|
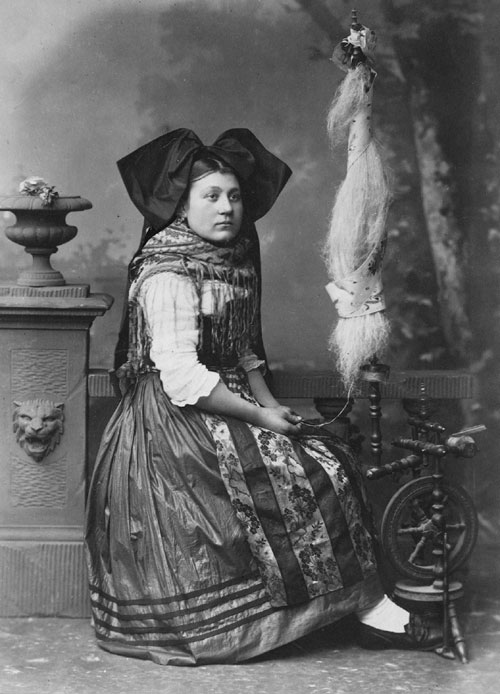
Spinning Wheel
A spinning wheel is a device for spinning thread or yarn from fibres. It was fundamental to the textile industry prior to the Industrial Revolution. It laid the foundations for later machinery such as the spinning jenny and spinning frame, which displaced the spinning wheel during the Industrial Revolution. Function The basic spinning of yarn involves taking a clump of fibres and teasing a bit of them out, then twisting it into a basic string shape. The spinner continues pulling and twisting the yarn in this manner to make it longer and longer while also controlling the thickness. Thousands of years ago, people began doing this onto a stick, called a spindle, which was a very lengthy process. The actual wheel part of a spinning wheel does not take the place of the spindle; instead, it automates the twisting process, allowing one to "twist" the thread without having to constantly do so manually, and also the size of the wheel lets one more finely control the amount of twis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Irfan Habib
Irfan Habib (born 10 August 1931) is an Indian historian of ancient and medieval India, following the methodology of Marxist historiography in his contributions to economic history. He is known for his strong stance against Hindutva. He has authored a number of books, notably the ''Agrarian System of Mughal India, 1556–1707'', an ''Atlas of the Mughal Empire: Political and Economic Maps with Detailed Notes'', and an ''Atlas of Ancient Indian History'' (with Faiz Habib). As the general editor, he is also the driving force behind the ''A People's History of India'' series, volumes of which continue to be released. Early and personal life Habib was born into an Indian Muslim family. He was the son of Mohammad Habib and Sohaila Habib (née Tyabji). His paternal grandfather was Mohammad Naseem, a wealthy barrister and member of the Indian National Congress, Congress party, and his maternal grandfather was Abbas Tyabji, sometime the Chief Justice of the High Court of Baroda state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
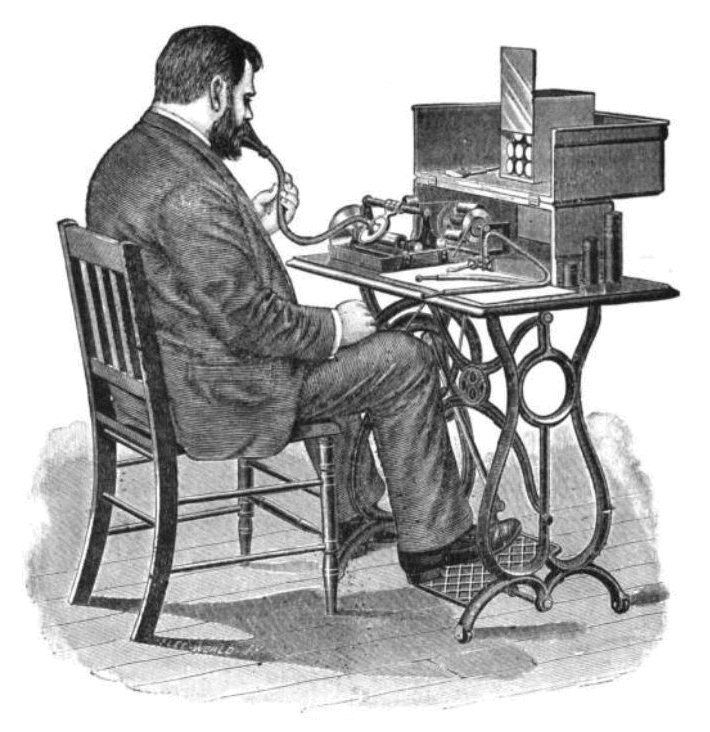
Treadle
A treadle (from , "to tread") is a foot-powered lever mechanism; it is operated by treading on it repeatedly. A treadle, unlike some other types of pedals, is not directly mounted on the crank (see treadle bicycle for a clear example). Most treadle machines convert reciprocating motion into rotating motion, using a mechanical linkage to indirectly connect one or two treadles to a crank. The treadle then turns the crank, which powers the machine. Other machines use treadles directly, to generate reciprocating motion. For instance, in a treadle loom, the reciprocating motion is used directly to lift and lower the harnesses or heddles; a common treadle pump uses the reciprocating motion to raise and lower pistons. Before the widespread availability of electric power, treadles were the most common way to power a range of machines. They are still widely used as a matter of preference and necessity. A human-powered machine gives the human operator close, instinctive control ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Braunschweig
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( ; from Low German , local dialect: ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Lower Saxony, Germany, north of the Harz Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker, which connects it to the North Sea via the rivers Aller (Germany), Aller and Weser. In 2024, it had a population of 272,417. The Braunschweig-Wolfsburg-Salzgitter region had 1.02 million residents including the cities Wolfsburg and Salzgitter, it is the second largest urban center in Lower Saxony after Hanover. The urban agglomeration of Braunschweig had a population of 551,000 with almost 45% having a migration background, making it the most diverse urban agglomeration in the whole Niedersachsen, state. The city consists of 37.5% immigrants (approximately 102,000) with a high amount of migrants coming from other European countries, Asia and Africa. 73% of the Germans residing in Braunschweig come from different parts of the country, particularly North Rhine West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Greenwood Publishing Group
Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. (GPG) was an educational and academic publisher (middle school through university level) which was part of ABC-Clio. Since 2021, ABC-Clio and its suite of imprints, including GPG, are collectively imprints of British publishing house Bloomsbury Publishing. The Greenwood name stopped being used for new books in 2023. Established in 1967 as Greenwood Press, Inc., and based in Westport, Connecticut, GPG published reference works under its Greenwood Press imprint; and scholarly, professional, and general-interest books under its related imprint, Praeger Publishers (). Also part of GPG was Libraries Unlimited, which published professional works for librarians and teachers. Both of the latter became stand-alone imprints of ABC-Clio, in 2008–2009, after its purchase of GPG. History 1967–1999 The company was founded as Greenwood Press, Inc. (GPI) in 1967 by Harold Mason, a librarian and antiquarian bookseller, and Harold Schwartz, who had a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacular language), size (few or many volumes), intent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Encyclopaedia Britannica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionary, dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on Linguistics, linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammar, grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distaff
A distaff (, , also called a rock"Rock." ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989.) is a tool used in spinning. It is designed to hold the unspun fibers, keeping them untangled and thus easing the spinning process. It is most commonly used to hold flax and sometimes wool, but can be used for any type of fibre. Fiber is wrapped around the distaff and tied in place with a piece of ribbon or string. The word comes from Low German ''dis'', meaning a bunch of flax, connected with staff. As an adjective, the term ''distaff'' is used to describe the female side of a family. The corresponding term for the male side of a family is the "spear" side. Form In Western Europe, there were two common forms of distaves, depending on the spinning method. The traditional form is a staff held under one's arm while using a spindle – see the figure illustration. It is about long, held under the left arm, with the right hand used in drawing the fibres from it."Distaff." ''The Oxford Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spindle (textiles)
A spindle is a straight spike, usually made from wood, used for spinning, twisting fibers such as wool, flax, hemp, and cotton into yarn. It is often weighted at either the bottom, middle, or top, commonly by a disc or spherical object called a whorl; many spindles, however, are weighted simply by thickening their shape towards the bottom, e.g. Orenburg and French spindles. The spindle may also have a hook, groove, or notch at the top to guide the yarn. Spindles come in many different sizes and weights depending on the thickness of the yarn one desires to spin. History The origin of the first wooden spindle is lost to history because the materials did not survive. Whorl-weighted spindles date back at least to Neolithic times; spindle whorls have been found in archaeological digs around the world. Possible remains of spindle whorls were found in a Natufian village at Nahal Ein Gev II archeological site, Israel, from 12000 years ago. A spindle is also part of traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vachana Sahitya
Vachana sahitya is a form of rhythmic writing in Kannada (see also Kannada poetry) that evolved in the 11th century and flourished in the 12th century, as a part of the Sharana movement. The word "vachanas" literally means "(that which is) said". These are readily intelligible prose texts. These writings are notable for their simplicity and directness, often addressing social issues and personal devotion. They were composed in Kannada by saints of the Lingayat faith, most notably Basavanna, Akka Mahadevi, and Allama Prabhu. Vachanas critique rituals and caste discrimination, advocating a form of worship centered on Shiva, envisioned as a universal god.Ishawaran, K. (1992), Speaking of Basava: Lingayat Religion and Culture in South Asia, Westview Press, ISBN 978-0813383897 Vachanas and Sharana movement More than 200 Vachana writers (''Vachanakaras'' also known as Sharanas) have been recorded and more than thirty of whom were women.Sastri (1955), p. 361Other well known Vachan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abdul Malik Isami
Abdul Malik Isami (1311–after 14 May 1350) was a 14th-century Indian historian and court poet. He wrote in the Persian language, under the patronage of Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah, the founder of the Bahmani Sultanate. He is best known for ''Futuh-us-Salatin'' (), a poetic history of the Muslim conquest of India. Early life Isami was born in 1311, possibly in Delhi. His father's name was 'Izz ul-Din 'Isami. His ancestor Fakhr Malik Isami had migrated from Baghdad to India during the reign of Iltutmish (). In a reference to himself, he says, "(My poetic disposition) said : 'Hindustan is your place — the birth place of your grandfather and forefathers.'" He referred to the city of Delhi as the "home of Islam". In 1327, the Delhi Sultanate ruler Muhammad bin Tughluq decided to move his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad in Deccan region. Several residents of Delhi, including Isami's family, were ordered to move to Daulatabad. His 90-year-old grandfather died during this journey. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |