|
Specificity Theory
As long as humans have experienced pain, they have given explanations for its existence and sought soothing agents to dull or cease the painful sensation. Archaeologists have uncovered clay tablets dating back as far as 5,000 BC which reference the cultivation and use of the opium poppy to bring joy and cease pain. In 800 BC, the Greek writer Homer wrote in his epic, The Odyssey, of Telemachus, a man who used opium to soothe his pain and forget his worries. Booth, Martin. Opium a history. London: Simon & Schuster, 1996. Print. While some cultures researched analgesics and allowed or encouraged their use, others perceived pain to be a necessary, integral sensation. Physicians of the 19th century used pain as a diagnostic tool, theorizing that a greater amount of personally perceived pain was correlated to a greater internal vitality, and as a treatment in and of itself, inflicting pain on their patients to rid the patient of evil and unbalanced humors. This article focuses both on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. Homer's ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language which shows a mixture of features of the Ionic and Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems were originally transmitted orally. Homer's epic poems shaped aspects of ancient Greek culture and education, fostering ideals of heroism, glory, and honor. To Plato, Homer was simply t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Specific Nerve Energies
The law of specific nerve energies, first proposed by Johannes Peter Müller in 1835, is that the nature of perception is defined by the pathway over which the sensory information is carried. Hence, the origin of the sensation is not important. Therefore, the difference in perception of seeing, hearing, and touch are not caused by differences in the stimuli themselves but by the different nervous structures that these stimuli excite. For example, pressing on the eye elicits sensations of flashes of light because the neurons in the retina send a signal to the occipital lobe. Despite the sensory input's being mechanical, the experience is visual. Quotation Here is Müller's statement of the law, from ''Handbuch der Physiologie des Menschen für Vorlesungen'', 2nd Ed., translated by Edwin Clarke and Charles Donald O'Malley: ::''The same cause, such as electricity, can simultaneously affect all sensory organs, since they are all sensitive to it; and yet, every sensory nerve reacts to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Heinrich Erb
Wilhelm Heinrich Erb (30 November 1840 – 29 October 1921) was a German neurologist. He was born in Winnweiler, and died in Heidelberg. Academic career In 1864 he received his medical degree from the University of Heidelberg, where for several years he served as an assistant to pathologist Nikolaus Friedreich (1825-1882). As a young man, he also worked for a period of time under Ludwig von Buhl (1816-1880) in Munich. In 1880 Erb attained the chair of special pathology at the University of Leipzig, where he was also appointed head of its policlinic. In 1883 he succeeded Friedreich at the University of Heidelberg, where he worked until his retirement in 1907. Psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin (1856-1926) and neurologists Ernst Julius Remak (1849-1911), Max Nonne (1861-1959) and Paul Julius Möbius (1853–1907) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timaeus (dialogue)
''Timaeus'' (; grc-gre, Τίμαιος, Timaios, ) is one of Plato's dialogues, mostly in the form of long monologues given by Critias and Timaeus, written 360 BC. The work puts forward reasoning on the possible nature of the physical world and human beings and is followed by the dialogue '' Critias''. Participants in the dialogue include Socrates, Timaeus, Hermocrates, and Critias. Some scholars believe that it is not the Critias of the Thirty Tyrants who appears in this dialogue, but his grandfather, who is also named Critias. It has been suggested from some traditions ( Diogenes Laertius (VIII 85) from Hermippus of Smyrna (3rd century BC) and Timon of Phlius ( 320 – 235 BC)) that ''Timaeus'' was influenced by a book about Pythagoras, written by Philolaus, although this assertion is generally considered false. Introduction The dialogue takes place the day after Socrates described his ideal state. In Plato's works, such a discussion occurs in the '' Republic''. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet. His poems included much natural history, including a statement of evolution and the relatedness of all forms of life. He was a member of the Darwin–Wedgwood family, which includes his grandsons Charles Darwin and Francis Galton. Darwin was a founding member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham, a discussion group of pioneering industrialists and natural philosophers. He turned down an invitation from George III to become Physician to the King. Early life and education Darwin was born in 1731 at Elston Hall, Nottinghamshire, near Newark-on-Trent, England, the youngest of seven children of Robert Darwin of Elston (1682–1754), a lawyer and physician, and his wife Elizabeth Hill (1702–97). The name Erasmus had been used by a number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonomia
''Zoonomia; or the Laws of Organic Life'' (1794-96) is a two-volume medical work by Erasmus Darwin dealing with pathology, anatomy, psychology, and the functioning of the body. Its primary framework is one of associationist psychophysiology. The book is now best remembered for its early ideas relating to the theory of evolution, specifically forms of developmentalism similar to Lamarckism. However, despite Erasmus Darwin's familial connection as grandfather to Charles Darwin, the proto-evolutionary ideas in ''Zoonomia'' did not have a lasting influence. Summary The first volume, published in 1794, is divided into 40 sections, on a range of topics related to the body, the senses, and disease. He classifies bodily and sensory motions as "irritative," "sensitive," "voluntary," and "associative." He presents theories on the production and classes of ideas, and seeks to explain the causes and mechanisms of sleep, reverie, vertigo, and drunkenness. He then discusses anatomy, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Nerve Ending
A free nerve ending (FNE) or bare nerve ending, is an unspecialized, afferent nerve fiber sending its signal to a sensory neuron. ''Afferent'' in this case means bringing information from the body's periphery toward the brain. They function as cutaneous nociceptors and are essentially used by vertebrates to detect noxious stimuli that often result in pain. Structure Free nerve endings are unencapsulated and have no complex sensory structures. They are the most common type of nerve ending, and are most frequently found in the skin. They penetrate the dermis and end in the stratum granulosum. FNEs infiltrate the middle layers of the dermis and surround hair follicles. Types Free nerve endings have different rates of adaptation, stimulus modalities, and fiber types. Rate of adaptation Different types of FNE can be rapidly adapting, intermediate adapting, or slowly adapting. A delta type II fibers are fast-adapting while A delta type I and C fibers are slowly adapting.Rolf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian Von Frey
Maximilian (Max) Ruppert Franz von Frey (16 November 1852 – 25 January 1932) was an Austrian-German physiologist who was born in Salzburg. He received his doctorate from the University of Leipzig in 1877, and subsequently worked at Carl Ludwig's Physiological Institute in Leipzig. Later he was a professor of physiology at the Universities of Würzburg and Zurich. Frey's primary work in Leipzig dealt with the circulatory system, and he is credited with developing an early prototype of a heart-lung machine. He is remembered for his work involving cutaneous sensory mechanoreceptors. During the 1890s, Frey proposed that pain is an independent tactile quality, alongside touch, heat and cold, and that it is associated with stimulation of high-threshold free nerve endings. He described the skin as a mosaic of discrete spots, each sensitive to one or another of these stimuli. He created a unique type of esthesiometer An esthesiometer (British spelling aesthesiometer) is a device for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
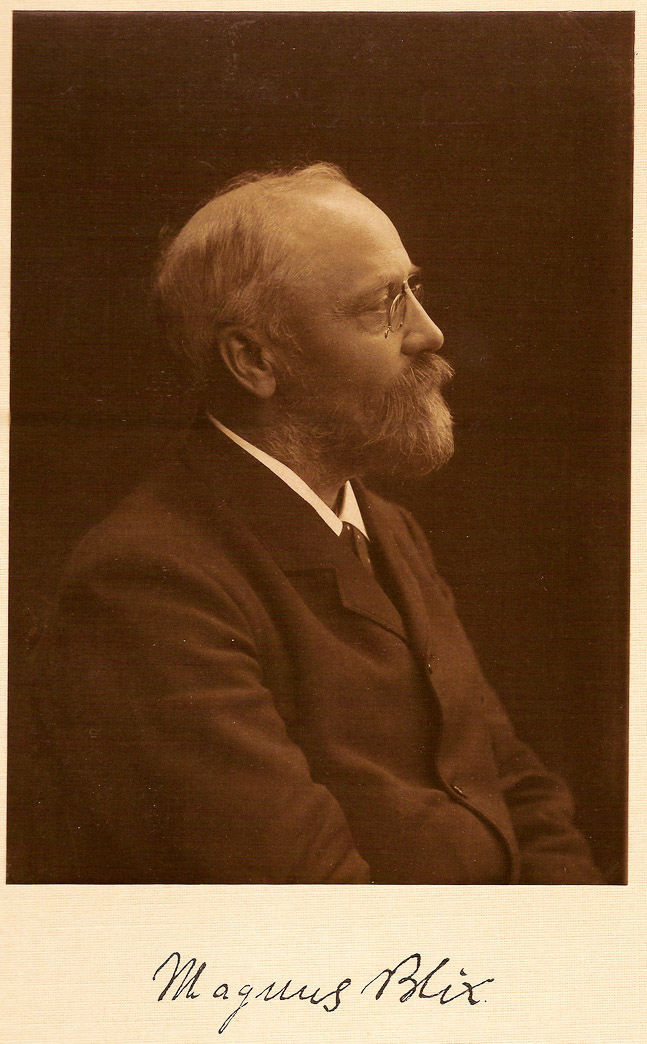
Magnus Blix
Magnus Gustaf Blix (25 December 1849 – 14 February 1904) was a Swedish physiologist born in the parish Säbrå, presently located in Härnösand Municipality. He is the grandfather of UN weapons inspector Hans Blix. During his career he was a professor at the Universities of Uppsala and Lund. Blix was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1892. Blix is best known for his work in the 1880s involving somatic sensation. He discovered that electrical stimulation on different points on the surface of the skin caused distinct warm or cool sensations. Subsequently he built a " temperature stimulator" which showed that a decreased skin temperature produced cool sensations from localized spots at separate skin locations. He also discovered that increased temperature induced warm sensations from different cutaneous locations. In addition he performed tests that involved localized tactile sensitivity. In 1881–82 Blix published his findings in two important do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Schiff
Moritz Schiff (28 January 1823, Frankfurt – 6 October 1896, Geneva) was a German physiologist and the elder brother of the chemist Hugo Schiff (1834-1915), particularly known for his staining technique. He made major contributions to human physiology, including studies of the circulatory system and the action of the vagus nerve. Unfortunately despite his independent and original spirit and being a much-cited author, he never reached the popularity of his contemporaries Emil du Bois-Reymond, Hermann von Helmholtz and Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard. Biography Born into a family of Jewish merchants, Mortiz Schiff can be considered as the archetype of the great nineteenth-century scientist, one of the pioneers of the experimental method in physiology as well as a polyglot, who published his articles in German, French or Italian indifferently. He began his studies in his hometown, at the Senckenberg Institute, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Krause
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Krause (12 July 1833 – 4 February 1910) was a German anatomist born in Hanover. He was the son of anatomist Karl Friedrich Theodor Krause (1797-1868). Krause studied at Göttingen, where he became member of Burschenschaft Hannovera (fraternity). In 1854 he earned his medical doctorate, and later (1860) became an associate professor at the University of Göttingen. In 1892 he was appointed head of the Anatomical Institute Laboratory in Berlin. Krause is known for the discovery and description of mechanoreceptors that were to become known as " Krause's corpuscles", sometimes referred to as "Krause's end-bulbs". His name is also associated with: * "Krause's membranes": defined as isotropic bands in striated muscle fiber that consist of disks of sarcoplasm and connect the individual fibrils. Also known as Z-Disc or Dobie's line. * "Krause respiratory bundle": a fiber bundle that is also known as the " solitary tract". Sometimes referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_Homer_and_his_Guide_(1874).jpg)