|
Strato Of Lampsacus
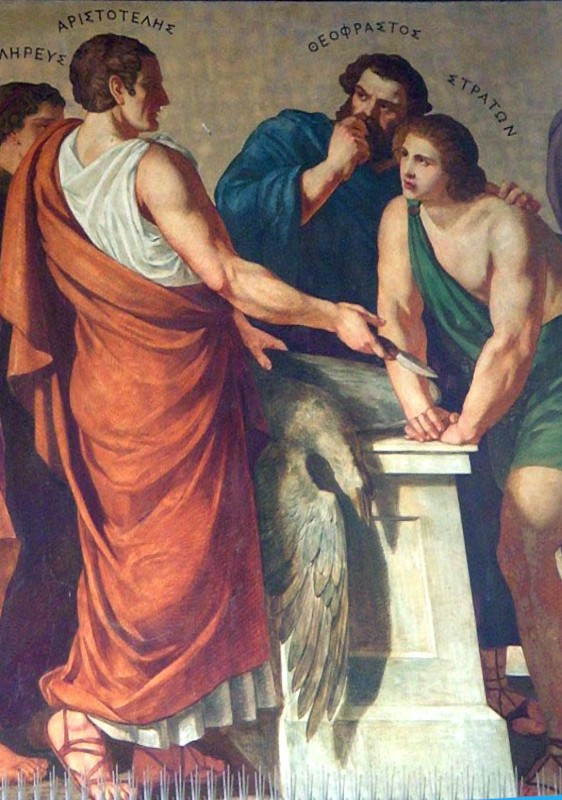
Strato of Lampsacus (; , – ) was a Peripatetic philosopher, and the third director ( scholarch) of the Lyceum after the death of Theophrastus. He devoted himself especially to the study of natural science, and increased the naturalistic elements in Aristotle's thought to such an extent, that he denied the need for an active god to construct the universe, preferring to place the government of the universe in the unconscious force of nature alone. Life Strato, son of Arcesilaus or Arcesius, was born in Lampsacus between 340 and 330 BCE. He might have known Epicurus during his period of teaching in Lampsacus between 310 and 306 BCE. He attended Aristotle's school in Athens, after which he went to Egypt as tutor to Ptolemy II, where he also taught Aristarchus of Samos. He returned to Athens after the death of Theophrastus (c. 287 BCE), succeeding him as head of the Lyceum. He died sometime between 270 and 268 BCE. Strato devoted himself especially to the study of natural science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Philosophy
Western philosophy refers to the Philosophy, philosophical thought, traditions and works of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratics. The word ''philosophy'' itself originated from the Ancient Greek (φιλοσοφία), literally, "the love of wisdom" , "to love" and σοφία ''Sophia (wisdom), sophía'', "wisdom". History Ancient The scope of ancient Western philosophy included the problems of philosophy as they are understood today; but it also included many other disciplines, such as pure mathematics and natural sciences such as physics, astronomy, and biology (Aristotle, for example, wrote on all of these topics). Pre-Socratics The pre-Socratic philosophers were interested in cosmology (the nature and origin of the universe), while rejecting unargued fables in place for argued theory, i.e., dogma superseded reason, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyceum (classical)
The Lyceum () was a temple in Athens dedicated to Apollo Lyceus ("Apollo the wolf-god"). It was best known for the Peripatetic school of philosophy founded there by Aristotle in 334 BC. Aristotle fled Athens in 323 BC, and the university continued to function after his lifetime under a series of leaders until the Roman general Sulla destroyed it during his assault on Athens in 86 BC. The remains of the Lyceum were discovered in modern Athens in 1996 in a park behind the Hellenic Parliament. The Lyceum The Lyceum had been used for philosophical debate long before Aristotle. Philosophers such as Prodicus of Ceos, Protagoras, and numerous rhapsodes had spoken there. The most famous philosophers to teach there were Isocrates, Plato (of The Academy), and the best-known Athenian teacher, Socrates.Stenudd, Stefan"Aristotle: His Life, Time, and Work" Stennud. N.p., n.d. Web. 30 October 2009. In addition to military training and educational pursuits, the Lyceum also housed At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle Theophrastus Strato Lebiedzki Rahl
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical period. His father, Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request of Philip II of Macedon, tutored his son Alexander the Great beginning in 343 BC. He established a library in the Lyceum, which helped him to produce many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Philosophy
Ethics is the philosophical study of moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to duties, like telling the truth and keeping promises. Virtue et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diogenes Laërtius
Diogenes Laërtius ( ; , ; ) was a biographer of the Greek philosophers. Little is definitively known about his life, but his surviving book ''Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers'' is a principal source for the history of ancient Greek philosophy. His reputation is controversial among scholars because he often repeats information from his sources without critically evaluating it. In many cases, he focuses on insignificant details of his subjects' lives while ignoring important details of their philosophical teachings and he sometimes fails to distinguish between earlier and later teachings of specific philosophical schools. However, unlike many other ancient secondary sources, Diogenes Laërtius tends to report philosophical teachings without trying to reinterpret or expand on them, and so his accounts are often closer to the primary sources. Due to the loss of so many of the primary sources on which Diogenes relied, his work has become the foremost surviving source on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists and the innovator of what became known as "Ciceronian rhetoric". Cicero was educated in Rome and in Greece. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. He greatly influenced both ancient and modern reception of the Latin language. A substantial part of his work has survived, and he was admired by both ancient and modern authors alike. Cicero adapted the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy in Latin and coined a large portion of Latin philosophical vocabulary via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He also supported the theory of Anaxagoras according to which the Sun was just another star. He likely moved to Alexandria, and he was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who later became the third head of the Peripatetic school in Greece. According to Ptolemy, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BC. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus estimated the sizes of the Sun and Moon as compared to Earth's size. He also estimated the distances from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. His estimate that the Sun was 7 times larger than Earth (while inaccurate by an order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the Great who founded the Ptolemaic Kingdom after the death of Alexander, and Queen Berenice I, originally from Macedon. During Ptolemy II's reign, the material and literary splendour of the Alexandrian court was at its height. He promoted the Musaeum, Museum and Library of Alexandria. In addition to Egypt, Ptolemy's empire encompassed much of the Aegean Islands, Aegean and Levant. He pursued an aggressive and expansionist foreign policy with mixed success. From 275 to 271 BC, he led the Ptolemaic Kingdom against the rival Seleucid Empire in the First Syrian War and extended Ptolemaic power into Cilicia and Caria, but lost control of Cyrenaica after the defection of his half-brother Magas of Cyrene, Magas. In the Chremonidean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northern coast of Egypt, the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to Egypt–Israel barrier, the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to Egypt–Sudan border, the south, and Libya to Egypt–Libya border, the west; the Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital, list of cities and towns in Egypt, largest city, and leading cultural center, while Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important hub of industry and tourism. With over 109 million inhabitants, Egypt is the List of African countries by population, third-most populous country in Africa and List of countries and dependencies by population, 15th-most populated in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicurus
Epicurus (, ; ; 341–270 BC) was an Greek philosophy, ancient Greek philosopher who founded Epicureanism, a highly influential school of philosophy that asserted that philosophy's purpose is to attain as well as to help others attain tranquil lives, characterized by freedom from fear and the absence of pain. Epicurus advocated that people were best able to pursue philosophy by living a self-sufficient life surrounded by friends; he and his followers were known for eating simple meals and discussing a wide range of philosophical subjects at "the Garden", the school he established in Athens. Epicurus taught that although the gods exist, they have no involvement in human affairs. Like the earlier philosopher Democritus, Epicurus claimed that all occurrences in the natural world are ultimately the result of tiny, invisible particles known as ''Atomism, atoms'' moving and interacting in empty space, though Epicurus also deviated from Democritus by proposing the idea of Clinamen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part of nature, human activity or humans as a whole are often described as at times at odds, or outright Anthropocentrism, separate and even superior to nature. During the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial Revolution, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions (Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Rousseau, American transcendentalism) or a mere decorum for divine providence or human history (Hegel, Marx). However, a vitalist vision of nature, closer to the pre-Socratic one, got reborn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |