|
Standing On The Shoulders Of Giants
The phrase "standing on the shoulders of giants" is a metaphor which means "using the understanding gained by major thinkers who have gone before in order to make intellectual progress". It is a metaphor of Dwarf (mythology), dwarfs standing on the shoulders of giants () and expresses the meaning of "discovering truth by building on previous discoveries". This concept has been dated to the 12th century and, according to John of Salisbury, is attributed to Bernard of Chartres. Its most familiar and popular expression occurs in a 1675 letter by Isaac Newton: "if I have seen further [than others], it is by standing on the shoulders of giants." Early references Middle Ages The earliest documented attestation of this aphorism appears in 1123 in William of Conches's Glosses on Priscian's ''Institutiones grammaticae''. Where Priscian says ''quanto juniores, tanto perspicaciores'' (young men simply can see more sharply), William writes: The ancients had only the books which they the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to create a likeness or an Analogy, analogy. Analysts group metaphors with other types of figurative language, such as antithesis, hyperbole, metonymy, and simile. According to Grammarly, "Figurative language examples include similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, allusions, and idioms." One of the most commonly cited examples of a metaphor in English literature comes from the "All the world's a stage" monologue from ''As You Like It'': All the world's a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances And one man in his time plays many parts, His Acts being seven ages. At first, the infant... :—William Shakespeare, ''As You Like It'', 2/7 This quotation expresses a metaphor because the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
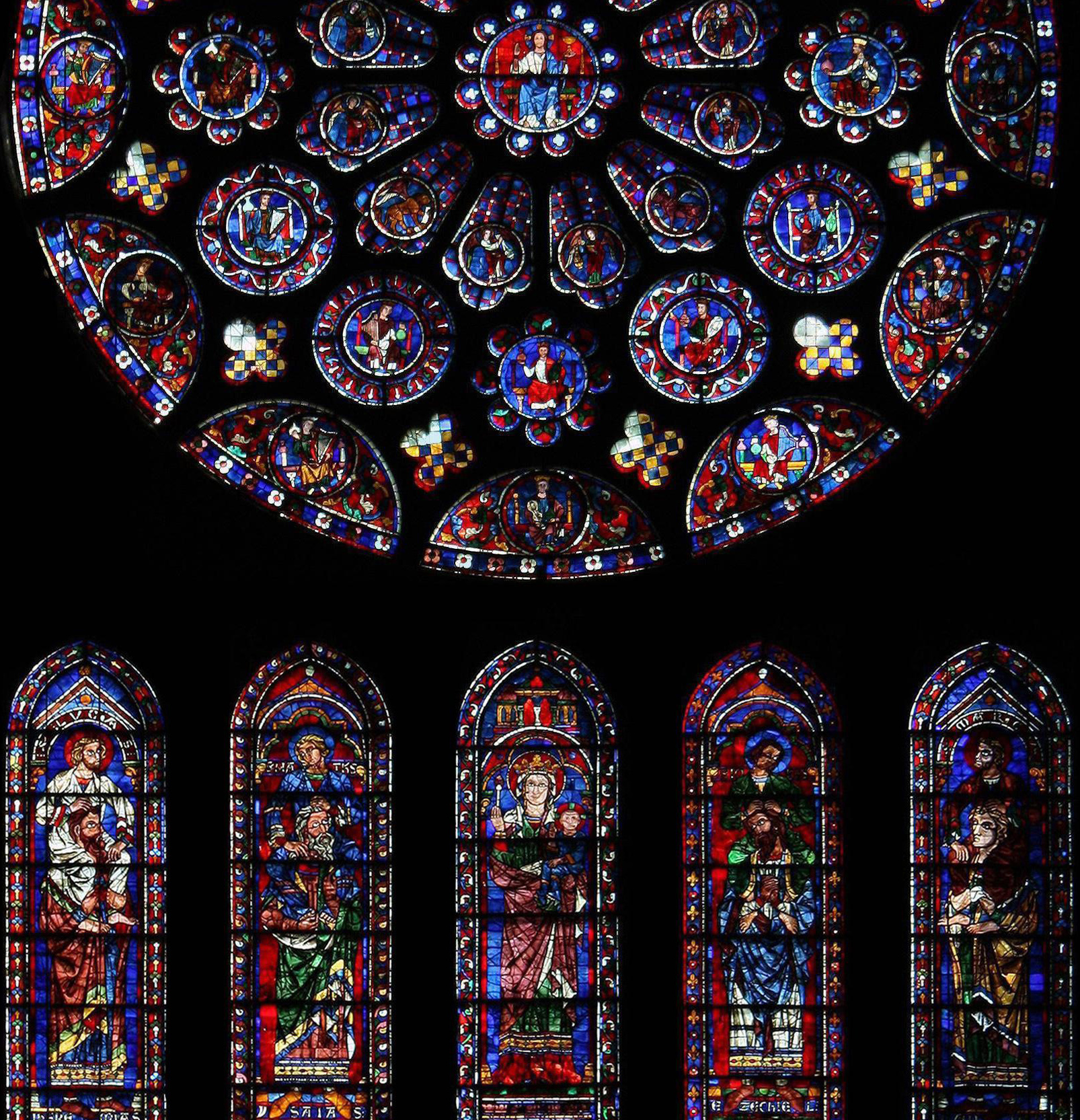
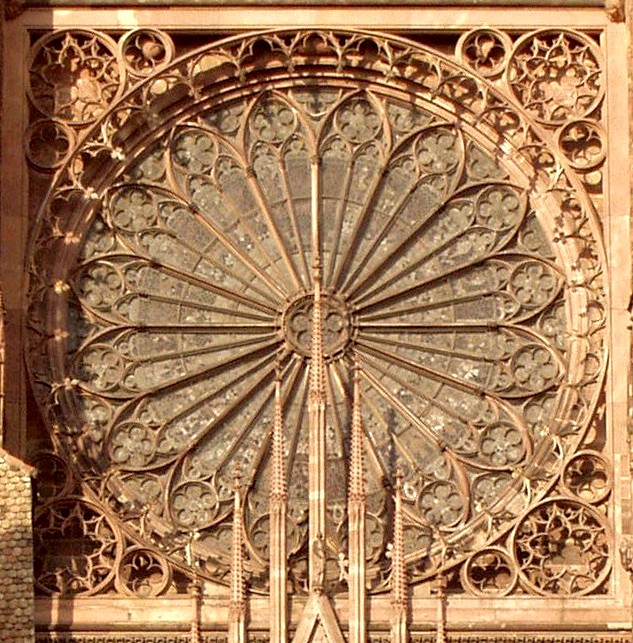
Rose Window
Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term ''rose window'' was not used before the 17th century and comes from the English flower name rose. The name "wheel window" is often applied to a window divided by simple spokes radiating from a central boss or opening, while the term "rose window" is reserved for those windows, sometimes of a highly complex design, which can be seen to bear similarity to a multi-petalled rose. Rose windows are also called "Catherine windows" after Saint Catherine of Alexandria, who was sentenced to be executed on a spiked breaking wheel. A circular window without tracery such as are found in many Italian churches, is referred to as an ocular window or Oculus (architecture), oculus. Rose windows are particularly characteristic of Gothic architecture and may be seen in all th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion Aveugle Cherchant Le Soleil
Orion may refer to: Common meanings * Orion (constellation), named after the mythical hunter * Orion (mythology), a hunter in Greek mythology Arts and media Fictional entities Characters and species * Orion (character), a DC Comics character * Orion (''Star Trek''), a sentient alien species * Orion, code name of Stephen J. Bartowski on the television show ''Chuck'' * Orion, in the fighting game '' Brawlhalla'' * Orions, a race in the '' Starfire'' board game and book series * Orion, a character from ''Power Rangers Super Megaforce'' * Captain Orion, in the Japanese series '' X-Bomber'' * Orion Pax, the former name of Optimus Prime. Orion Black, the father of Sirius Black and Regulus Black, in the Harry Potter Series Vessels * ''Orion'', a spaceplane in the film ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' * ''Orion'', a spaceship in '' Raumpatrouille Orion'' (''Space Patrol Orion'' in English), the first German science fiction television series * ''"Orion"''-class spaceship, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Luis Vives
Juan Luis Vives y March (; ; ; ; 6 March 6 May 1540) was a Spaniards, Spanish (Valencian people, Valencian) scholar and Renaissance humanist who spent most of his adult life in the southern Habsburg Netherlands. His beliefs on the soul, insight into early medical practice, and perspective on emotions, memory and learning earned him the title of the "father" of modern psychology. Vives was the first to shed light on some key ideas that established how psychology is perceived today. Early life Luis Vives was born in Valencia (city in Spain), Valencia to a ''converso'' family which had converso, converted from Judaism to Christianity, in the case of his mother's side of the family, several decades before the Alhambra Decree. While still in Spain, he attended the University of Valencia (Estudi General), where he was taught by Jerome Amiguetus and Daniel Siso. Vives later recalled that the school was dominated by scholasticism, with the dialectic and disputation playing a central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
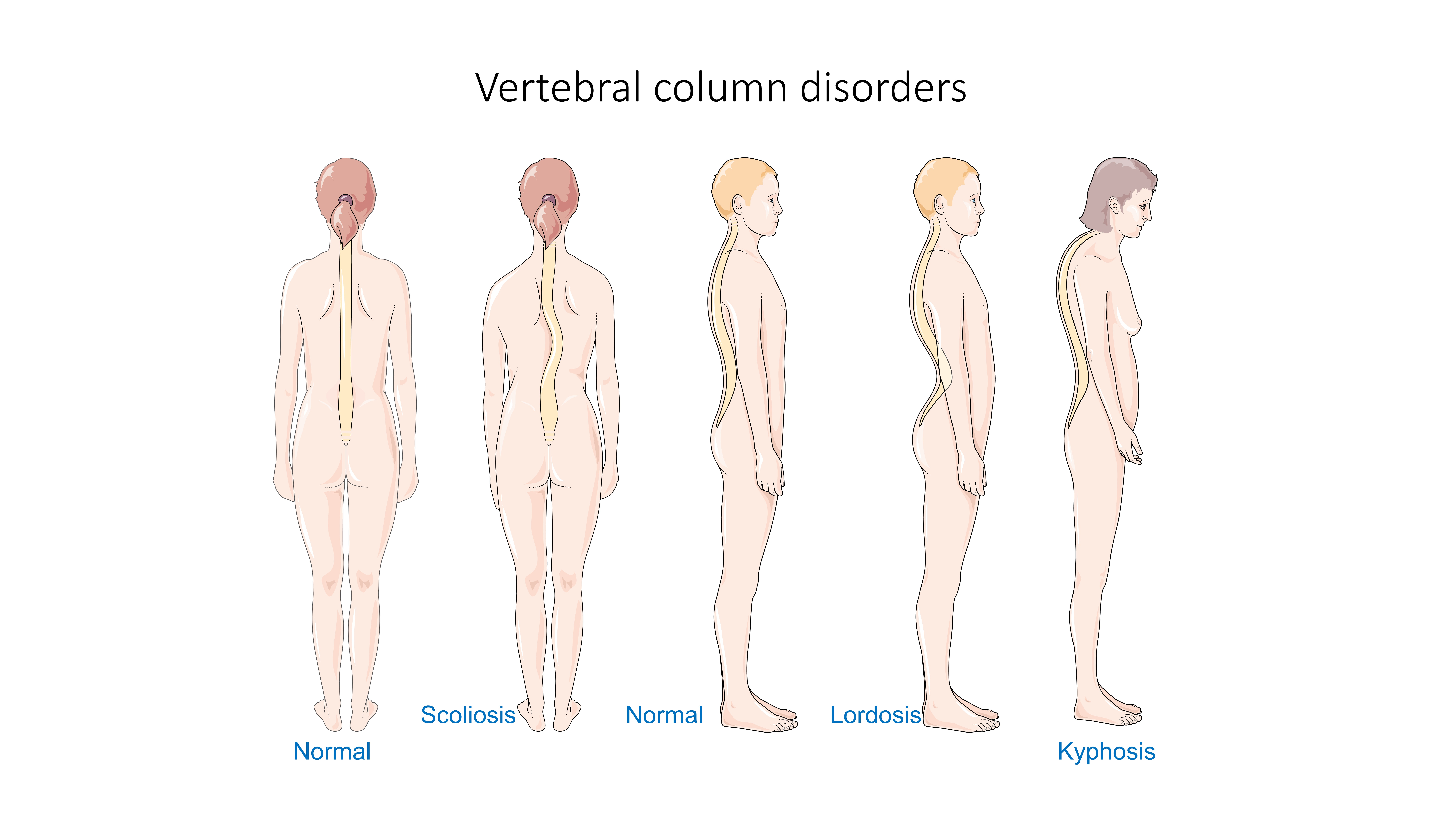
Kyphosis
Kyphosis () is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the Spinal column, spine as it occurs in the Thoracic spine, thoracic and sacrum, sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the Cervical spine, cervical and Lumbar spine, lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constable And Robinson
Constable & Robinson Ltd. is an imprint of Little, Brown which publishes fiction and non-fiction books and ebooks. History Constable & Co. was founded in 1795 by Archibald Constable, and became the publisher of works by Sir Walter Scott. In 1897, Constable released the well-known horror novel, Bram Stoker's ''The Un-Dead'', albeit with a last-minute title change to ''Dracula''. In 1813, the company was the first publishing company to give an author advance against royalties. In 1821, it introduced the standard three-volume novel, and in 1826, with the launch of the book series '' Constable's Miscellany'', it became the first publisher to produce mass-market literary editions. By 1921, Constable & Robinson Ltd. was the first publishing house to advertising books on the London Underground. Ralph Arnold joined the firm in 1936, rising to chairman between 1958 and 1961. In his memoir ''Orange Street and Brickhole Lane'' (1963) he described the firm as having "a strangely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Descartes
René Descartes ( , ; ; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and Modern science, science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of inquiry, and he connected the previously separate fields of geometry and algebra into analytic geometry. Descartes spent much of his working life in the Dutch Republic, initially serving the Dutch States Army, and later becoming a central intellectual of the Dutch Golden Age. Although he served a Dutch Reformed Church, Protestant state and was later counted as a Deism, deist by critics, Descartes was Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic. Many elements of Descartes's philosophy have precedents in late Aristotelianism, the Neostoicism, revived Stoicism of the 16th century, or in earlier philosophers like Augustine of Hippo, Augustine. In his natural philosophy, he differed from the Scholasticism, schools on two major point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living things at microscopic scale in 1665, using a compound microscope that he designed. Hooke was an impoverished scientific inquirer in young adulthood who went on to become one of the most important scientists of his time. After the Great Fire of London in 1666, Hooke (as a surveyor and architect) attained wealth and esteem by performing more than half of the Boundary (real estate), property line surveys and assisting with the city's rapid reconstruction. Often vilified by writers in the centuries after his death, his reputation was restored at the end of the twentieth century and he has been called "England's Leonardo da Vinci, Leonardo [da Vinci]". Hooke was a Fellow of the Royal Society and from 1662, he was its first Curator of Experimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton (par Vertue)
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, achieved the first great unification in physics and established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for formulating infinitesimal calculus, though he developed calculus years before Leibniz. Newton contributed to and refined the scientific method, and his work is considered the most influential in bringing forth modern science. In the , Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. He used his mathematical description of gravity to derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and Book of Numbers, Numbers, and later succeeded Moses as leader of the Israelite tribes in the Book of Joshua of the Hebrew Bible. His name was Hoshea ( ''Hōšēaʿ'', Literal translation, lit. 'Save') the son of Nun (Bible), Nun, of the tribe of Ephraim, but Moses called him "Yehoshua" (translated as "Joshua" in English),''Bible'' the name by which he is commonly known in English. According to the Bible, he was born in Ancient Egypt, Egypt prior to the Exodus. The Hebrew Bible identifies Joshua as one of The Twelve Spies, the twelve spies of Israel sent by Moses to explore the land of Canaan. In and after the death of Moses, he led the Israelite tribes in the conquest of Canaan, and allocated lands to the tribes. According to chronology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaiah Di Trani
Isaiah di Trani ben Mali (the Elder) (c. 1180 – c. 1250) (), better known as the RID, was a prominent Italian Talmudist. Biography Isaiah originated in Trani, an ancient settlement of Jewish scholarship, and lived probably in Venice. He carried on a correspondence with Simhah of Speyer and with Simḥah's two pupils, Isaac ben Moses of Vienna and Abigdor Cohen of Vienna. Isaiah himself probably lived for some time in the Orient. He left a learned son, David, and a daughter, with whose son, Isaiah ben Elijah di Trani, he has often been confounded. Works Isaiah was a very prolific writer. He wrote: ''Nimmukim'' or ''Nimmukei Homesh,'' a commentary on the Pentateuch, consisting mainly of glosses on Rashi which show him to have been, as Güdemann says, an acute critic rather than a dispassionate exegete. The work has been printed as an appendix to Azulai's ''Penei Dawid'' (Leghorn, 1792); extracts from it have been published in Stern's edition of the Pentateuch (Vie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosafot
The Tosafot, Tosafos or Tosfot () are Middle Ages, medieval commentaries on the Talmud. They take the form of critical and explanatory glosses, printed, in almost all Talmud editions, on the outer margin and opposite Rashi's notes. The authors of the Tosafot are known as Tosafists; for a listing (see List of Tosafists.) Meaning of name The word ''tosafot'' literally means "additions". The reason for the title is a matter of dispute among modern scholars. Many of them, including Heinrich Graetz, think the glosses are so-called as additions to Rashi's commentary on the Talmud. In fact, the period of the Tosafot began immediately after Rashi had written his commentary; the first tosafists were Rashi's sons-in-law and grandsons, and the Tosafot consist mainly of strictures on Rashi's commentary. Others, especially Isaac Hirsch Weiss, object that many tosafot — particularly those of Isaiah di Trani — have no reference to Rashi. Weiss, followed by other scholars, assert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |