|
Sommers–Bausch Observatory
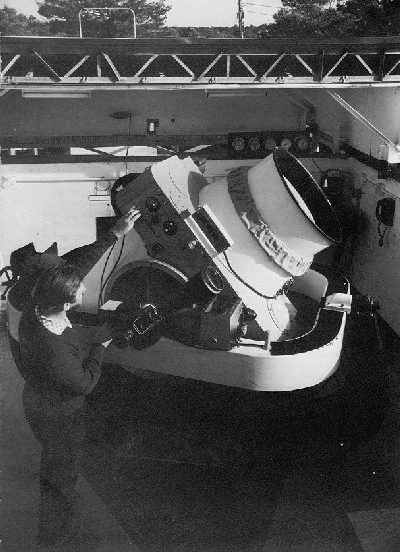
Sommers–Bausch Observatory is an astronomical observatory operated by the University of Colorado, Boulder on its main campus. The building was initially completed in 1953 and named after Elmer E. Sommers and Carl L. Bausch. It is operated by the university's Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences (APS), which primarily utilizes the facilities and equipment of the observatory for teaching as well as some research. Telescopes include two 20" Planewave CDK telescopes on Software Bisque Taurus 500 encoder mounts, a 24" Boller and Chivens Cassegrain reflectors, and a 10-inch aperture heliostat (solar telescope). The observatory also possesses multiple smaller telescopes and ancillary equipment. The observatory also houses the lab classroom and the computer lab for the APS department. History In 1949, the University of Colorado received a bequest of $49,054 from the estate of Mayme Sommers in memory of her husband Elmer E. Sommers. These funds were used to construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado, United States. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado system. CU Boulder is a member of the Association of American Universities, considered a Public Ivy and is classified among R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity. The university consists of nine colleges and schools and offers over 150 academic programs, enrolling more than 35,000 students as of January 2022. In 2021, the university attracted the support of over $634 million for research and spent $536 million on research and development according to the National Science Foundation, ranking it 50th in the nation. It receives the most NASA astrophysics technology grants of all academic institutions and is the only university in the world that has sent instruments to all planets in the Solar System. The Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. The term ''observatoire'' has been used in French since at least 1976 to denote any institution that compiles and presents data on a particular subject (such as public health observatory) or for a particular geographic area (European Audiovisual Observatory). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space observatory, space-based, airborne observatory, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Historically, ground-based observatories were as simple as containing a mural instrument (for measuring the angle between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Bisque
Software Bisque, Inc. (formerly named ''Computer Assist Services'') is a corporation based in Golden, Colorado that develops robotics telescope mounts and accessories and publishes software used in astronomy. It was founded in 1984 by current president and CEO, Stephen M. Bisque. History Bisque initially developed and marketed custom financial software and also sold a DOS-based astronomy program named '' TheSky''. At that time, the company was based in Bisque's home in Golden, Colorado. In 1990, Bisque hired his brothers Thomas, Daniel and Matthew. Together they ported TheSky for DOS to Windows 3.0. In 1992, ''TheSky for Windows'' was released. The product has been under continuous development since it was first released in the early 1980s; the current version is known as TheSkyX. Products Software Bisque has since developed and sold many astronomy-related products, including: * TheSky, TheSkyX Astronomy Software, Camera Add On, Dome Add On, and TPoint Add On * TheSky Pocket Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boller And Chivens
Boller and Chivens was an American manufacturer of high-quality telescopes and spectrographs headquartered in South Pasadena, California. History Founded about 1946 by Harry Berthold Boller (1915-1997) and Clyde Cuthbertson Chivens (1915-2008). the company was acquired in 1965 by Perkin-Elmer. In the 1950s, Boller and Chivens collaborated with Perkin-Elmer to develop and manufacture the large-aperture Baker-Nunn satellite tracking camera for the United States Vanguard space satellite program. In culture A 41-cm (16-inch) Boller and Chivens Cassegrain reflector originally housed at the Harvard-Smithsonian Oak Ridge Observatory in Massachusetts is available for public use at the National Air and Space Museum's Public Observatory Project on the National Mall The National Mall is a Landscape architecture, landscaped park near the Downtown, Washington, D.C., downtown area of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States. It contains and borders a number of museums o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
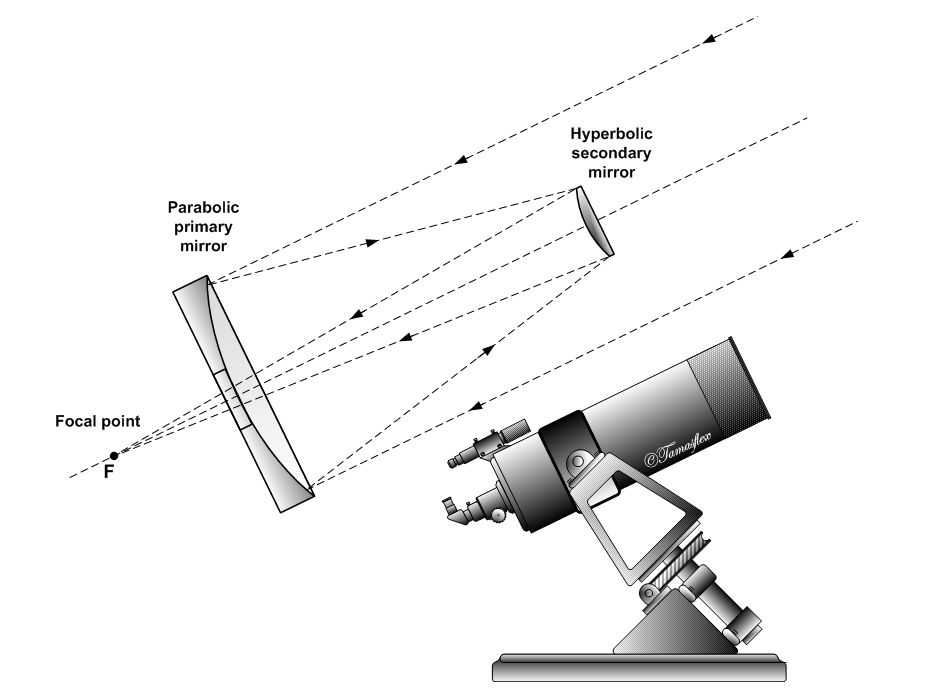
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and Antenna (radio), radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the Focus (optics), focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a Telephoto lens, telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliostat
A heliostat () is a device that reflects sunlight toward a target, turning to compensate for the Sun's apparent motion. The reflector is usually a plane mirror. The target may be a physical object, distant from the heliostat, or a direction in space. To do this, the reflective surface of the mirror is kept perpendicular to the bisector of the angle between the directions of the Sun and the target as seen from the mirror. In almost every case, the target is stationary relative to the heliostat, so the light is reflected in a fixed direction. According to contemporary sources the heliostata, as it was called at first, was invented by Willem 's Gravesande (1688–1742). Other contenders are Giovanni Alfonso Borelli (1608–1679) and Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736). A heliostat designed by George Johnstone Storey is in the Science Museum Group collection. Currently, most heliostats are used for daylighting or for the production of concentrated solar power, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Astronomical Society
The American Astronomical Society (AAS, sometimes spoken as "double-A-S") is an American society of professional astronomers and other interested individuals, headquartered in Washington, DC. The primary objective of the AAS is to promote the advancement of astronomy and closely related branches of science, while the secondary purpose includes enhancing astronomy education and providing a political voice for its members through lobbying and grassroots activities. Its current mission is to enhance and share humanity's scientific understanding of the universe as a diverse and inclusive astronomical community. History The society was founded in 1899 through the efforts of George Ellery Hale. The constitution of the group was written by Hale, George Comstock, Edward Morley, Simon Newcomb and Edward Charles Pickering. These men, plus four others, were the first Executive Council of the society; Newcomb was the first president. The initial membership was 114. The AAS name of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Altitude Observatory
The High Altitude Observatory (HAO) is a laboratory of the US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). HAO operates the Mauna Loa Solar Observatory on Hawaii (island), Hawaii and a research institute in Boulder, Colorado. Its staff conduct research and provide support and facilities for the solar-terrestrial physics research community. Topics covered include solar physics, the heliosphere, and the effects of space weather on Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, and upper atmosphere. HAO was originally founded in 1940 as a branch of the Harvard College Observatory, was transferred to the University of Colorado in the late 1940s, before becoming part of NCAR when the latter was founded in 1960. Mission and vision HAO's mission is to understand the behavior of the Sun and its impact on the Earth, to support, enhance, and extend the capabilities of the university community and the broader scientific community, nationally and internationally, and to foster the transfer of kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble Space Telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories program, Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible spectrum, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Project
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space program that studied the planet Jupiter and Moons of Jupiter, its moons, as well as several other Solar System bodies. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, the Galileo (spacecraft), ''Galileo'' spacecraft consisted of an orbiter and an atmospheric entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by on the STS-34 mission, and arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravity assist planetary flyby, flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit Jupiter. The spacecraft then launched the first probe to directly measure its atmosphere. Despite suffering major antenna problems, ''Galileo'' achieved the first asteroid flyby, of 951 Gaspra, and discovered the first asteroid moon, Dactyl (moon), Dactyl, around 243 Ida. In 1994, ''Galileo'' observed Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9's collision with Jupiter. Jupiter's atmospheric composition and ammonia clouds were recorded, as were the volcanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |