|
Standard Wind Tunnel Models
Standard wind tunnel models, also known as reference models, calibration models () or test check-standards are objects of relatively simple and precisely defined shapes, having known aerodynamic characteristics, that are tested in wind tunnels. Standard models are used in order to verify, by comparison of wind tunnel test results with previously published results, the complete measurement chain in a wind tunnel, including wind tunnel structure, quality of the airstream, model positioning, transducers and force balances, data acquisition system and data reduction software.Reed T.D., Pope T.C., Coksey T.M."Calibration of Transonic and Supersonic Wind Tunnels" NASA CR 2920, NASA, 1977Pope A."Wind Tunnel Calibration Techniques" AGARDograph 54, AGARD, 1961 More specifically, standard wind tunnel models are used for: *confirmation of the reliability of the data from a new wind tunnel by comparison with results from other wind tunnel facilities; *providing baselines for correlation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NACA 0012 Airfoil
The NACA airfoil series is a set of standardized airfoil shapes developed by this agency, which became widely used in the design of aircraft wings. Origins NACA initially developed the numbered airfoil system which was further refined by the United States Air Force at Langley Research Center. According to the NASA website: Four-digit series The NACA four-digit wing sections define the profile by: # First digit describing maximum camber as percentage of the chord. # Second digit describing the distance of maximum camber from the airfoil leading edge in tenths of the chord. # Last two digits describing maximum thickness of the airfoil as percent of the chord. For example, the NACA 2412 airfoil has a maximum camber of 2% located 40% (0.4 chords) from the leading edge with a maximum thickness of 12% of the chord. The NACA 0015 airfoil is symmetrical, the 00 indicating that it has no camber. The 15 indicates that the airfoil has a 15% thickness to chord length ratio: it is 15% a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
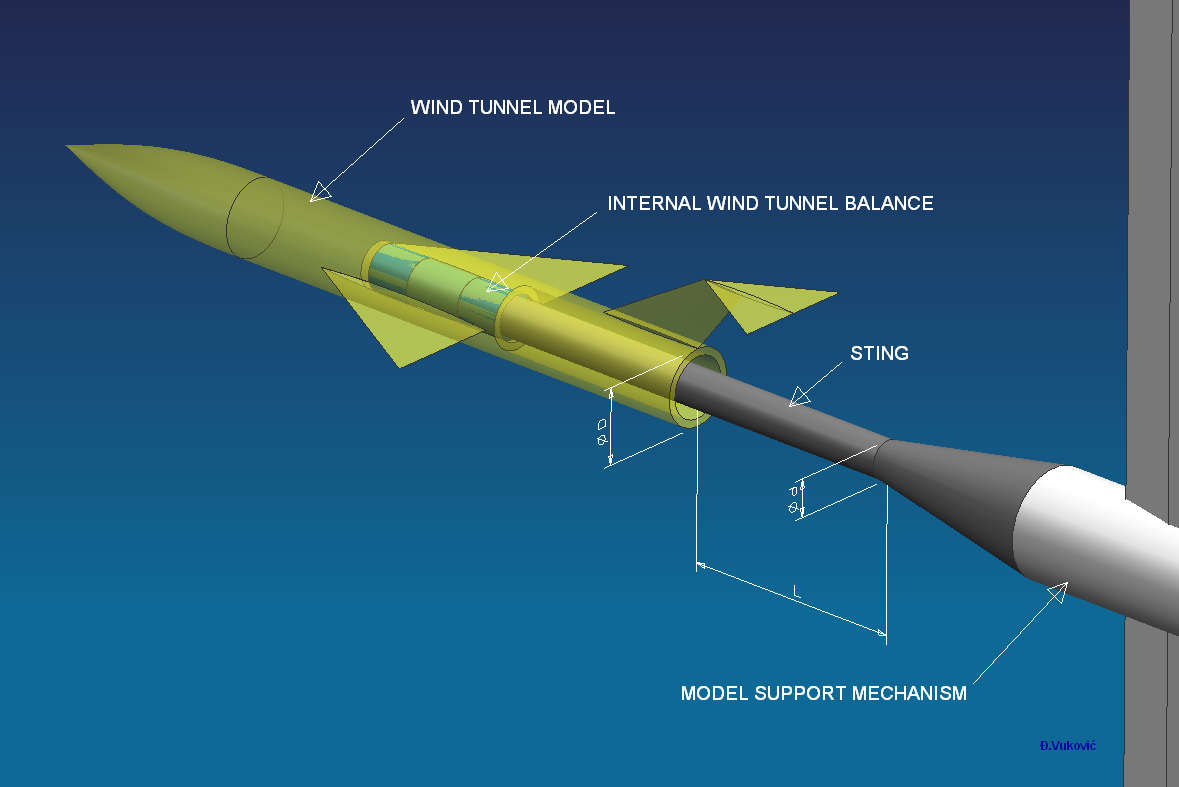
Sting (fixture)
In experimental fluid mechanics, a sting is a test fixture on which models are mounted for testing, e.g. in a wind tunnel. A sting is usually a long shaft attaching to the downstream end of the model so that it does not much disturb the flow over the model. The rear end of a sting usually has a conical fairing blending into the (wind tunnel) model support structure. For minimum aerodynamic interference a sting should be as long as possible and have as small a diameter as possible, within the structural safety limits. Critical length of a sting (beyond which its influence on the flow around the model is small) is mostly dependent on Reynolds number. If the flow at the rear end of a model (model base) is laminar, the critical sting length can be as much as 12-15 base diameters.A.Pope, "Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line segment joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil cross section parallel to the direction of the airflow. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the leading edge. L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the main chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil, the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIRA Ltd
HORIBA MIRA Ltd. (formerly the Motor Industry Research Association) is an automotive engineering and development consultancy company headquartered near Nuneaton, Warwickshire, United Kingdom. It provides product engineering, research, testing, information and certification services to the automotive sector. Its headquarters are in the MIRA Technology Park Enterprise Zone. On 14 July 2015 MIRA announced that it was being bought by the Japanese-owned testing equipment group Horiba. History Origins MIRA was formed in 1946 and was mostly government-funded. It is based just off the A5 near the junction with the A444 near Nuneaton, Warwickshire, where over six hundred staff work, with another establishment in Basildon in Essex. The company dates back to the foundation of the Cycle Engineers' Institute (CEI) in 1898, which became the Incorporated Institution of Automobile Engineers (IAE) in 1906. The IAE became the Automotive Branch of the IMechE in 1946. The IAE and the Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
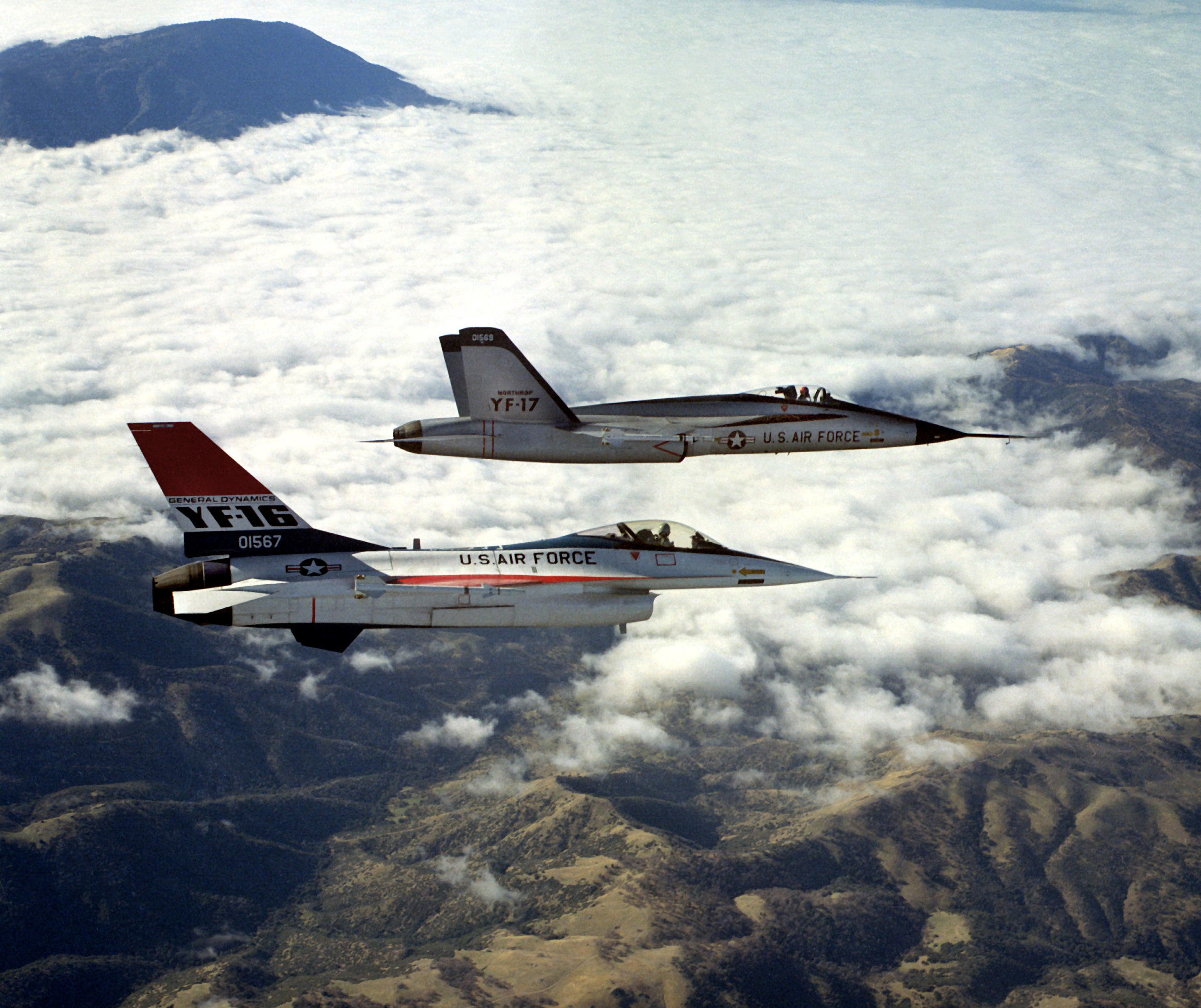
F-16
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is an American single-engine supersonic multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather multirole aircraft with over 4,600 built since 1976. Although no longer purchased by the U.S. Air Force, improved versions are being built for export. In 1993, General Dynamics sold its aircraft manufacturing business to the Lockheed Corporation, which became part of Lockheed Martin after a 1995 merger with Martin Marietta. The F-16's key features include a frameless bubble canopy for enhanced cockpit visibility, a side-mounted control stick to ease control while maneuvering, an ejection seat reclined 30 degrees from vertical to reduce the effect of g-forces on the pilot, and the first use of a relaxed static stability/fly-by-wire flight control system that helps to make it an agile aircraft. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Entry
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass ( ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8 km/s for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ONERA
The Office National d'Études et de Recherches Aérospatiales ( English: National office for aerospace studies and research) or ONERA, dubbed ''The French Aerospace Lab'' in English, is the French national aerospace research center. Originally founded as the ''Office National d’Études et de Recherches Aéronautiques'' (National Office for Aeronautical Studies and Research) in 1946, it was relabeled in 1963. It is France's leading research center in aerospace and defense. It covers all disciplines and technologies in the field. Numerous high-profile French and European aerospace programs have passed through the ONERA since its creation including the Ariane family of launch vehicles, the Concorde supersonic airliner, the Dassault Mirage family of fighter aircraft and the Rafale, the Dassault Falcon family of business jets, Aérospatiale and later Airbus projects, missiles, engines, radars and many more. Under the supervision of the Ministry of the Armed Forces, it is a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta-wing
A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ). Although long studied, the delta wing did not find significant practical applications until the Jet Age, when it proved suitable for high-speed subsonic and supersonic flight. At the other end of the speed scale, the Rogallo flexible wing proved a practical design for the hang glider and other ultralight aircraft. The delta wing form has unique aerodynamic characteristics and structural advantages. Many design variations have evolved over the years, with and without additional stabilising surfaces. General characteristics Structure The long root chord of the delta wing and minimal area outboard make it structurally efficient. It can be built stronger, stiffer and at the same time lighter than a swept wing of equivalent aspect ratio and lifting capability. Because of this it is easy and relatively inexpensive to build—a substantial fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGARD-B Wind Tunnel Model
AGARD-B is a Standard wind tunnel models, standard wind tunnel model (calibration model) that is used to verify, by comparison of test results with previously published data, the measurement chain in a wind tunnel. Together with its derivative #AGARD-C, AGARD-C it belongs to a family of AGARD standard wind tunnel models. Its origin dates to the year 1952, and the Second Meeting of the AGARD Wind Tunnel and Model Testing Panel in Rome, Italy, when it was decided to define two standard wind tunnel model configurations (AGARD-A and AGARD-B) to be used for exchange of test data and comparison of test results of same models tested in different wind tunnels. The idea was to establish standards of comparison between wind tunnels and improve the validity of wind tunnel tests. Among the standard wind tunnel models, AGARD model configuration B (AGARD-B) has become by far the most popular. Initially intended for the supersonic wind tunnels, the AGARD-B configuration has since been tested in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |