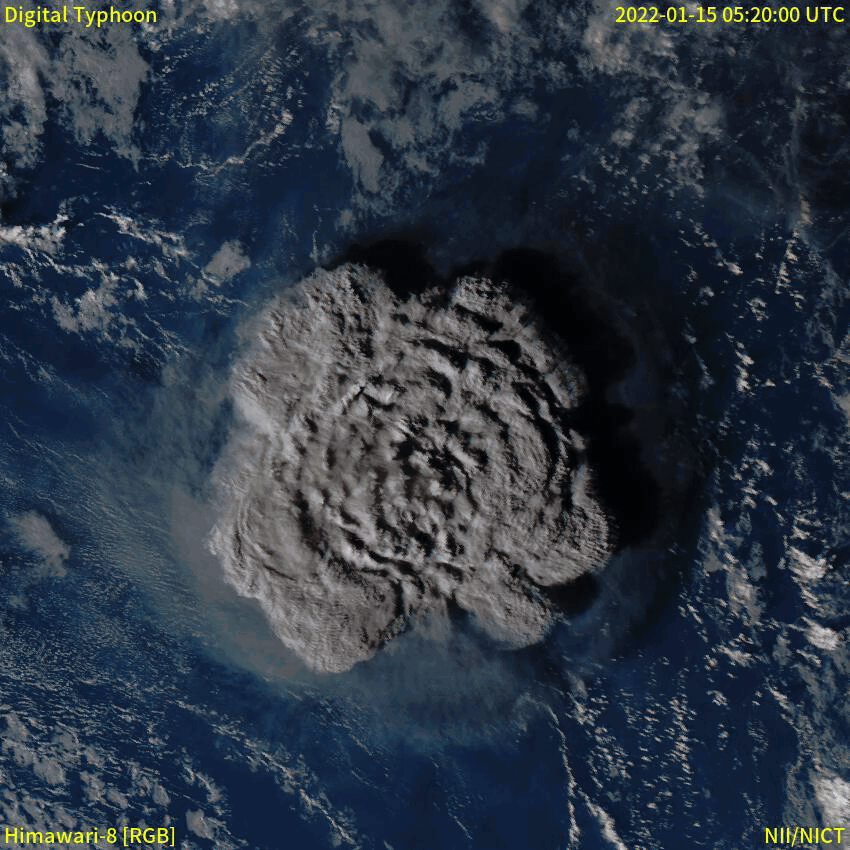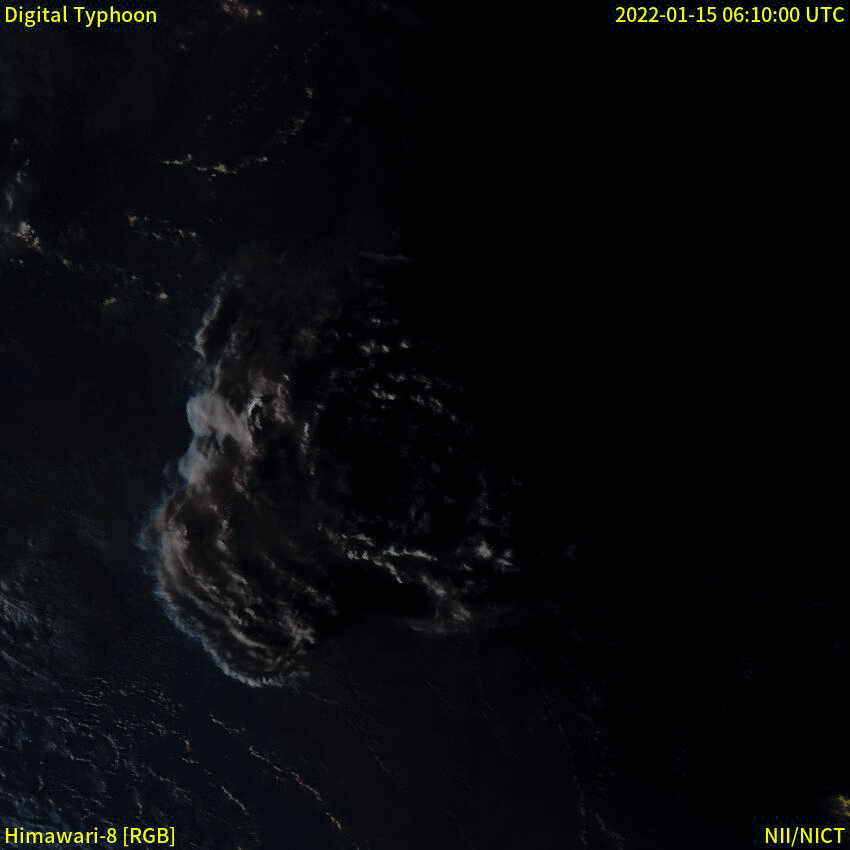
Strombolian Eruption
In volcanology, a Strombolian eruption is a type of volcanic eruption with relatively mild blasts, typically having a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 1 or 2. Strombolian eruptions consist of ejection of incandescent Scoria, cinders, lapilli, and volcanic bombs, to altitudes of tens to a few hundreds of metres. The eruptions are small to medium in volume, with sporadic violence. This type of eruption is named for the Italy, Italian volcano Stromboli. The tephra typically glows red when leaving the vent, but its surface cools and assumes a dark to black colour and may significantly solidify before impact. The tephra accumulates in the vicinity of the vent, forming a cinder cone. Cinder is the most common product; the amount of volcanic ash is typically rather minor. The lava flows are more viscous, and therefore shorter and thicker, than the corresponding Hawaiian Eruption, Hawaiian eruptions; it may or may not be accompanied by production of pyroclastic rock. Instead the gas coale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Rock
Pyroclastic rocks are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroclasts. Pyroclastic rocks are a type of volcaniclastic deposit, which are deposits made predominantly of volcanic particles. 'Phreatic' pyroclastic deposits are a variety of pyroclastic rock that forms from volcanic steam explosions and they are entirely made of accidental clasts. 'Phreatomagmatic' pyroclastic deposits are formed from explosive interaction of magma with groundwater. The word ''pyroclastic'' is derived from the Greek , meaning fire; and , meaning broken. Unconsolidated accumulations of pyroclasts are described as tephra. Tephra may become lithified to a pyroclastic rock by cementation or chemical reactions as the result of the passage of hot gases (fumarolic alteration) or groundwater (e.g. hydrothermal alteration and diagenesis) and burial, or, if it is emplaced at temperatures so hot that the soft gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ) is a Somma volcano, somma–stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes forming the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large volcanic cone, cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera, resulting from the collapse of an earlier, much higher structure. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD destroyed the Roman Empire, Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum, Oplontis, Stabiae and other settlements. The eruption ejected a cloud of Volcanic rock, stones, Volcanic ash, ash and volcanic gases to a height of , Volcanic eruption, erupting Lava, molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of per second. More than 1,000 people are thought to have died in the eruption, though the exact toll is unknown. The only surviving witness account consists of two letters by Pliny the Younger to the historian Tacitus. Vesuvius has erupted ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Cumbre Vieja Volcanic Eruption
An eruption at the Cumbre Vieja complex volcano, volcanic ridge, comprising the southern half of the Spain, Spanish island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, took place between 19 September and 13 December 2021. It was the first volcanic eruption on the island since the Teneguía#1971 eruption, eruption of Teneguía in 1971. At 85 days, it is the longest known and the most damaging volcanic eruption on La Palma since records began. The total damage caused by the volcano amounts up to 843 million euros. The lava flow covered over , prompting the evacuation of around 7,000 people. The lava flow was about wide at its widest point, about long and reached the sea, destroying more than 3,000 buildings, cutting the coastal highway and forming a new peninsula, as well as an extensive system of Tajogaite#Lava tubes, lava tubes. The town of Todoque, including its easternmost neighbourhood Los Campitos (Los Llanos de Aridane), Los Campitos, was completely destroyed by lava, which also reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Etna
Mount Etna, or simply Etna ( or ; , or ; ; or ), is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina, Italy, Messina and Catania. It is located above the Convergent boundary, convergent plate margin between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is one of the tallest active volcanoes in Europe, and the tallest peak in Italy south of the Alps with a current height (September 2024) of , though this varies with summit eruptions. For instance, in 2021 the southeastern crater reached a height of , but was then surpassed by the Voragine crater after the summer 2024 eruptions. Etna covers an area of with a basal circumference of . This makes it by far the largest of the three volcanism in Italy, active volcanoes in Italy, being about two and a half times the height of the next largest, Mount Vesuvius. Only Teide, Mount Teide on Tenerife in the Canary Islands surpasses it in the whole of the Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plinian Eruption
Plinian eruptions or Vesuvian eruptions are volcanic eruptions characterized by their similarity to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which destroyed the ancient Roman cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii. The eruption was described in a letter written by Pliny the Younger, after the death of his uncle Pliny the Elder. Plinian eruptions eject columns of volcanic debris and hot gases high into the stratosphere, the second layer of Earth's atmosphere. They eject a large amount of pumice and have powerful, continuous gas-driven eruptions. Eruptions can end in less than a day, or continue for days or months. The longer eruptions begin with production of clouds of volcanic ash, sometimes with pyroclastic surges. The amount of magma ejected can be so large that it depletes the magma chamber below, causing the top of the volcano to collapse, resulting in a caldera. Fine ash and pulverized pumice can be deposited over large areas. Plinian eruptions are often accompanied by loud s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruption Column
An eruption column or eruption plume is a cloud of super-heated Volcanic ash, ash and tephra suspended in volcanic gas, gases emitted during an explosive eruption, explosive volcanic eruption. The volcanic materials form a vertical column or Plume (fluid dynamics), plume that may rise many kilometers into the air above the vent of the volcano. In the most explosive eruptions, the eruption column may rise over , penetrating the stratosphere. Injection of Particulate, aerosols into the stratosphere by volcanoes is a major cause of short-term Volcanic winter, climate change. A common occurrence in explosive eruptions is ''column collapse'' when the eruption column is or becomes too dense to be lifted high into the sky by air convection, and instead falls down the slopes of the volcano to form pyroclastic flows or pyroclastic surge, surges (although the latter is less dense). On some occasions, if the material is not dense enough to fall, it may create pyrocumulonimbus clouds. Forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Explosivity Index
The volcanic explosivity index (VEI) is a scale used to measure the size of explosive volcanic eruptions. It was devised by Christopher G. Newhall of the United States Geological Survey and Stephen Self in 1982. Volume of products, eruption cloud height, and qualitative observations (using terms ranging from "gentle" to "mega-colossal") are used to determine the explosivity value. The scale is open-ended with the largest eruptions in history given a magnitude of 8. A value of 0 is given for non-explosive eruptions, defined as less than of tephra ejected; and 8 representing a supervolcanic eruption that can eject (240 cubic miles) of tephra and have a cloud column height of over . The scale is logarithmic, with each interval on the scale representing a tenfold increase in observed ejecta criteria, with the exception of between VEI-0, VEI-1 and VEI-2. Classification With indices running from 0 to 8, the VEI associated with an eruption is dependent on how much volcanic materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxysm At Etna, 16-17 November 2013
Paroxysmal attacks or paroxysms are a sudden recurrence or intensification of symptoms, such as a spasm or seizure. These short, frequent symptoms can be observed in various clinical conditions. They are usually associated with multiple sclerosis or pertussis, but they may also be observed in other disorders such as encephalitis, head trauma, stroke, autism, asthma, trigeminal neuralgia, breath-holding spells, epilepsy, malaria, tabes dorsalis, Behçet's disease, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). It has also been noted as a symptom of gratification disorder in children. The word ''paroxysm'' means 'sudden attack, outburst' and comes . Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', on Perseus Paroxysmal attacks in various disorders h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churn Turbulent Flow
Churn turbulent flow is a two-phase gas/liquid flow regime characterized by a highly-agitated flow where gas bubbles are sufficient in numbers to both interact with each other and, while interacting, coalesce to form larger distorted bubbles with unique shapes and behaviors in the system. This flow regime is created when there is a large gas fraction in a system with a high gas and low liquid velocity. It is an important flow regime to understand and model because of its predictive value in nuclear reactor vessel boiling flow. Occurrence A flow in which the number of bubbles is low is called ideally-separated bubble flow. The bubbles don’t interact with each other. As the number of bubbles increase they start colliding each other. A situation then arises where they tend to coalesce to form cap bubbles, and the new flow pattern formed is called churn turbulent flow. The bubbles occurring in such a flow can be classified in small, large, and distorted bubbles. The small bubbles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Erebus
Mount Erebus () is the southernmost active volcano on Earth, located on Ross Island in the Ross Dependency in Antarctica. With a summit elevation of , it is the second most prominent mountain in Antarctica (after Mount Vinson) and the second-highest volcano in Antarctica (after the dormant Mount Sidley). It is the highest point on Ross Island, which is also home to three inactive volcanoes: Mount Terror, Mount Bird, and Mount Terra Nova. It makes Ross Island the sixth-highest island on Earth. The mountain was named by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841 for his ship, HMS ''Erebus''. The volcano has been active for around 1.3 million years and has a long-lived lava lake in its inner summit crater that has been present since at least the early 1970s. On 28 November 1979, Air New Zealand Flight 901 crashed on Mount Erebus, killing all 257 people on board. Geology and volcanology Mount Erebus is the world's southernmost active volcano. It is the current eruptive cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parícutin
Parícutin (or Volcán de Parícutin, also accented Paricutín) is a cinder cone volcano located in the Mexican state of Michoacán, near the city of Uruapan and about west of Mexico City. The volcano surged suddenly from the cornfield of local farmer Dionisio Pulido in 1943, attracting both popular and scientific attention. Parícutin presented the first occasion for modern science to document the full life cycle of an eruption of this type. During the volcano's nine years of activity, scientists sketched and mapped it and took thousands of samples and photographs. By 1952, the eruption had left a cone and significantly damaged an area of more than with the ejection of stone, volcanic ash and lava. Three people were killed, two towns were completely evacuated and buried by lava, and three others were heavily affected. Hundreds of people had to permanently relocate, and two new towns were created to accommodate their migration. Although the larger region still remains highly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |