|
Solar Eclipse Of August 12, 1942
A partial solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, August 12, 1942, with a magnitude of 0.0561. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Antarctica. This was the last of 72 solar eclipses in Solar Saros 115. Eclipse details Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse. Eclipse season This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. This can occur only when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are exactly or very closely aligned (in syzygy) with Earth between the other two, which can happen only on the night of a full moon when the Moon is near either lunar node. The type and length of a lunar eclipse depend on the Moon's proximity to the lunar node. When the moon is totally eclipsed by the Earth, it takes on a reddish color that is caused by the planet when it completely blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon surface, as only the light reflected from the lunar surface has been refracted by Earth's atmosphere. This light appears reddish due to the Rayleigh scattering of blue light, the same reason sunrise and sunsets are more orange than during the day. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
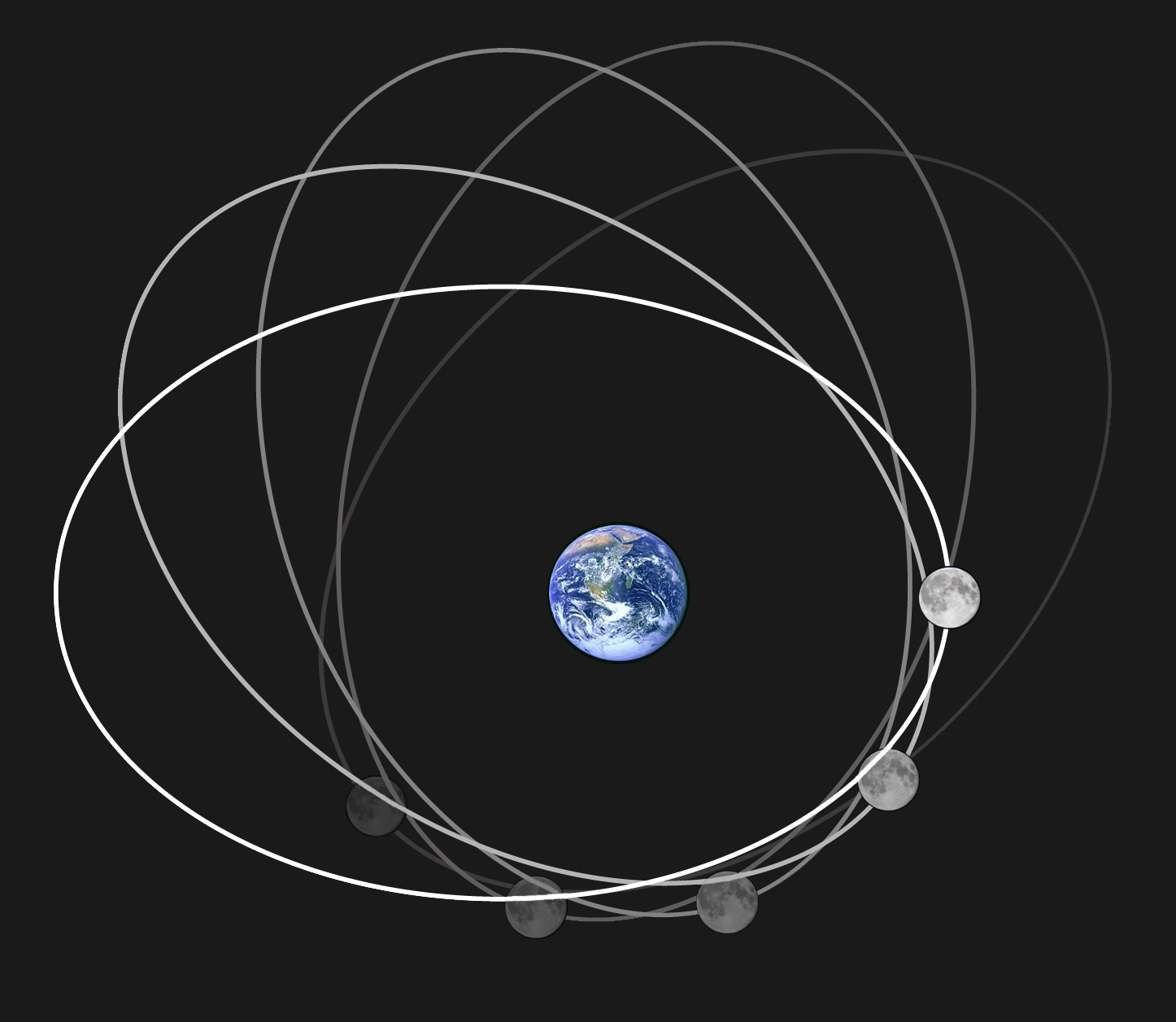
Moon's Orbit
The Moon orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the stars in about 27.32 days (a tropical month and sidereal month) and one revolution relative to the Sun in about 29.53 days (a synodic month). Earth and the Moon orbit about their barycentre (common centre of mass), which lies about from Earth's centre (about 73% of its radius), forming a satellite system called the Earth–Moon system. On average, the distance to the Moon is about from Earth's centre, which corresponds to about 60 Earth radii or 1.282 light-seconds. With a mean orbital velocity of 1.022 km/s (0.635 miles/s, 2,286 miles/h), the Moon covers a distance approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most satellites of other planets in that its orbit is close to the ecliptic plane instead of to its primary's (in this case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital plane is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of June 12, 2029
A partial solar eclipse will occur on Tuesday, June 12, 2029. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. The eclipse will be visible from Northern and Central Europe, northern Russia, Arctic, Greenland Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ..., and northern North America. Images Animated path Related eclipses Solar eclipses 2029–2032 Saros 118 It is a part of Saros cycle 118, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 72 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on May 24, 803 AD. It contains total eclipses from Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of July 22, 1971
A partial solar eclipse occurred on July 22, 1971. This was the 70th and final solar eclipse from Solar Saros 116. Half-Saros cycle Solar Saros 116 and Lunar Saros 109 Solar eclipse of June 19, 1917 Solar eclipse of June 30, 1935 July 1944 lunar eclipse Solar eclipse of July 11, 1953 July 1962 lunar eclipse Solar eclipse of July 22, 1971 July 1980 lunar eclipse August 1998 lunar eclipse August 2016 lunar eclipse Related eclipses Solar eclipses of 1971–1974 Metonic cycle Half-Saros cycle A solar eclipse will be preceded and followed by lunar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, ''The half-saros'' This solar eclipse is related to two penumbral lunar eclipses of Lunar Saros 109 Saros cycle series 109 for lunar eclipses occurred at the moon's descending node, 18 years 11 and 1/3 days. It contained either 71 or 72 events, depending on multiple calculation Summary Lunar Saros series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of August 31, 1913
A partial solar eclipse occurred on August 31, 1913. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared rad ..., thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Related eclipses Solar eclipses of 1913–1917 Metonic series References External links 1913 8 31 1913 in science 1913 8 31 August 1913 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of July 31, 1924
This is a list of solar eclipses in the 20th century. During the period 1901 to 2000 there were 228 solar eclipses of which 78 were partial, 73 were annular (two Solar eclipse#Terminology for central eclipse, non-central), 71 were total (three non-central) and 6 were hybrids. The greatest number of eclipses in one year was five, in 1935, and one month, July 2000, had two eclipses. Notable eclipses of the 20th century * Solar eclipse of May 29, 1919, 29 May 1919: this total eclipse was photographed by Arthur Eddington to verify general relativity (see Eddington experiment) * Solar eclipse of June 20, 1955, 20 June 1955: longest total eclipse between 1901 and 2000, lasting a maximum of 7 minutes and 8 seconds * Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973, 30 June 1973: a Concorde jet flew along the path, thereby extending the length of totality to 74 min. * Solar eclipse of March 29, 1987, 29 March 1987: second hybrid eclipse in less than one year, the first being on Solar eclipse of October 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of July 11, 1953
A partial solar eclipse occurred on July 11, 1953. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared rad ..., thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Related eclipses Solar eclipses of 1953–1956 Metonic series References External links * http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEplot/SEplot1951/SE1953Jul11P.GIF 1953 7 11 1953 in science 1953 7 11 July 1953 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of September 12, 1931
A partial solar eclipse occurred on September 12, 1931. A solar eclipse A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six month ... occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. This was the 72nd and final event from Solar Saros 114. It started in 651 AD and ended in 1931. Related eclipses Solar eclipses 1931–1935 Metonic series References External links 1931 9 12 1931 in science September 1931 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August 1951 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on August 17, 1951. The northern edges of the moon entered the southern edge of the earth's penumbral shadow, leading to visually minimal dimming. Visibility Related lunar eclipses Lunar year series Metonic cycle (19 years) This is the third of five Metonic lunar eclipses. See also *List of lunar eclipses *List of 20th-century lunar eclipses A total of 229 lunar eclipses took place in the 20th century: 83 penumbral, 65 partial and 81 total. See also: Lists of lunar eclipses, List of 19th-century lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses List Eclipses from 2001 to ... Notes External links * 1951-08 1951 in science {{lunar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August 1933 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, August 5, 1933. Visibility Related lunar eclipses Tritos series * Followed: Lunar eclipse of March 23, 1951 Tzolkinex * Preceded: Lunar eclipse of June 25, 1926 See also *List of lunar eclipses *List of 20th-century lunar eclipses A total of 229 lunar eclipses took place in the 20th century: 83 penumbral, 65 partial and 81 total. See also: Lists of lunar eclipses, List of 19th-century lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses List Eclipses from 2001 to ... Notes External links * 1933-08 1933 in science {{lunar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of June 30, 1935
A partial solar eclipse occurred on June 30, 1935. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared rad ..., thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Related eclipses Solar eclipses 1935–1938 Metonic series References External links * http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEplot/SEplot1901/SE1935Jun30P.GIF 1935 06 30 1935 in science 1935 06 30 June 1935 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |