|
Staircase Maneuver
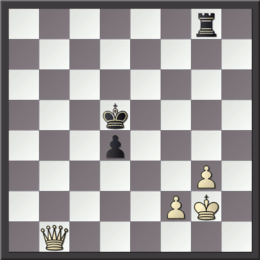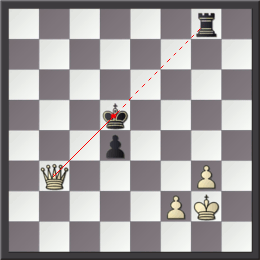
The staircase maneuver (or staircase movement) is a tactical motif that employs the idea of a series of checks, or alternation between pins and checks, to advance a queen, rook, or king along a diagonal via a series of stepped orthogonal moves. Examples Staircase maneuvers tend to occur in queen and pawn endgames, where the defender has advanced pawns on the seventh . Here the attacking queen alternates between black and white squares giving pins and checks until it reaches an open file to deliver the final mate. In the diagram, if Black's pawn on b2 had already on b1, the game would be drawn. White mates in 12, however, using the staircase maneuver: :1.Qc3 Kb1 2.Qd3+ Ka1 3.Qd4 Kb1 4.Qe4+ Ka1 5.Qe5 Kb1 6.Qf5+ Ka1 7.Qf6 Kb1 8.Qg6+ Ka1 9.Qg7 Kb1 10.Qh7+ Ka1 11.Qh8 Kb1 12.Qh1 In the game Tarrasch–Alekhine, Piešt'any 1922, after 33...Be6 (first diagram), if play had continued instead 34.Qc6 Rf3 35.Qxe4 Bd5 36.Qa4 Qxg2+ 37.Kxg2 (second diagram), a staircase maneuver result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactic
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Check (chess)
In chess and similar games, check is a condition that occurs when a player's king is under threat of on the opponent's next turn. A king so threatened is said to be ''in check''. A player must get out of check if possible by moving the king to an unattacked square, interposing a piece between the threatening piece and the king, or capturing the threatening piece. If the player cannot remove the check by any of these options, or if using any of these options would result in the player being in check by another piece, the game ends in checkmate and the player loses. Players cannot make any move that puts their own king in check. Overview A check is the result of a move that places the opposing king under an immediate threat of capture by one (or, in rare cases, two) of the player's pieces. Making a move that checks is sometimes called "giving check". Even if a piece is pinned against the player's own king, it may still give check. For example, in the diagrammed position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pin (chess)
In chess, a pin is a tactic in which a defending piece cannot move out of an attacking piece's line of attack without exposing a more valuable defending piece. Moving the attacking piece to effect the pin is called ''pinning''; the defending piece restricted by the pin is described as ''pinned''. Only a piece that can move any number of squares along a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal line (i.e. a bishop, rook, or queen) can pin. Any piece can be pinned except the king. The pin is one of the most powerful chess tactics. The inverse of a pin is a ''skewer'', in which a more valuable piece under direct attack may move to expose a less valuable piece to an attack. Types Absolute pin An ''absolute pin'' is one where the piece shielded by the pinned piece is the king. In this case it is illegal to move the pinned piece out of the line of attack, as that would place one's king in check (see diagram). A piece pinned in this way can still give check or defend another piece fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonality
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of '' perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendicular'' is more specifically used for lines and planes that intersect to form a right angle, whereas ''orthogonal'' is used in generalizations, such as ''orthogonal vectors'' or ''orthogonal curves''. ''Orthogonality'' is also used with various meanings that are often weakly related or not related at all with the mathematical meanings. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics Optics In optics, polarization states are said to be ort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Versus Pawn Endgame
The chess endgame of a queen versus pawn (with both sides having no other pieces except the kings) is usually an easy win for the side with the queen. However, if the pawn has advanced to its seventh rank it has possibilities of reaching a draw, and there are some drawn positions with the pawn on the sixth rank. This endgame arises most often from a race of pawns to promote. The side with the queen is the ''attacker'' and the side with the pawn the ''defender''. Assume that the attacker has the move. If the pawn is not beyond its sixth rank, the attacker (to move) usually wins easily, but there are a few exceptions. The winning process is to either get the queen on a square in front of the pawn and moving the king over to help win the pawn or to check the defending king until it is forced in front of the pawn and using that tempo to bring the attacking king closer, until it can assist in winning the pawn. After the pawn is won, the attacker has an elementary checkmate. Quee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open File
An open file in chess is a with no pawns of either color on it. In the diagram, the e-file is an open file. An open file can provide a line of attack for a rook or queen. Having rooks or queens on open files or half-open files is considered advantageous, as it allows a player to attack more easily, since a rook or queen can move down the file to penetrate the opponent's position. Strategic advantage A common strategic objective for a rook or queen on an open file is to reach its seventh or eighth (the opponent's second or first rank). Controlling the seventh rank is generally worth at least a pawn, as it threatens all the opponent's yet-unmoved pawns to some degree. Controlling the eighth rank is likely to force the opposing king into a more exposed position and puts pressure on any remaining pieces, or if the rank is already clear, allows unobstructed movement behind the enemy forces. Aron Nimzowitsch first recognized the power of a on an open file, writing in his famous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game. In chess, the king is never actually captured. The player loses as soon as their king is checkmated. In formal games, it is usually considered good etiquette to resign an inevitably lost game before being checkmated. If a player is not in check but has no legal moves, then it is '' stalemate'', and the game immediately ends in a draw. A checkmating move is recorded in algebraic notation using the hash symbol "#", for example: 34.Qg3#. Examples A checkmate may occur in as few as two moves on one side with all of the pieces still on the board (as in fool's mate, in the opening phase of the game), in a middlegame position (as in the 1956 game called the Game of the Century between Donald Byrne and Bobby Fischer), or after many moves with as few as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draw (chess)
In chess, there are a number of ways that a game can end in a draw, in which neither player wins. Draws are codified by various rules of chess including stalemate (when the player to move is not in check (chess), check but has no legal move), threefold repetition (when the same position occurs three times with the same player to move), and the fifty-move rule (when the last fifty successive moves made by both players contain no or pawn (chess), pawn move). Under the standard FIDE rules, a draw also occurs in a ''dead position'' (when no sequence of legal moves can lead to checkmate), most commonly when neither player has sufficient to checkmate the opponent. Unless specific tournament rules forbid it, players may draw by agreement, agree to a draw at any time. Ethical considerations may make a draw uncustomary in situations where at least one player has a reasonable chance of winning. For example, a draw could be called after a move or two, but this would likely be thought unsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegbert Tarrasch
Siegbert Tarrasch (; 5 March 1862 – 17 February 1934) was a German chess player, considered to have been among the strongest players and most influential theoreticians of the late 19th and early 20th century. Life Tarrasch was born in Breslau, in what was then Prussian Silesia and now is Poland. Having finished school in 1880, he left Breslau to study medicine in Berlin and then in Halle. With his family, he settled in Nuremberg, Bavaria, and later in Munich, setting up a successful medical practice. He had five children. Tarrasch was Jewish, converted to Christianity in 1909, and was a patriotic German who lost a son in World War I, yet he faced antisemitism in the early stages of the Third Reich. Chess career A medical doctor by profession, Tarrasch may have been the best player in the world in the early 1890s. He scored heavily against the ageing World Champion Wilhelm Steinitz in tournaments (+3−0=1) but refused an opportunity to challenge Steinitz for the world tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Alekhine
Alexander Aleksandrovich Alekhine. He disliked when Russians sometimes pronounced the of as , , which he regarded as a Yiddish distortion of his name, and insisted that the correct Russian pronunciation was . (March 24, 1946) was a Russian and French chess player and the fourth World Chess Championship, World Chess Champion, a title he held for two reigns. By the age of 22, Alekhine was already among the strongest chess players in the world. During the 1920s, he won most of the tournaments in which he played. In 1921, Alekhine left Soviet Russia and emigrated to France, which he represented after 1925. In 1927, he became the fourth World Chess Champion by defeating José Raúl Capablanca. In the early 1930s, Alekhine dominated tournament play and won two top-class tournaments by large margins. He also played first board for France in five Chess Olympiads, winning individual prizes in each (four medals and a brilliancy prize). Alekhine offered Capablanca a rematch on the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windmill (chess)
In chess, a windmill (or seesaw) is a tactic in which a piece repeatedly gains while simultaneously creating an inescapable series of alternating direct and discovered checks. Because the opponent must attend to check every move, they are unable to prevent their pieces from being captured; thus, windmills, while very rare, tend to be extremely powerful. A windmill most commonly consists of a rook supported by a bishop. The bishop typically sits on the long diagonal (see Fianchetto), while the rook moves to the seventh (White) or second (Black) rank and checks the king, who is forced to the corner due to a friendly piece (usually a knight, but it can also be another rook) blocking it. Moving the rook leads to a discovered check by the bishop, giving the player a tempo by forcing their opponent to move the king. The rook then moves back to its original spot, and the process repeats until no more pieces can be captured. Windmills can also be done with other pieces, as seen in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Oxford Companion To Chess
''The Oxford Companion to Chess'' is a reference book on the game of chess written by David Vincent Hooper and Kenneth Whyld. The book is written in an encyclopedia format. The book belongs to the Oxford Companions series. Details The first edition of the book was published in 1984 by Oxford University Press. The second edition (1992) has over 2,500 entries, including rules of chess, rules, list of chess terms, terms, chess strategy, strategies, chess tactics, tactics, over 500 brief biographies of famous players, and entries on more than 700 named chess opening, openings and opening variations. In the back of the book is a comprehensive index of opening variations and sub-variations, listing 1,327 named variations. The book also discusses variants from other countries (such as shogi or xiangqi), chess variants (such as three dimensional chess), and some forms of fairy chess. Editions * First published in 1984 by Oxford University Press * Reissued in paperback (with correction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |