|
South Western Ghats Moist Deciduous Forests
The South Western Ghats moist deciduous forests is an ecoregion in the Western Ghats of southern India with tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests. This biome covers the Nilgiri Hills between elevation of in Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu states. Geography The ecoregion has an area of . It includes the southern ranges of the Western Ghats, including the Agastyamalai and Anamalai, and the eastward spurs or slopes of the Nilgiri Hills and Palani Hills. The forests of Wayanad in northern Kerala mark the transition to the North Western Ghats moist deciduous forests to the north. To the west, the Malabar Coast moist forests ecoregion lies in the coastal strip between the 250 meter contour and the Malabar Coast. To the east, the ecoregion transitions to the South Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests ecoregion in the drier rain shadow of the Western Ghats. It surrounds the South Western Ghats montane rain forests ecoregion, which lies above 1000 meters elevation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chital
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also called spotted deer, chital deer and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben in 1777. A moderate-sized deer, male chital reach and females at the shoulder. While males weigh , females weigh around . It is sexually dimorphic; males are larger than females, and antlers are present only on males. The upper parts are golden to rufous, completely covered in white spots. The abdomen, rump, throat, insides of legs, ears, and tail are all white. The antlers, three-pronged, are nearly long. Etymology The vernacular name "chital" (pronounced ) comes from ''cītal'' (), derived from the Sanskrit word ' (चित्रल), meaning "variegated" or "spotted". The name of the cheetah has a similar origin. Variations of "chital" include "cheetal" and "cheetul". Other common names for the chital are Indian spotted deer (or simply the spotted deer) and axis dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toona Ciliata
''Toona ciliata'' is a forest tree in the mahogany family which grows throughout South Asia from Afghanistan to Papua New Guinea and Australia. Names It is commonly known as the red cedar (a name shared by other trees), tone, toon or toona (also applied to other members of the genus '' Toona''), Australian red cedar, Burma cedar, Indian cedar, Moulmein cedar or the Queensland red cedar. It is also known as Indian mahogany. Indigenous Australian names include Polai in the Illawarra. Woolia on the Richmond River, Mamin & Mugurpul near Brisbane, and Woota at Wide Bay. Also called Ai saria in Timor-Leste. Description The tree has extended compound leaves up to 90 cm with 10-14 pairs of leaflets which are narrow and taper towards the tip. Each leaflet is between 4.5 and 16 cm long. The species can grow to around in height and its trunk can reach in girth with large branches that create a spreading crown. It is one of Australia's few native deciduous trees, with the lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombax Ceiba
''Bombax ceiba'', like other trees of the genus ''Bombax'', is commonly known as cotton tree. More specifically, it is sometimes known as Malabar silk-cotton tree; red silk-cotton; red cotton tree; or ambiguously as silk-cotton or kapok, both of which may also refer to ''Ceiba pentandra''. This Asian tropical tree has a straight tall trunk and its leaves are deciduous in winter. Red flowers with 5 petals appear in the spring before the new foliage. It produces a capsule (fruit), capsule which, when ripe, contains white fibres like cotton. Its trunk bears spikes to deter attacks by animals. Although its stout trunk suggests that it is useful for timber, its wood is too soft to be very useful. Description ''Bombax ceiba'' grows to an average of 20 meters, with old trees up to 60 meters in wet tropical regions. The trunk and limb bear numerous conical spines particularly when young, but get eroded when older. The leaves are palmate with about 6 leaflets radiating from a central poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alstonia Scholaris
''Alstonia scholaris'', commonly called blackboard tree, scholar tree, milkwood or devil's tree in English, is an evergreen tree in the oleander and frangipani family Apocynaceae. Its natural range is from Pakistan to China, and south to northern Australia. It is a toxic plant, but is used traditionally for myriad diseases and complaints. It is called 'Saptaparna' in India and is the sacred tree of the 2nd Jain tirthankar Ajitnatha. It was first described by Linnaeus in 1767, who gave it the name ''Echites scholaris''. Description ''Alstonia scholaris'' is a large tree growing up to tall (rarely to 60 m), with narrow buttressess that extend well up the trunk, giving it a fluted appearance. The bark is gray to pale gray with numerous lenticels, and all parts of the plant exude copious amounts of white sap when broken or cut. The leaves are glossy dark green above and pale below, and they are arranged in whorls of four to eight, with petioles (leaf stalks) around long. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albizia Procera
''Albizia procera'', commonly known as white siris or karoi tree, is a species of large tree found natively in southeast Asia and India. It is most commonly found in open forests, but may also be found on the margins of rain forests and in monsoon and gallery forests. It is considered an invasive species in South Africa. The genus name ''Albizia'' honors the Florentine naturalist Filippo del Albizzi, while the species name is derived from the Latin word 'procerus', meaning 'very tall or high'. Description ''A. procera'' is typically between 7 and 15 meters tall, although occasionally it reaches 30 meters in height. It is deciduous, going leafless in the dry season (August–September). The leaves are bi-pinnate, with 2–5 pairs of sub-opposite pinnae and a 10–30 centimeter rachis.Orwa C, A Mutua, Kindt R , Jamnadass R, S Anthony. 2009 Agroforestree Database:a tree reference and selection guide version 4.0 (http://www.worldagroforestry.org/sites/treedbs/treedatabases.asp ) T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albizia Odoratissima
''Albizia odoratissima'', a member of the family Fabaceae, is a fast-growing, deciduous tree reaching in height, a diameter of , and native to large parts of India (where it is known as கருவாகை, Kali siris or black siris), Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Sri Lanka (where it is known as Ceylon rosewood) and China. It is one of the top nitrogen-fixing trees. The species' wide range of habitat, usefulness and rapid growth of about in height annually, has led to an extensive distribution in the tropics and occasionally in the temperate zones, despite young plants' being susceptible to frost. It has become naturalised over large swathes of Tropical Africa, extending from Kenya down the east coast through Tanzania, Malawi and Zimbabwe as far south as Mozambique, and is grown in Johannesburg, South Africa. It has also become feral in Central America and Florida in the United States. It will tolerate a wide range of soil types, but does best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adina Cordifolia
''Adina cordifolia'', synonym ''Haldina cordifolia'', is a flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to southern Asia, from India east to China and Vietnam and south to Peninsular Malaysia. ''Adina cordifolia'' is a deciduous tree that can grow well over 20 metres high. The flowers may be insignificant individually but can be seen as attractive when they bloom together in inflorescences with a circumference of 20–30 mm. They are usually yellow often tinged with a shade of pink. ''A. cordifolia'' usually blossoms during winter (dry season) months. The bark of the tree acts as an antiseptic. Gallery File:Haldina cordifolia (Haldu) in Ananthagiri forest, AP W IMG 9369.jpg, At Ananthagiri Hills, Andhra Pradesh, India File:Haldina cordifolia (Haldu) in Ananthagiri forest, AP W IMG 9367.jpg, At Ananthagiri Hills, India Image: Haldina cordifolia 1.jpg, Trunk at Udawatta Kele Sanctuary, Sri Lanka Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) refers to the combined processes which move water from the Earth's surface (open water and ice surfaces, bare soil and vegetation) into the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, Canopy interception, canopies, and water bodies) and transpiration (evaporation that occurs through the stomata, or openings, in plant leaves). Evapotranspiration is an important part of the local water cycle and climate, and measurement of it plays a key role in water resource management Irrigation, agricultural irrigation. Definition ''Evapotranspiration'' is defined as: "The combined processes through which water is transferred to the atmosphere from open water and ice surfaces, bare soil and vegetation that make up the Earth’s surface." Evapotranspiration is a combination of evaporation and transpiration, measured in order to better understand crop water requirements, irrigation scheduling, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
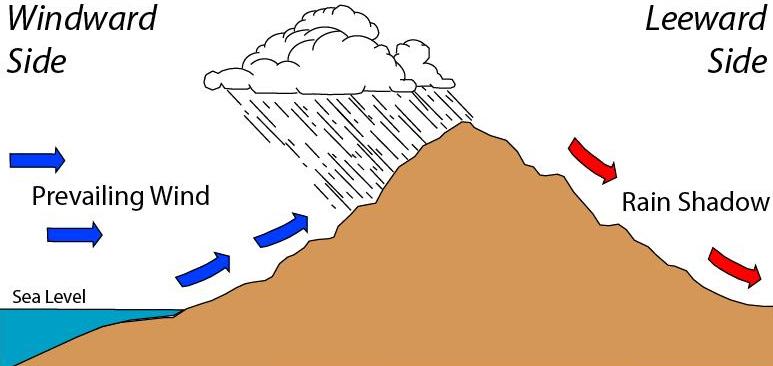
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing sea breeze, onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is orographic lift, driven upslope towards the summit, peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to Precipitation, precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of arid, dry climate region behind the ridge, mountain crests. This climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast () is the southwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. It generally refers to the West Coast of India, western coastline of India stretching from Konkan to Kanyakumari. Geographically, it comprises one of the wettest regions of the subcontinent, which includes the southern tip of Goa, Kanara region of Karnataka, all of Kerala and Kanyakumari region of Tamil Nadu. Kuttanad, which is the point of the List of extreme points of India#Altitudes, lowest altitude in India, lies on the Malabar Coast. Kuttanad, also known as ''The Rice Bowl of Kerala'', is among the few places in the world where cultivation takes place below sea level. The peak of Anamudi, which is also the point of highest altitude in India outside the Himalayas, lies parallel to the Malabar Coast on the Western Ghats. The region parallel to the Malabar Coast gently slopes from the eastern highland of Western Ghats ranges to the western coastal lowland. The moisture-laden winds of the Southwest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayanad
Wayanad () is a district in the north-east of the Indian state of Kerala, with its administrative headquarters at the municipality of Kalpetta. It is the only plateau in Kerala. The Wayanad Plateau forms a continuation of the Mysore Plateau, the southern portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is set high in the Western Ghats with altitudes ranging from 700 to 2,100 meters. Vellari Mala, a high peak situated on the trijunction of Wayanad, Malappuram, and Kozhikode districts, is the highest point in Wayanad district. The district was formed on 1 November 1980 as the 12th district in Kerala, by carving out areas from Kozhikode and Kannur districts. An area of 885.92 km2 in the district is forested. Wayanad has three municipal towns— Kalpetta, Mananthavady and Sulthan Bathery. There are many indigenous tribes in this area. The Kabini River, a tributary of the Kaveri River, originates at Wayanad. Wayanad district, along with the Chaliyar valley in the neighbouring Nilam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |