|
Sorter (other)
Sorter may refer to: * Sorter (logistics), a system that sorts products according to destination * Card sorter, a machine to sort computer punched card * Cash sorter machine, a machine used for sorting banknotes * Coin sorter, a machine used for sorting coins * Keirsey Temperament Sorter, a self-assessed personality questionnaire * Sorting algorithm In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a List (computing), list into an Total order, order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending ..., an algorithm to put elements of a list into order See also * Sort (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
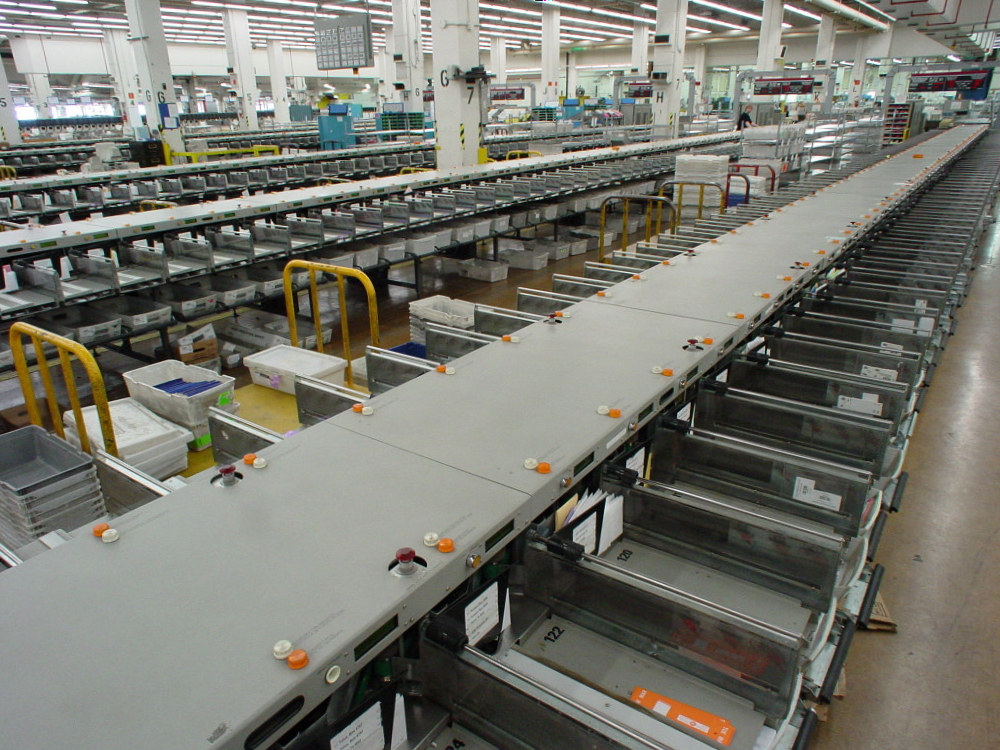
Sorter (logistics)
In logistics, a sorter is a system which performs sortation of products (goods, luggage, mail, etc.) according to their destinations.Patrick M McGuire, ''Conveyors: Application, Selection, and Integration''6.3. Sorters/ref> A common type of sorter is a conveyor A conveyor system is a common piece of mechanical handling equipment that moves materials from one location to another. Conveyors are especially useful in applications involving the transport of heavy or bulky materials. Conveyor systems allow ...-based system. While they may be based on other conveyor systems, usually sorters are unique types of conveyors. Sortation is the process of identifying items on a conveyor system, and diverting them to specific destinations. Sorters are applied to different applications depending upon the product and the requested rate. Common elements of sorters A feeder system whose sole purpose to feed the products into the sorter in proper orientation and with proper spacing, so that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Card Sorter
A punched card sorter is a machine for sorting decks of punched cards. Sorting was a major activity in most facilities that processed data on punched cards using unit record equipment. The work flow of many processes required decks of cards to be put into some specific order as determined by the data punched in the cards. The same deck might be sorted differently for different processing steps. A popular family of sorters, the IBM 80 series sorters, sorted input cards into one of 13 pockets depending on the holes punched in a selected column and the sorter's settings. Basic operation The basic operation of a card sorter is to take a punched card, examine a single column, and place the card into a selected pocket. There are twelve rows on a punched card, and thirteen pockets in the sorter; one pocket is for blanks, rejects, and errors. Cards are normally passed through the sorter face down with the bottom edge ("9-edge") first. A small metal brush or optical sensor is positioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cash Sorter Machine
A currency-counting machine is a machine that counts money—either stacks of banknotes or loose collections of coins. Counters may be purely mechanical or use electronic components. The machines typically provide a total count of all money, or count off specific batch sizes for wrapping and storage. Currency counters are commonly used in vending machines to determine what amount of money has been deposited by customers. In some modern automated teller machines, currency counters allow for cash deposits without envelopes, since they can identify which notes have been inserted instead of just how many. The user is given the chance to review the automatic counter's idea of the quantity and kinds of the inserted banknotes before the deposit is complete. The above physical machines count cash easily. However, today, various money counter online tools are available on the Internet that make the task error-free and easy. One only needs to put the value of notes and coins on those t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keirsey Temperament Sorter
The Keirsey Temperament Sorter (KTS) is a self-assessed personality questionnaire. It was first introduced in the book '' Please Understand Me''. The KTS is closely associated with the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI); however, there are significant practical and theoretical differences between the two personality questionnaires and their associated different descriptions. Historical development :''See also Historical Development of Theories of the Four Temperaments'' David Keirsey became familiar with the work of Ernst Kretschmer and William Sheldon after WWII in the late 1940s. Keirsey developed the Temperament Sorter after being introduced to the MBTI in 1956. Tracing the idea of temperament back to the ancient Greeks, Keirsey developed a modern temperament theory in his books ''Please Understand Me'' (1978), ''Portraits of Temperament'' (1988), ''Presidential Temperament'' (1992), ''Please Understand Me II'' (1998), ''Brains and Careers'' (2008), and ''Personology'' (201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorting Algorithm
In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a List (computing), list into an Total order, order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending. Efficient sorting is important for optimizing the Algorithmic efficiency, efficiency of other algorithms (such as search algorithm, search and merge algorithm, merge algorithms) that require input data to be in sorted lists. Sorting is also often useful for Canonicalization, canonicalizing data and for producing human-readable output. Formally, the output of any sorting algorithm must satisfy two conditions: # The output is in monotonic order (each element is no smaller/larger than the previous element, according to the required order). # The output is a permutation (a reordering, yet retaining all of the original elements) of the input. Although some algorithms are designed for sequential access, the highest-performing algorithms assum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |