|
Stratocumulus Cloud
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the whole being at a lower height, usually below . Weak convective currents create shallow cloud layers (see also: sea of clouds) because of drier, stable air above preventing continued vertical development. Historically, in English, this type of cloud has been referred to as a twain cloud for being a combination of two types of clouds. Description Stratocumulus clouds are rounded clumps or patches of white to dark gray clouds that normally form in groups. The individual cloud elements, which cover more than 5 degrees of arc each, can connect with each other and are sometimes arranged in a regular pattern. Occurrence Vast areas of subtropical and polar ocean The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convection, convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in cumulonimbus clouds. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce Heavy rain (meteorology), heavy rain and sometimes Thundersnow, snow, Ice pellets, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms can produce little or Dry thunderstorm, no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may thunderstorm training, line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or #Severe thunderstorms, severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulonimbus
Cumulonimbus () is a dense, towering, vertical cloud, typically forming from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere that builds upward carried by powerful buoyant air currents. Above the lower portions of the cumulonimbus the water vapor becomes ice crystals, such as snow and graupel, the interaction of which can lead to hail and to lightning formation, respectively. When causing thunderstorms, these clouds may be called thunderheads. Cumulonimbus can form alone, in clusters, or along squall lines. These clouds are capable of producing lightning and other dangerous severe weather, such as tornadoes, hazardous winds, and large hailstones. Cumulonimbus progress from overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds and may further develop as part of a supercell. Cumulonimbus is abbreviated as Cb. Description Towering cumulonimbus clouds are typically accompanied by smaller cumulus clouds. The cumulonimbus base may extend several kilometres (miles) across, or be as small as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulus Congestus
Cumulus congestus or towering cumulus clouds are a species of cumulus that can be based in the low- to middle-height ranges. They achieve considerable vertical development in areas of deep, moist convection. They are an intermediate stage between cumulus mediocris and cumulonimbus, sometimes producing rainshowers, snow, or ice pellets. Precipitation that evaporates before reaching the surface is virga. Description Cumulus congestus clouds are characteristic of unstable regions of atmosphere that are undergoing convection. They are often characterized by sharp outlines and great vertical development. Since strong updrafts produce (and primarily compose) them, the clouds are typically taller than they are wide; cloud tops can reach , or higher in the tropics. Cumulus congestus clouds are formed by the development of cumulus mediocris generally, though they can also be formed from altocumulus castellanus or stratocumulus castellanus, which are forms of cumulus castellanus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
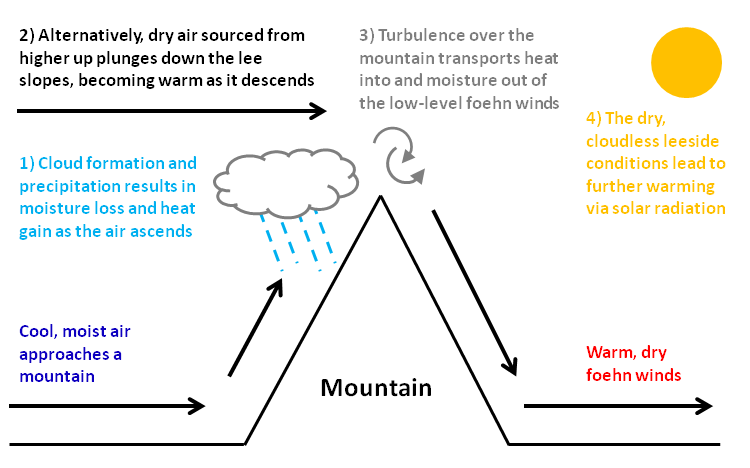
Foehn Wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and in Serbo-Croatian and Slovene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Inversion
In meteorology, an inversion (or temperature inversion) is a phenomenon in which a layer of warmer air overlies cooler air. Normally, air temperature gradually decreases as altitude increases, but this relationship is reversed in an inversion. An inversion traps air pollution, such as smog, near the ground. An inversion can also suppress convection by acting as a "cap". If this cap is broken for any of several reasons, convection of any humidity can then erupt into violent thunderstorms. Temperature inversion can cause freezing rain in cold climates. Normal atmospheric conditions Usually, within the lower atmosphere (the troposphere) the air near the surface of the Earth is warmer than the air above it, largely because the atmosphere is heated from below as solar radiation warms the Earth's surface, which in turn then warms the layer of the atmosphere directly above it, e.g., by thermals ( convective heat transfer). Air temperature also decreases with an increase in al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (; also written windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimbostratus Cloud
A nimbostratus cloud is a multilevel, amorphous, nearly uniform, and often dark-grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow, or sleet, but no lightning or thunder. in the Oxford Dictionaries Online. Although it is usually a low-based stratiform cloud, it actually forms most commonly in the middle level of the troposphere and then spreads vertically into the low and high levels. Nimbostratus usually produces precipitation over a wide area. The prefix '' nimbo-'' comes from the Latin word ', which means "rain bearing cloud" Downward-growing nimbostratus can have the same vertical extent as most large upward-growing [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altostratus Cloud
Altostratus is a middle-altitude cloud genus made up of water droplets, ice crystals, or a mixture of the two. Altostratus clouds are formed when large masses of warm, moist air rise, causing water vapor to condense. Altostratus clouds are usually gray or blueish featureless sheets, although some variants have wavy or banded bases. The sun can be seen through thinner altostratus clouds, but thicker layers can be quite Opacity (optics), opaque. Altostratus clouds usually predict the arrival of warm fronts. Once altostratus clouds associated with a warm front arrive, continuous rain or snow will usually follow in the next 12 to 24 hours. Although altostratus clouds predict the arrival of warmer, wetter weather, they themselves do not produce significant precipitation. Thunderstorms can be embedded in altostratus clouds, however, bringing showers. Because altostratus clouds can contain ice crystals, they can produce some optical phenomena like iridescence and Corona (optical phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratus Cloud
Stratus clouds are low-level clouds characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective or cumuliform clouds formed by rising thermals. The term ''stratus'' describes flat, hazy, featureless clouds at low altitudes varying in color from dark gray to nearly white. The word ''stratus'' comes from the Latin prefix ''Strato-'', meaning "layer" or "sheet". Stratus clouds may produce a light drizzle or a small amount of snow. These clouds are essentially above-ground fog formed either through the lifting of morning fog or through cold air moving at low altitudes. Some call these clouds "high fog" for their fog-like form. Formation Stratus clouds form when weak vertical currents lift a layer of air off the ground and it depressurizes, following the lapse rate. This causes the relative humidity to increase due to the adiabatic cooling. This occurs in environments where atmospheric ''stability'' is abundant. Description Stratus clouds look like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
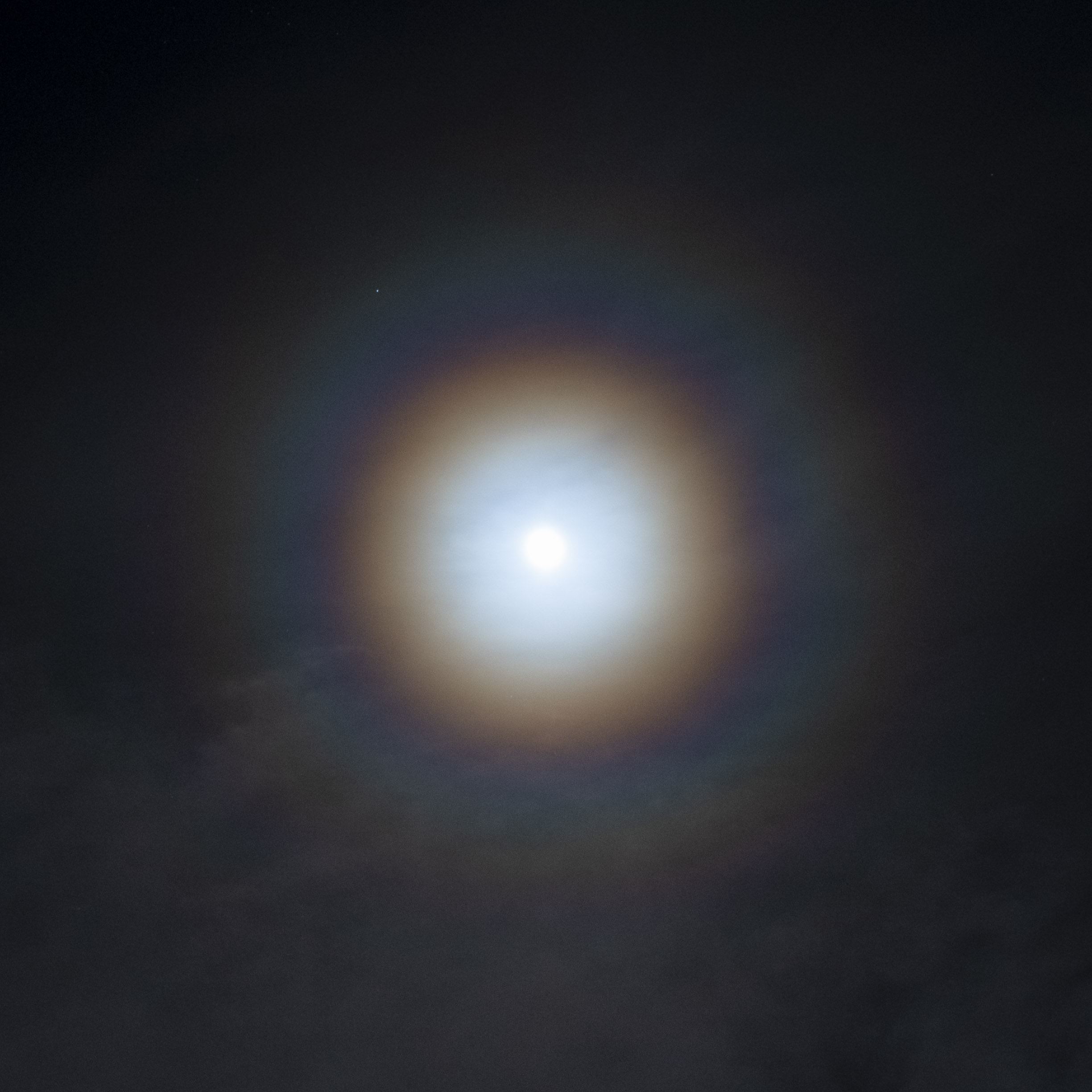
Corona (optical Phenomenon)
In meteorology, a corona (plural ''coronae'') is an optical phenomenon produced by the diffraction of sunlight or moonlight (or, occasionally, bright starlight or planetlight) by individual small water droplets and sometimes tiny ice crystals of a cloud or on a foggy glass surface. In its full form, a corona consists of several concentric, pastel-colored rings around the celestial object and a central bright area called an ''aureole''. The aureole is often (especially in case of the Moon) the only visible part of the corona and has the appearance of a bluish-white disk which fades to reddish-brown towards the edge. The angular diameter of a corona depends on the sizes of the water droplets involved; smaller droplets produce larger coronae. For the same reason, the corona is the most pronounced when the size of the droplets is most uniform. Coronae differ from halos in that the latter are formed by refraction (rather than diffraction) from comparatively large rather than sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crepuscular Rays
Crepuscular rays, sometimes colloquially referred to as god rays, are sunbeams that originate when the Sun appears to be just above or below a layer of clouds, during the twilight period. Crepuscular rays are noticeable when the contrast between light and dark is most obvious. Crepuscular comes from the Latin word , meaning "twilight". Crepuscular rays usually appear orange because the path through the atmosphere at dawn and dusk passes through up to 40 times as much air as rays from a high Sun at noon. Particles in the air scatter short-wavelength light (blue and green) through Rayleigh scattering much more strongly than longer-wavelength yellow and red light. Loosely, the term ''crepuscular rays'' is sometimes extended to the general phenomenon of rays of sunlight Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |