|
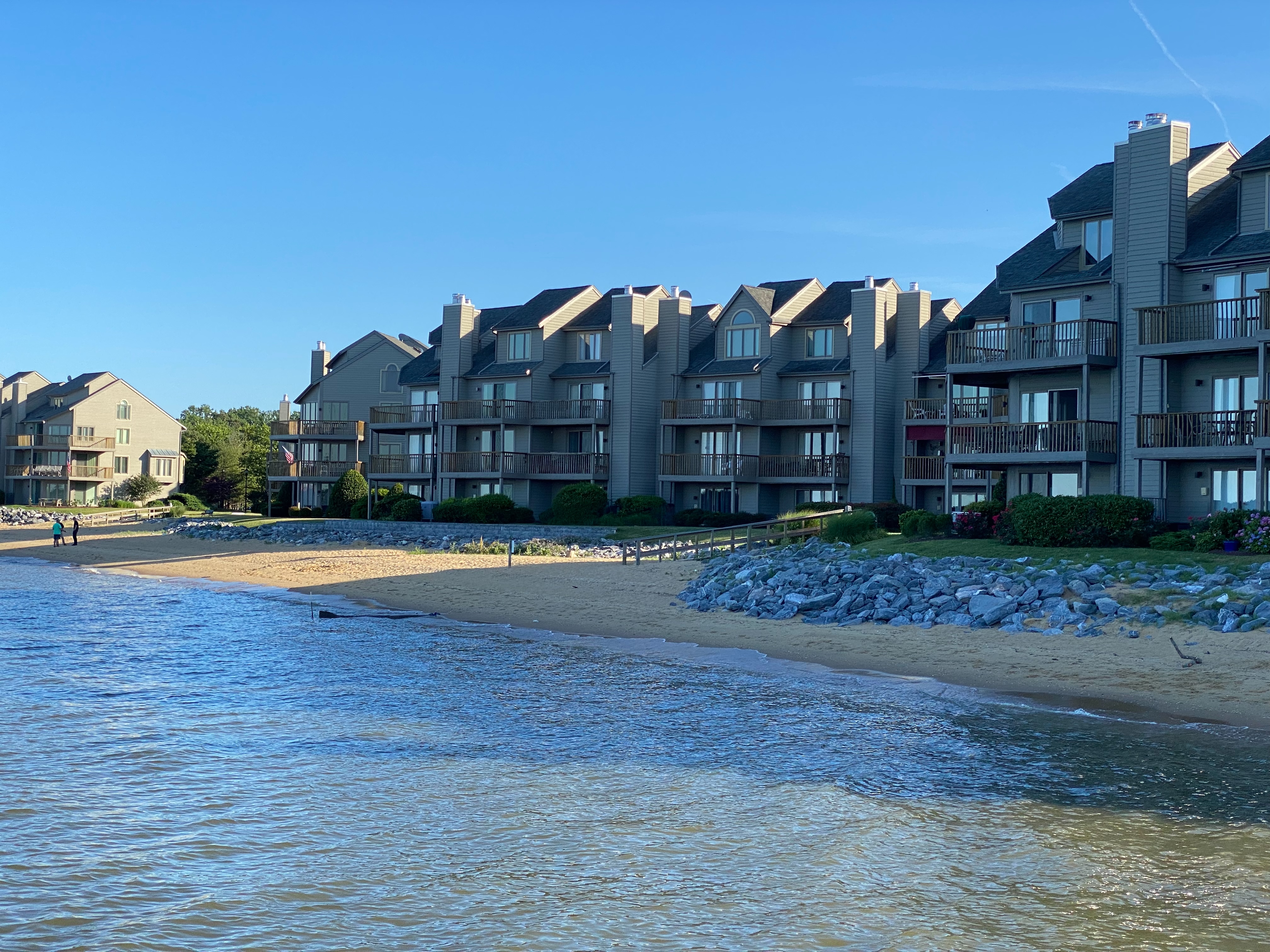
Sparrow's Beach
Sparrow's Beach was a beachfront resort on the Chesapeake Bay that catered to African American patrons during segregation in the American South. Located just south of Annapolis, Maryland, Sparrow's Beach was established as a recreational area during the Jim Crow-era when African-Americans were denied entry into 'Whites-only' establishments. Other nearby beachfront resorts used for this purpose included Carr's Beach, Elktonia Beach, Bembe Beach, Highland Beach, Venice Beach, Oyster Harbor, and Arundel-on-the-Bay. In August 2022, the City of Annapolis purchased what remains of Sparrow's Beach, Carr's Beach, and Elktonia Beach to preserve the land as a park. History Frederick Carr and Mary Wells Carr, Black Americans, purchased 180 acres of waterfront property on the Annapolis Neck peninsula in 1902. In 1926, they established a beachfront resort called Carr's Beach on the land. Their daughter, Elizabeth Carr Smith, operated Carr's Beach. Their younger daughter, Florence Carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
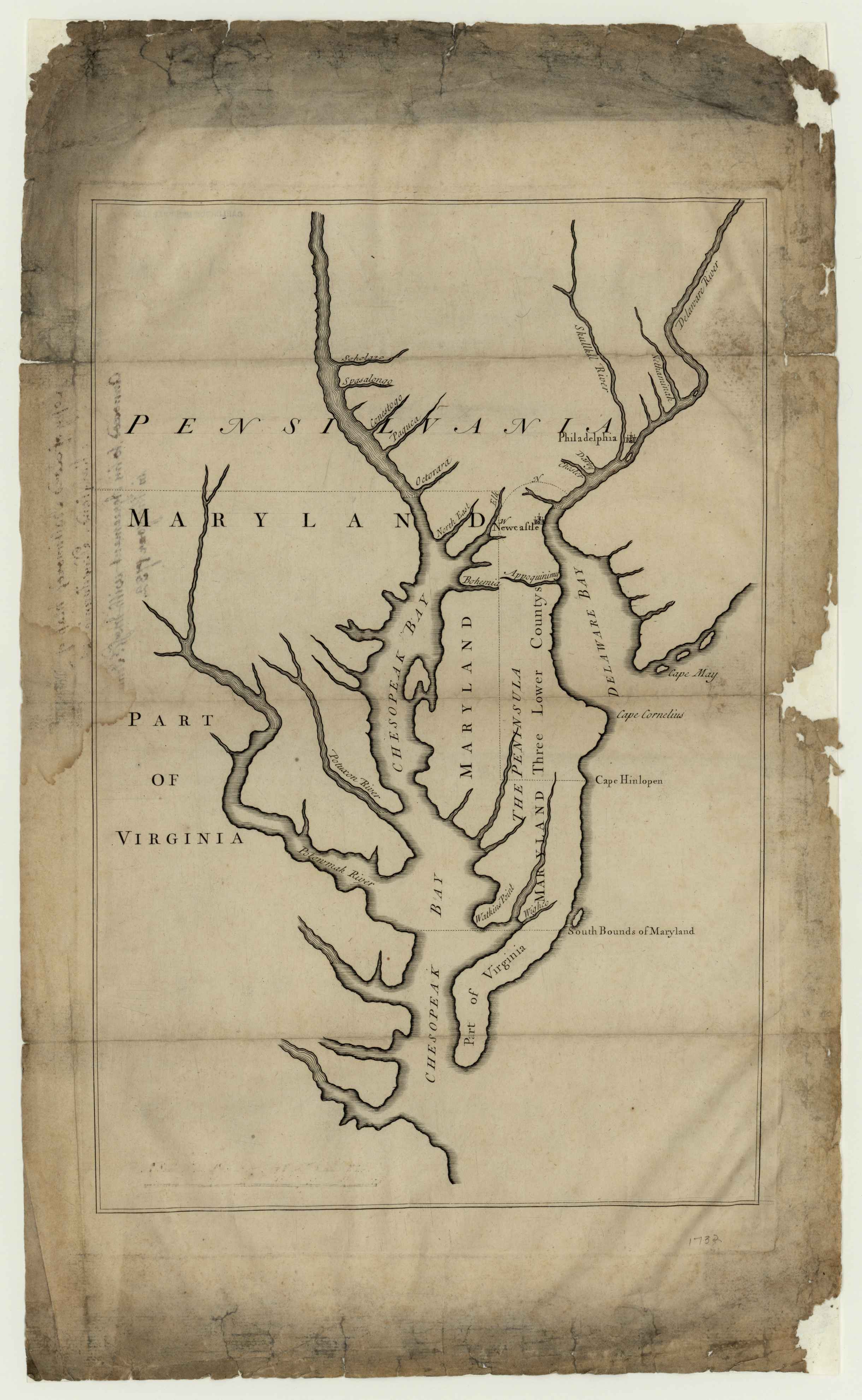
Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles (headland), Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the bay's drainage basin, which covers parts of six states (New York (state), New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia) and all of Washington, D.C. The bay is approximately long from its northern headwaters in the Susquehanna River to its outlet i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annapolis Neck Peninsula
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east of Washington, D.C., Annapolis forms part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The 2020 census recorded its population as 40,812, an increase of 6.3% since 2010. This city served as the seat of the Confederation Congress, formerly the Second Continental Congress, and temporary national capital of the United States in 1783–1784. At that time, General George Washington came before the body convened in the new Maryland State House and resigned his commission as commander of the Continental Army. A month later, the Congress ratified the Treaty of Paris of 1783, ending the American Revolutionary War, with Great Britain recognizing the independence of the United States. The city and state capitol was also the site of the 1786 Annap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Sites In Maryland
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Conservation Fund
The Conservation Fund is a U.S. nonprofit organization with a dual charter to pursue environmental preservation and economic development. From 2008–2018, it has placed more than 500,000 acres under conservation management through a program whose goal is to purchase and permanently protect working forests. Since its founding in 1985, the organization has protected land and water in all 50 states, including parks, historic battlefields, and wild areas. The Fund works with community and government leaders, businesses, landowners, conservation nonprofits and other partners to integrate economic and environmental objectives. The Conservation Fund was founded in 1985 by Pat Noonan, former head of the Nature Conservancy. The current CEO is Larry Selzer. About 140 full-time staff work in the Fund's headquarters, located in Arlington, Virginia, and in offices in several states across the U.S. including California, Florida, Michigan, Minnesota, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Oregon, Tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east, as well as with the Atlantic Ocean to its east, and the national capital and federal district of Washington, D.C. to the southwest. With a total area of , Maryland is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, ninth-smallest state by land area, and its population of 6,177,224 ranks it the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 18th-most populous state and the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, fifth-most densely populated. Maryland's capital city is Annapolis, Maryland, Annapolis, and the state's most populous city is Baltimore. Maryland's coastline was first explored by Europeans in the 16th century. Prior to that, it was inhabited by several Native Americans in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake Conservancy
Chesapeake Conservancy is a non-profit organisation, whose aim is to use technology and advocacy to support conservation of the Chesapeake Bay estuary on the east coast of the United States. The group is based in Annapolis, Maryland. History In December 2016, the organisation announced that Robert Stanton, former director of the National Park Service, and Anne Scott, a philanthropic investment manager, had joined the board of directors, replacing outgoing board members Patrick Noonan, Stephen Adkins and Lloyd Beatty, Jr. Board of directors The current board of directors of the conservancy includes: *President and CEO: Joel E. Dunn *Chair: Randall W. Larrimore *Vice Chair: Mark Belton *Treasurer: Leslie Delgran *Secretary: Marc Guenter Bunting *Maite Arce *Thad Bench *Michael Brubaker *Matthew Earl *Colin Harrington *Verna Harrison *Jeffery More *Stephanie Meeks *John G. Neely *Dr. Mamie A. Parker *John J. Reynolds *Chief G. Anne Richardson, Rappahannock Tribe *Jeff Sabot * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blacks Of The Chesapeake Foundation
Black is a racial classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid- to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin and often additional phenotypical characteristics are relevant, such as facial and hair-texture features; in certain countries, often in socially based systems of racial classification in the Western world, the term "black" is used to describe persons who are perceived as dark-skinned compared to other populations. It is most commonly used for people of sub-Saharan African ancestry, Indigenous Australians and Melanesians, though it has been applied in many contexts to other groups, and is no indicator of any close ancestral relationship whatsoever. Indigenous African societies do not use the term ''black'' as a racial identity outside of influences brought by Western cultures. Contemporary anthropologists and other scientists, while recognizing the reality of biological vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxury Waterfront Townhomes In Maryland
Luxury may refer to: *Luxury goods, an economic good or service for which demand increases more than proportionally as income rises *Luxury tax, a tax on products not considered essential, such as speedboats or diamonds. **Luxury tax (sports), a surcharge put on the aggregate payroll of a sports team to the extent to which it exceeds a predetermined guideline level set by the league *Luxury car, an expensive automobile *Luxury train, an expensive tourist train *Luxury yacht, an expensive privately owned, professionally crewed yacht *Luxury apartment, a type of property that is intended to provide its occupant with higher-than-average levels of comfort, quality and convenience *Luxury hotel, a high-quality amenities, full-service accommodations and the highest level of personalized services *Luxury resort, an exclusive vacation facility *Luxury box, term for a special seating section in arenas, stadiums and other sports venues *Luxury magazine, magazines devoted to fine craft and lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Vaughan
Sarah Lois Vaughan (, March 27, 1924 – April 3, 1990) was an American jazz singer and pianist. Nicknamed "Sassy" and "List of nicknames of jazz musicians, The Divine One", she won two Grammy Awards, including the Lifetime Achievement Award, and was nominated for a total of nine Grammy Awards. She was given an NEA Jazz Masters Award in 1989. Critic Scott Yanow wrote that she had "one of the most wondrous voices of the 20th century". Early life Vaughan was born in Newark, New Jersey, to Asbury "Jake" Vaughan, a carpenter by trade who played guitar and piano, and Ada Vaughan, a laundress who sang in the church choir, migrants from Virginia. The Vaughans lived in a house on Brunswick Street in Newark for Vaughan's entire childhood. Jake was deeply religious. The family was active in New Mount Zion Baptist Church at 186 Thomas Street. Vaughan began piano lessons at the age of seven, sang in the church choir, and played piano for rehearsals and services. Sarah and her family were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
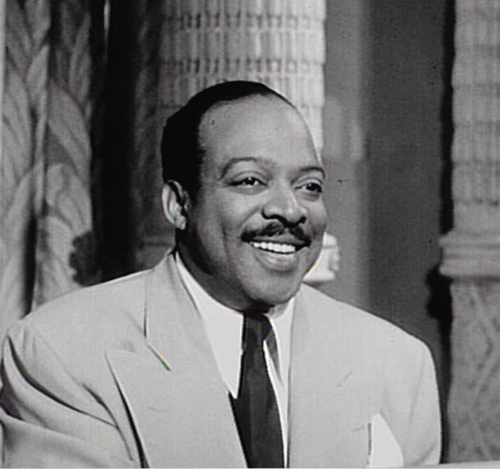
Count Basie
William James "Count" Basie (; August 21, 1904 – April 26, 1984) was an American jazz pianist, organist, bandleader, and composer. In 1935, he formed the Count Basie Orchestra, and in 1936 took them to Chicago for a long engagement and their first recording. He led the group for almost 50 years, creating innovations like the use of two "split" tenor saxophones, emphasizing the rhythm section, riffing with a big band, using arrangers to broaden their sound, his minimalist piano style, and others. Many musicians came to prominence under his direction, including the tenor saxophonists Lester Young and Herschel Evans, the guitarist Freddie Green, trumpeters Buck Clayton and Harry "Sweets" Edison, plunger trombonist Al Grey, and singers Jimmy Rushing, Helen Humes, Dennis Rowland, Thelma Carpenter, and Joe Williams (jazz singer), Joe Williams. As a composer, Basie is known for writing such jazz standards as "Blue and Sentimental", "Jumpin' at the Woodside" and "One O'Clock Jump" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billie Holiday
Billie Holiday (born Eleanora Fagan; April 7, 1915 – July 17, 1959) was an American jazz and swing music singer. Nicknamed "Lady Day" by her friend and music partner, Lester Young, Holiday made significant contributions to jazz music and pop music, pop singing. Her vocal style, strongly influenced by jazz instrumentalists, inspired a new way of manipulating Phrase (music), phrasing and tempo. Holiday was known for her vocal delivery and Jazz improvisation, improvisational skills. After a turbulent childhood, Holiday began singing in nightclubs in Harlem where she was heard by producer John Hammond (record producer), John Hammond, who liked her voice. Holiday signed a recording contract with Brunswick Records, Brunswick in 1935. Her collaboration with Teddy Wilson produced the hit "What a Little Moonlight Can Do", which became a jazz standard. Throughout the 1930s and 1940s, Holiday had mainstream success on labels such as Columbia Records, Columbia and Decca Records, Decca. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |