|
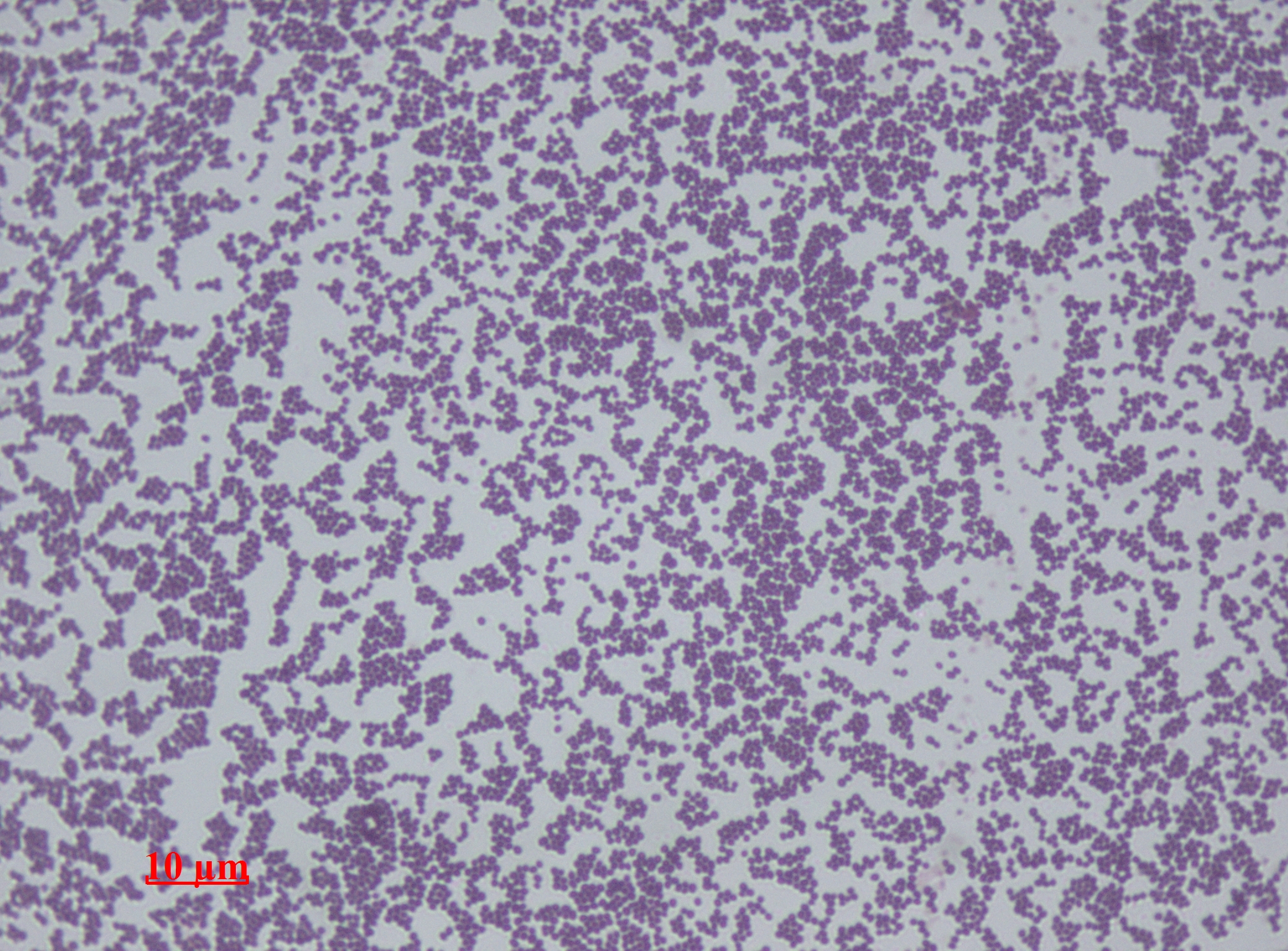
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. It is part of the human flora, normal human microbiota, typically the skin flora, skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually Pathogenic bacteria, pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally Hospital-acquired infection, hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environments. S.I. Paul et al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Julius Rosenbach
Friedrich Julius Rosenbach, also known as Anton Julius Friedrich Rosenbach, (16 December 1842 – 6 December 1923) was a German physician and microbiologist. He is credited for differentiating ''Staphylococcus aureus'' and ''Staphylococcus albus'', which is now called ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'', in 1884. He also described and named ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. Rosenbach's disease is also named in his honor. Biography Rosenbach was born in Emmerthal, Grohnde an der Weser on 16 December 1842. He studied in Heidelberg, Göttingen, Vienna, Paris, and Berlin. He obtained his doctorate in 1867. He married Franziska Merkel on 12 May 1877. Rosenbach died on 6 December 1923 in Göttingen. Literature *''Ueber einige pathologische Veränderungen nach subcutaner Injection von Quecksilber bei Thieren (Kaninchen).'' Doctoral dissertation, 1867. Also in [Henle and Pfeuffer's] ''Zeitschrift für rationelle Medicin'', Leipzig and Heidelberg. *''Untersuchungen über den Einfluss von Carbols� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Epidermids
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of ''Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from ), and suffixed by the (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staphylococcus bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at risk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
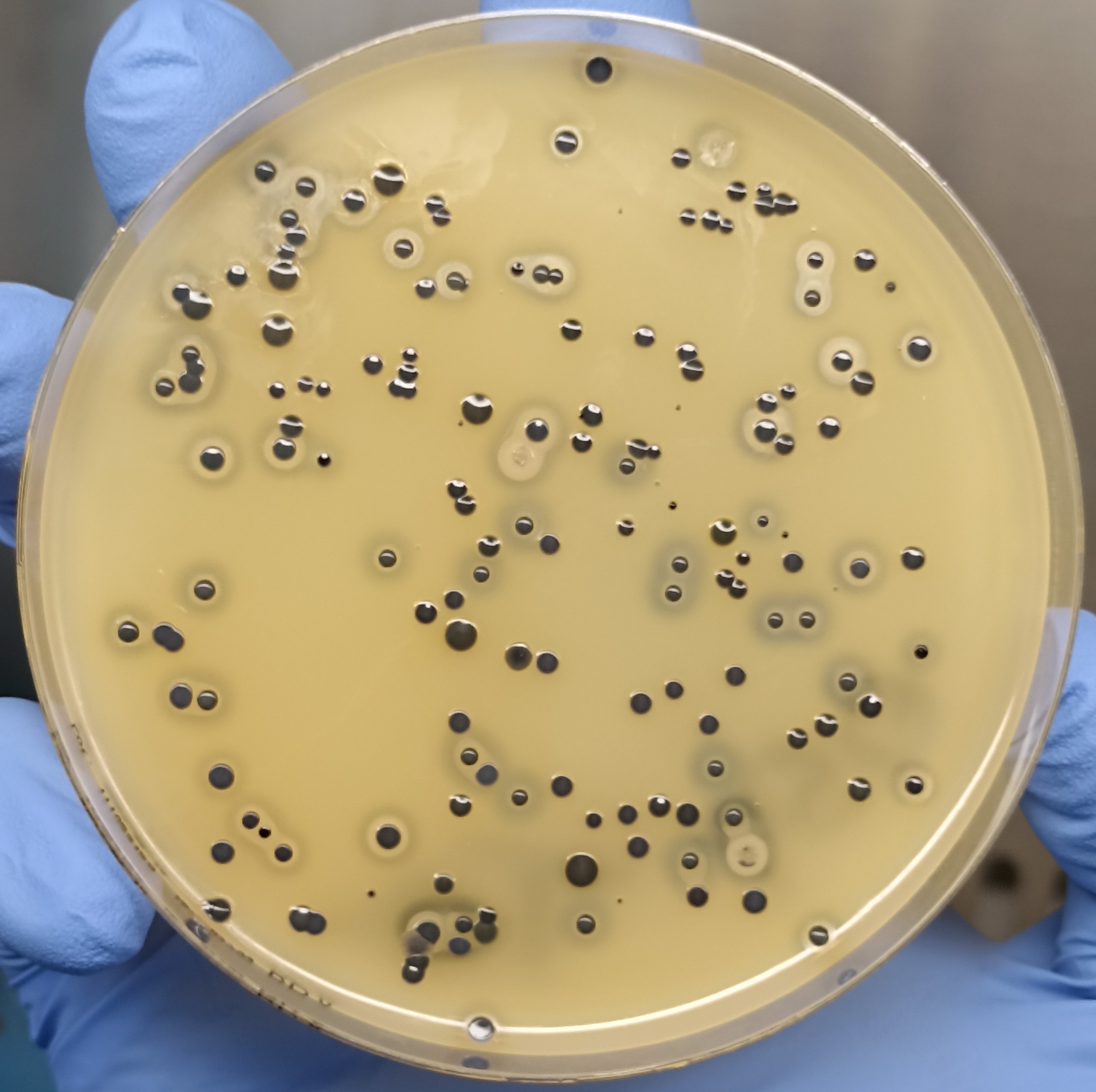
Baird-Parker Agar
Baird-Parker agar is a type of agar used for the selective isolation of gram-positive ''Staphylococci'' species. It contains lithium chloride and tellurite to inhibit the growth of alternative microbial flora, while the included pyruvate and glycine promote the growth of ''Staphylococci''. ''Staphylococcus'' colonies show up black in colour with clear zones produced around them. History Baird-Parker Agar From Liofilchem first published an academic article about this agar medium for the purposes of improved diagnostics and isolating coagulase-positive ''Staphylococci'' in 1962. He developed this agar medium from the tellurite-glycine formulation of Zebovitz ''et al'' and improved its reliability in isolating coagulase-positive staphylococci from foods. Baird-Parker added egg yolk emulsion as a diagnostic agent and sodium pyruvate to protect damaged cells and aid their recovery. It is now widely recommended by national and international bodies for the isolation of coagulase-pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferrin
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Iron(III), Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is encoded by the ''TF'' gene and produced as a 76 Dalton (unit), kDa glycoprotein. Transferrin glycoproteins bind iron tightly, but reversibly. Although iron bound to transferrin is less than 0.1% (4 mg) of total body iron, it forms the most vital iron pool with the highest rate of turnover (25 mg/24 h). Transferrin has a molecular weight of around 80 atomic mass unit, kDa and contains two specific high-affinity Fe(III) binding sites. The affinity of transferrin for Fe(III) is extremely high (association constant is 1020 M−1 at pH 7.4) but decreases progressively with decreasing pH below neutrality. Transferrins are not limited to only binding to iron but also to different metal ions. These glycoproteins are located in various b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Saprophyticus
''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' is a Gram-positive coccus belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. ''S. saprophyticus'' is a common cause of community-acquired urinary tract infections. History ''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' was not recognized as a cause of urinary tract infections until the early 1970s, more than 10 years after its original demonstration in urine specimens. Prior to this, the presence of coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) in urine specimens was dismissed as contamination. Epidemiology and pathogenesis In humans, ''S. saprophyticus'' is found in the normal flora of the female genital tract and perineum. It has been isolated from other sources, too, including meat and cheese products, vegetables, the environment, and human and animal gastrointestinal tracts. ''S. saprophyticus'' causes 10–20% of urinary tract infections (UTIs). In females 17–27 years old, it is the second-most common cause of community-acquired UTIs, after ''Escherichia coli''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novobiocin
Novobiocin, also known as albamycin, is an aminocoumarin antibiotic that is produced by the actinomycete ''Streptomyces niveus'', which has recently been identified as a subjective synonym for ''S. spheroides'' a member of the class Actinomycetia. Other aminocoumarin antibiotics include clorobiocin and coumermycin A1. Novobiocin was first reported in the mid-1950s (then called streptonivicin). Clinical use It is active against ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' and may be used to differentiate it from the other coagulase-negative ''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'', which is resistant to novobiocin, in culture. Novobiocin was licensed for clinical use under the tradename Albamycin (Upjohn) in the 1960s. Its efficacy#Pharmacology, efficacy has been demonstrated in Clinical trial#Pre clinical studies, preclinical and Clinical trial, clinical trials. The oral form of the drug has since been withdrawn from the market due to lack of efficacy. A combination product of novobiocin and tetrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatinase
Gelatinases are enzymes capable of degrading gelatin through hydrolysis, playing a major role in degradation of extracellular matrix and tissue remodeling. Gelatinases are a type of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), a family of enzymes that depend on zinc as a cofactor and can break down parts of the extracellular matrix. MMPs have multiple subgroups, including gelatinase A () and gelatinase B (). Gelatinases are assigned a variety of Enzyme Commission numbers: gelatinase A uses 3.4.24.24, and gelatinase B uses 3.4.24.35, in which the first three numbers are same. The first digit, 3, is the class. Class 3 enzymes are hydrolases, enzymes that catalyze hydrolysis reactions, that is, they cleave bonds in presence of water. The next digit represents sub-class 4, or proteases, which are enzymes who hydrolyze peptide bonds in proteins. The next number is the sub-subclass of 24, which consists of metalloendopeptidases which contain metal ions in their active sites, in this case zinc, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urease
Ureases (), functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous Bacteria, Archaea, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates. Ureases are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high molecular weight. Ureases are distinct from Urecases are important in degrading avian faecal matter, which is rich in uric acid, the breakdown product of which is urea, which is then degraded by urease as described here. These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia: : (NH2)2CO + H2O CO2 + 2NH3 The hydrolysis of urea occurs in two stages. In the first stage, ammonia and carbamic acid are produced. The carbamate spontaneously and rapidly hydrolyzes to ammonia and carbonic acid. Urease activity increases the pH of its environment as ammonia is produced, which is basic. History Urease activity was first identified in 1876 by Frédéric Alphonse Musculus as a soluble ferment. In 1926, James B. Sumner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate Reductase Test
The nitrate reductase test is a test to differentiate between bacteria based on their ability or inability to reduce nitrate (NO3−) to nitrite (NO2−) using anaerobic respiration. Procedure Various assays for detecting nitrate reduction have been described.V.B.D. Skerman, A guide to the identification of the genera of bacteria, The Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, MD, p.218 - 220 (1967). One method is performed as follows: #Inoculation, Inoculate nitrate broth with an isolate and incubate for 48 hours. #Add two nitrate tablets to the sample. If the bacterium produces nitrate reductase, the broth will turn a deep red within 5 minutes at this step. #If no color change is observed, then the result is inconclusive. Add a small amount of zinc to the broth. If the solution remains colorless, then both nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase are present. If the solution turns red, nitrate reductase is not present. References Bacteriology Tests {{bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation (biochemistry)
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduced by donating their electrons to other organic molecules (cofactors, coenzymes, etc.). Fermentation is important in several areas of human society. Humans have used fermentation in the production and preservation of food for 13,000 years. It has been associated with health benefits, unique flavor profiles, and making products have better texture. Humans and their livestock also benefit from fermentation from the microbes in the gut that release end products that are subsequently used by the host for energy. Perhaps the most commonly known use for fermentation is at an industrial level to produce commodity chemicals, such as ethanol and lactate. Ethanol is used in a variety of alcoholic beverages (beers, wine, and spirits) while lactate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to transfer chemical energy from nutrients to ATP, with the flow of electrons to an electron acceptor, and then release waste products. If the electron acceptor is oxygen, the process is more specifically known as aerobic cellular respiration. If the electron acceptor is a molecule other than oxygen, this is anaerobic cellular respiration. Fermentation, which is also an anaerobic process, is not respiration, as no external electron acceptor is involved. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, producing large amounts of energy (ATP). Respiration i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facultative Anaerobe
A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent. Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are ''Staphylococcus'' spp., ''Escherichia coli'', ''Salmonella'', ''Listeria'' spp., '' Shewanella oneidensis'' and ''Yersinia pestis''. Certain eukaryotes are also facultative anaerobes, including pupfish, fungi such as ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and many aquatic invertebrates such as nereid polychaetes. It has been observed that in mutants of '' Salmonella typhimurium'' that underwent mutations to be either obligate aerobes or anaerobes, there were varying levels of chromatin-remodeling proteins. The obligate aerobes were later found to have a defective DNA gyrase subunit A gene ('' gyrA''), while obligate anaerobes were defective in topoisomerase I (''topI''). This indicates that topoisomerase I and its associated relaxation of chromosomal DNA is requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |