|
Stop Words
Stop words are the words in a stop list (or ''stoplist'' or ''negative dictionary'') which are filtered out ("stopped") before or after processing of natural language data (i.e. text) because they are deemed to have little semantic value or are otherwise insignificant for the task at hand. There is no single universal list of stop words used by all natural language processing (NLP) tools, nor any agreed upon rules for identifying stop words, and indeed not all tools even use such a list. Therefore, any group of words can be chosen as the stop words for a given purpose. The "general trend in nformation retrievalsystems over time has been from standard use of quite large stop lists (200–300 terms) to very small stop lists (7–12 terms) to no stop list whatsoever". History of stop words A predecessor concept was used in creating some concordances. For example, the first Hebrew concordance, Isaac Nathan ben Kalonymus's , contained a one-page list of unindexed words, with nonsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Major tasks in natural language processing are speech recognition, text classification, natural-language understanding, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, though at the time that was not articulated as a problem separate from artificial intelligence. The proposed test includes a task that involves the automated interpretation and generation of natural language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Take That
Take That are an English pop group formed in Manchester in 1990. The group currently consists of Gary Barlow, Howard Donald and Mark Owen. The original line-up also featured Jason Orange and Robbie Williams. Barlow is the group's lead singer and primary songwriter, with Owen and Williams initially providing backing vocals, and Donald and Orange serving primarily as dancers. The group have had 28 top-40 singles, 20 top-10 and 17 top-5 singles on the UK Singles Chart, 12 of which have reached number one. They have also had nine number-one albums on the UK Albums Chart. Internationally, the band have had 56 number-one singles and 42 number-one albums. They have received eight Brit Awards, including Best British Group and Best British Live Act. In 2012 they received an Ivor Novello Award for Outstanding Contribution to British Music. According to the British Phonographic Industry (BPI), Take That has been certified for sales of 14.4 million albums and 14 million singles in the UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
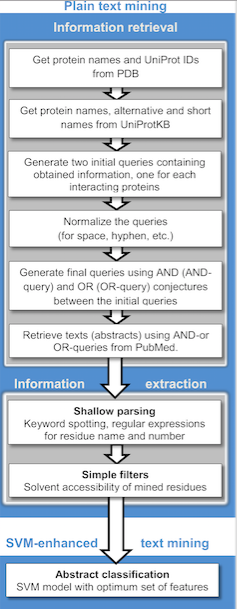
Text Mining
Text mining, text data mining (TDM) or text analytics is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extracting information from different written resources." Written resources may include websites, books, emails, reviews, and articles. High-quality information is typically obtained by devising patterns and trends by means such as statistical pattern learning. According to Hotho et al. (2005), there are three perspectives of text mining: information extraction, data mining, and knowledge discovery in databases (KDD). Text mining usually involves the process of structuring the input text (usually parsing, along with the addition of some derived linguistic features and the removal of others, and subsequent insertion into a database), deriving patterns within the structured data, and finally evaluation and interpretation of the output. 'High quality' in text mining usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stemming
In linguistic morphology and information retrieval, stemming is the process of reducing inflected (or sometimes derived) words to their word stem, base or root form—generally a written word form. The stem need not be identical to the morphological root of the word; it is usually sufficient that related words map to the same stem, even if this stem is not in itself a valid root. Algorithms for stemming have been studied in computer science since the 1960s. Many search engines treat words with the same stem as synonyms as a kind of query expansion, a process called conflation. A computer program or subroutine that stems word may be called a ''stemming program'', ''stemming algorithm'', or ''stemmer''. Examples A stemmer for English operating on the stem ''cat'' should identify such strings as ''cats'', ''catlike'', and ''catty''. A stemming algorithm might also reduce the words ''fishing'', ''fished'', and ''fisher'' to the stem ''fish''. The stem need not be a word, for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Query Expansion
Query expansion (QE) is the process of reformulating a given query to improve retrieval performance in information retrieval operations, particularly in the context of query understanding. In the context of search engines, query expansion involves evaluating a user's input (what words were typed into the search query area, and sometimes other types of data) and expanding the search query to match additional documents. Query expansion involves techniques such as: * Finding synonyms of words, and searching for the synonyms as well * Finding semantically related words (e.g. antonyms, meronyms, hyponyms, hypernyms) * Finding all the various morphological forms of words by stemming each word in the search query * Fixing spelling errors and automatically searching for the corrected form or suggesting it in the results * Re-weighting the terms in the original query Query expansion is a methodology studied in the field of computer science, particularly within the realm of natural lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index (search Engine)
Search engine indexing is the collecting, parsing, and storing of data to facilitate fast and accurate information retrieval. Index design incorporates interdisciplinary concepts from linguistics, cognitive psychology, mathematics, informatics, and computer science. An alternate name for the process, in the context of search engines designed to find web pages on the Internet, is '' web indexing''. Popular search engines focus on the full-text indexing of online, natural language documents. Media types such as pictures, video, audio, and graphics are also searchable. Meta search engines reuse the indices of other services and do not store a local index whereas cache-based search engines permanently store the index along with the corpus. Unlike full-text indices, partial-text services restrict the depth indexed to reduce index size. Larger services typically perform indexing at a predetermined time interval due to the required time and processing costs, while agent-based search ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filler (linguistics)
In linguistics, a filler, filled pause, hesitation marker or planner (sometimes called crutches) is a sound or word that participants in a conversation use to signal that they are pausing to think but are not finished speaking.Juan, Stephen (2010).Why do we say 'um', 'er', or 'ah' when we hesitate in speaking? These are not to be confused with placeholder names, such as ''thingamajig''. Fillers fall into the category of formulaic language, and different languages have different characteristic filler sounds. The term filler also has a separate use in the syntactic description of wh-movement constructions (see below). Usage Every conversation involves turn-taking, which means that whenever someone wants to speak and hears a pause, they do so. Pauses are commonly used to indicate that someone's turn has ended, which can create confusion when someone has not finished a thought but has paused to form a thought; in order to prevent this confusion, they will use a filler word such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
To Be Or Not To Be
"To be, or not to be" is a speech given by Prince Hamlet in the so-called "nunnery scene" of William Shakespeare's play ''Hamlet'' (Act 3, Scene 1). The speech is named for the opening phrase, itself among the most widely known and quoted lines in modern English literature, and has been referenced in many works of theatre, literature and music. In the speech, Hamlet contemplates death and suicide, weighing the pain and unfairness of life against the alternative, which might be worse. It is not clear that Hamlet is thinking of his own situation since the speech is entirely in an abstract, somewhat academic register that accords with Hamlet's status as a (recent) student at Wittenberg University. Furthermore, Hamlet is not alone as he speaks because Ophelia is on stage waiting for him to see her, and Claudius and Polonius have concealed themselves to hear him. Even so, Hamlet seems to consider himself alone and there is no definite indication that the others hear him before he a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial intelligence (AI). It has been referred to as "the most powerful company in the world" by the BBC and is one of the world's List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands. Google's parent company, Alphabet Inc., is one of the five Big Tech companies alongside Amazon (company), Amazon, Apple Inc., Apple, Meta Platforms, Meta, and Microsoft. Google was founded on September 4, 1998, by American computer scientists Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Together, they own about 14% of its publicly listed shares and control 56% of its stockholder voting power through super-voting stock. The company went public company, public via an initial public offering (IPO) in 2004. In 2015, Google was reorganized as a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |