|
Social Inertia
In psychology and sociology, social inertia or cultural inertia is the resistance to change or the permanence of stable relationships possibly outdated in societies or social groups. Social inertia is the opposite of social change. Overview The idea of social inertia can be traced back to French sociologist Pierre Bourdieu. According to Bourdieu, each person occupies a position in a social space, which consists of his or her social class as well as social relationships and social networks. Through the individual's engagement in the social space, he or she develops a set of behaviors, lifestyle and habits (which Bourdieu referred to as habitus) which often serve to maintain the status quo. Thus, people are encouraged to "accept the social world as it is, to take it for granted, rather than to rebel against it, to counterpose to it different, even antagonistic, possibles." This can explain the continuity of the social order through time. Sociologists have examined how economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Equal Opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. For example, the intent of equal employment opportunity is that the important jobs in an organization should go to the people who are Meritocracy, most qualified – persons most likely to perform ably in a given task – and not go to persons for reasons deemed arbitrary or irrelevant, such as circumstances of birth, upbringing, having well-connected Nepotism, relatives or Cronyism, friends, Religious discrimination, religion, Sexism, sex, ethnicity, Racism, race, caste, or involuntary personal attributes such as Ableism, disability, Ageism, age. According to proponents of the concept, chances for advancement should be open to everybody without regard for wealth, status, or membership in a Social privilege, privileged group. The idea is to remove arbitrariness from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Psychology Today
''Psychology Today'' is an American media organization with a focus on psychology and human behavior. The publication began as a bimonthly magazine, which first appeared in 1967. The print magazine's reported circulation is 275,000 as of 2023. The ''Psychology Today'' website features therapist and health professional directories and hundreds of blogs written by a wide variety of psychologists, psychiatrists, counselors, social workers, medical doctors, marriage and family therapists, anthropologists, sociologists, and science journalists. ''Psychology Today'' is among the oldest media outlets with a focus on behavioral science. Its mission is to cover all aspects of human behavior so as to help people better manage their own health and wellness, adjust their mindset, and manage a range of mental health and relationship concerns. ''Psychology Today'' content and its therapist directory are found in 20 countries worldwide. ''Psychology Today'''s therapist directory is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environment, environmental, legal, social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in statistics or economics there are two main measures: ''absolute poverty'' which compares income against the amount needed to meet basic needs, basic personal needs, such as food, clothing, and Shelter (building), shelter; secondly, ''relative poverty'' measures when a person cannot meet a minimum level of living standards, compared to others in the same time and place. The definition of ''relative poverty'' varies from one country to another, or from one society to another. Statistically, , most of the world's population live in poverty: in Purchasing Power Parity, PPP dollars, 85% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or religious organization, organizations, that generally relate humanity to supernatural, transcendence (religion), transcendental, and spirituality, spiritual elements—although there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. It is an essentially contested concept. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacredness, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). and a supernatural being or beings. The origin of religious belief is an open question, with possible explanations including awareness of individual death, a sense of community, and dreams. Religions have sacred histories, narratives, and mythologies, preserved in oral traditions, sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Social Order
The term social order can be used in two senses: In the first sense, it refers to a particular system of social structures and institutions. Examples are the ancient, the feudal, and the capitalist social order. In the second sense, social order is contrasted to social chaos or disorder and refers to a stable state of society in which the existing social structure is accepted and maintained by its members. The problem of order or Hobbesian problem, which is central to much of sociology, political science and political philosophy, is the question of how and why it is that social orders exist at all. Sociology Thomas Hobbes is recognized as the first to clearly formulate the problem, to answer which he conceived the notion of a social contract. Social theorists (such as Karl Marx, Émile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons, and Jürgen Habermas) have proposed different explanations for what a social order consists of, and what its real basis is. For Marx, it is the relations of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Law Enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term encompasses police, courts and corrections. These three components of the criminal justice system may operate independently of each other or collectively through the use of record sharing and cooperation. Throughout the world, law enforcement are also associated with protecting the public, life, property, and keeping the peace in society. The concept of law enforcement dates back to ancient times, and forms of law enforcement and police have existed in various forms across many human societies. Modern state legal codes use the term law enforcement officer or peace officer to include every person vested by the legislating state with police power or authority; traditionally, anyone sworn or badged who can arrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reputation
The reputation or prestige of a social entity (a person, a social group, an organization, or a place) is an opinion about that entity – typically developed as a result of social evaluation on a set of criteria, such as behavior or performance. Reputation is a ubiquitous, spontaneous, and highly efficient mechanism of social control. It is a subject of study in social, management, and technological sciences. Its influence ranges from competitive settings, like markets, to cooperative ones, like firms, organizations, institutions and communities. Furthermore, reputation acts on different levels of agency: individual and supra-individual. At the supra-individual level, it concerns groups, communities, collectives and abstract social entities (such as firms, corporations, organizations, countries, cultures and even civilizations). It affects phenomena of different scales, from everyday life to relationships between nations. Reputation is a fundamental instrument of social order, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
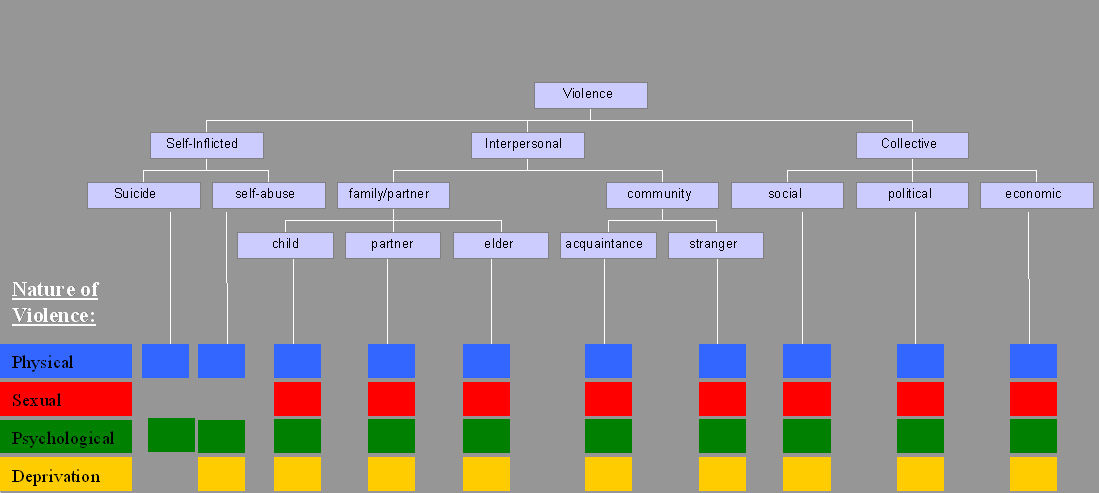
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Culture Of Honor (Southern United States)
The traditional culture of the Southern United States has been called a "culture of honor", that is, a culture where people avoid intentionally offending others, and maintain a reputation for not accepting improper conduct by others. A theory as to why the American South had or may have had this culture is an assumed regional belief in retribution to enforce one's rights and deter predation against one's family, home, and possessions.Nisbett, R.E., & Cohen, D. (1996). ''Culture of honor: The psychology of violence in the South''. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. Background The "culture of honor" in the Southern United States is hypothesized by some social scientists to have its roots in the livelihoods of the settlers who first inhabited the region. Unlike those from the densely populated South East England and East Anglia, who settled in New England, the Southern United States was settled by herders from Scotland, Northern Ireland, Northern England, and the West Country. David Hackett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Formal Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are disagreements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Social Mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given society. This movement occurs between layers or tiers in an open system of social stratification. Open stratification systems are those in which at least some value is given to achieved status characteristics in a society. The movement can be in a ''downward'' or ''upward'' direction. Markers for social mobility such as education and class, are used to predict, discuss and learn more about an individual or a group's mobility in society. Typology Mobility is most often quantitatively measured in terms of change in economic mobility such as changes in income or wealth. Occupation is another measure used in researching mobility which usually involves both quantitative and qualitative analysis of data, but other studies may concentrate on soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |