|
Space Vehicle Launch Preparation
The preparation of a space vehicle for rocket launch, launch (known by the European Space Agency (ESA) as a launch campaign), includes launch vehicle#Vehicle assembly, assembly of the launch vehicle, integration of the Payload (air and space craft), payload, fueling of the vehicle, and preparing the launch pad, the rocket range, launch range and tracking stations. The length of time required for this process generally varies with the size and complexity of the vehicle, and the state of maturity of its development. Parallel campaigns Arianespace, the contractor responsible for launching the Ariane 5 for the European Space Agency, can conduct two Ariane 5 ECA launch campaigns in parallel at the Guyana Space Centre. References Spaceflight {{space-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Vehicle
A space vehicle is the combination of a spacecraft and its launch vehicle which carries it into space. The earliest space vehicles were expendable launch systems, using a single or multistage rocket to carry a relatively small spacecraft in proportion to the total vehicle size and mass. An early exception to this, the Space Shuttle, consisted of a reusable orbital vehicle carrying crew and payload, supported by an expendable external propellant tank and two reusable solid-fuel booster rockets. Reusable launch systems are currently being developed by private industry. Early spacecraft or space vehicles were sometimes known as " spaceships", a term which comes from science fiction to designate a hypothetical vehicle which travels beyond low Earth orbit and is 100% reusable, needing only to be refueled like an airplane. History In the 1865 Jules Verne novel ''From the Earth to the Moon'', successful attempts are made to launch three people in a projectile with the goal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Launch
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage rocket, but the term is more general and also encompasses vehicles like the Space Shuttle. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to high operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles use chemical prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payload (air And Space Craft)
Payload is the object or the entity that is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload. In a commercial context (i.e., an airline or air freight carrier), payload may refer only to revenue-generating cargo or paying passengers. A payload of ordnance carried by a combat aircraft is sometimes alternatively referred to as the aircraft's warload. For a rocket, the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile, the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; their total weight is referred to as the throw-weight. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Pad
A launch pad is an above-ground facility from which a rocket-powered missile or space vehicle is vertically launched. The term ''launch pad'' can be used to describe just the central launch platform (mobile launcher platform), or the entire complex (launch complex). The entire complex will include a ''launch mount'' or ''launch platform'' to physically support the vehicle, a service structure with umbilicals, and the infrastructure required to provide liquid-propellant rocket, propellants, cryogenic fluids, electrical power, communications, telemetry, rocket assembly, payload processing, storage facilities for propellants and gases, equipment, access roads, and drainage. Most launch pads include fixed service structures to provide one or more access platforms to assemble, inspect, and maintain the vehicle and to allow access to the spacecraft, including the loading of crew. The pad may contain a Flame deflector, flame deflection structure to prevent the intense heat of the roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Range
A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word ''spaceport''—and even more so ''cosmodrome''—has traditionally referred to sites capable of launching spacecraft into Earth orbit or on interplanetary trajectories. However, rocket launch sites for sub-orbital spaceflights are also sometimes called spaceports, especially as new and proposed facilities for suborbital commercial spaceflight are often branded as "spaceports." Space stations and proposed future lunar bases are also sometimes referred to as spaceports, particularly when envisioned as nodes for further interplanetary travel. Spaceports are evolving beyond traditional government-run complexes into multi-functional aerospace hubs, increasingly driven by private companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic. A prominent example is Starbase, a private spaceport operated by SpaceX in Boca Chica, Texas. Starb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking Station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves from astronomical radio sources. Ground stations may be located either on the surface of the Earth, or in its atmosphere. Earth stations communicate with spacecraft by transmitting and receiving radio waves in the super high frequency (SHF) or extremely high frequency (EHF) bands (e.g. microwaves). When a ground station successfully transmits radio waves to a spacecraft (or vice versa), it establishes a telecommunications link. A principal telecommunications device of the ground station is the parabolic antenna. Ground stations may have either a fixed or itinerant position. Article 1 § III of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Radio Regulations describes various types of stationary and mobile ground stations, and their interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a Small-lift launch vehicle, small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a Medium-lift launch vehicle, medium-to-Heavy-lift launch vehicle, heavy-lift rocket. Arianespace is a subsidiary of ArianeGroup, a joint venture between Airbus and Safran. European space launches are carried out as a collaborative effort between private companies and government agencies. The role of Arianespace is to market Ariane 6 launch services, prepare missions, and manage customer relations. At the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana, the company oversees the team responsible for integrating and preparing launch vehicles. The rockets themselves are designed and manufactured by other companies: ArianeGroup for the Ariane 6 and Avio for the Vega. The launch infrastructure at the CSG is owned by the European Space Agency, while the land itself belongs to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
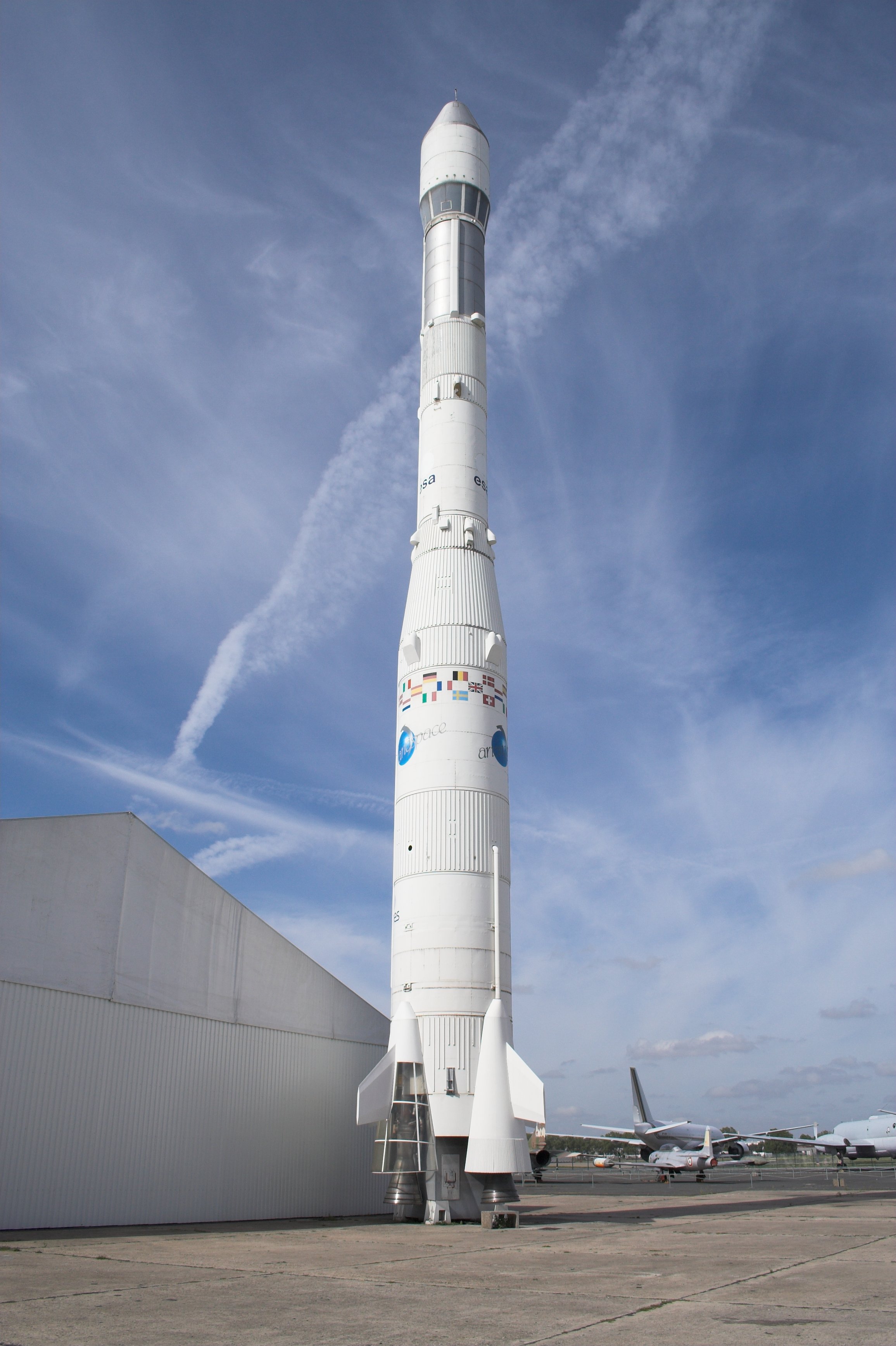
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), low Earth orbit (LEO) or further into space. The launch vehicle had a streak of 82 consecutive successful launches between 9 April 2003 and 12 December 2017. Since 2014, Ariane 6, a direct successor system, first launched in 2024. The system was designed as an expendable launch vehicle by the ''Centre national d'études spatiales'' (CNES), the French government's space agency, in cooperation with various European partners. Despite not being a direct derivative of its predecessor launch vehicle program, it was classified as part of the Ariane rocket family. Aérospatiale, and later ArianeGroup, was the prime contractor for the manufacturing of the vehicles, leading a multi-country consortium of other European con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guyana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, an overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximately north of the equator at a latitude of 5°. In operation since 1968, it is a suitable location for a spaceport because of its near equatorial location and open sea to the east and north. At CSG, space launches are conducted by several European private companies and government agencies working together. The CSG land itself is managed by CNES, the French national space agency. The launch infrastructure built on the CSG land is owned by the European Space Agency. The private company Arianespace operates the launches including planning missions, handling customer relationships and overseeing the team at CSG that integrates and prepares vehicles for launch. The rockets themselves are designed and produced by other companies, ArianeGroup for the Ariane 6 and Avio for the Vega. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |