|
Slavery Among The Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
Slavery was widely practiced by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, both prior to European colonisation and subsequently. Slavery and related practices of forced labor varied greatly between regions and over time. In some instances, traditional practices may have continued after European colonisation. North America Slaves were traded across trans-continental trade networks in North America before European arrival. Many of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, such as the Haida and Tlingit, were traditionally known as fierce warriors and slave-traders, raiding as far south as California.Ames, Kenneth M.; Maschner, Herbert D. G. (1999). ''Peoples of the northwest coast: their archaeology and prehistory.'' London: Thames & Hudson, p. 196.Green, Jonathan S. (1915). ''Journal of a tour on the north west coast of America in the year 1829, containing a description of a part of Oregon, California and the north west coast and the numbers, manners and customs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yurok
The Yurok people are an Algic-speaking Indigenous people of California that has existed along the or "Health-kick-wer-roy" (now known as the Klamath River) and on the Pacific coast, from Trinidad south of the Klamath’s mouth almost to Crescent City along the north coast. The people of the Yurok Tribe traditionally identify as , a Yurok word simply meaning "the people." Some historic documents, like the Yurok Tribe's unratified treaty with the Government of the United States (GoUS), refer to the Yurok Tribe as the Lower Klamath, Pulikla, or Poh-lik Indians to distinguish the people of the Yurok Tribe from the "Upper Klamath" or "Peh-tsick" Indians, who are now known as the Karuk Tribe. The name Yurok is derived from the Karuk word , meaning "downriver people; i.e. Yurok Indians".Andrew Garrett, Susan Gehr, Erik Hans Maier, Line Mikkelsen, Crystal Richardson, and Clare Sandy. (November 2, 2021) ''Karuk; To appear in The Languages and Linguistics of Indigenous North America: A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuas
The Nahuas ( ) are a Uto-Nahuan ethnicity and one of the Indigenous people of Mexico, with Nahua minorities also in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. They comprise the largest Indigenous group in Mexico, as well as the largest population out of any North American Indigenous people group who are native speakers of their respective Indigenous language. Amongst the Nahua, this is Nahuatl. When ranked amongst all Indigenous languages across the Americas, Nahuas list third after speakers of Guaraní and Quechua. The Mexica (Aztecs) are of Nahua ethnicity, as are their historical enemies and allies of the Spaniards: the Tlaxcallans (Tlaxcaltecs). The Toltecs which predated both groups are often thought to have been Nahua as well. However, in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share a common identity. Their Nahuan languages, or Nahuatl, consist of many variants, several of which are mutually uninte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trust (law)
A trust is a legal relationship in which the owner of property, or any transferable right, gives it to another to manage and use solely for the benefit of a designated person. In the English common law, the party who entrusts the property is known as the "settlor", the party to whom it is entrusted is known as the "trustee", the party for whose benefit the property is entrusted is known as the "beneficiary", and the entrusted property is known as the "corpus" or "trust property". A ''testamentary trust'' is an irrevocable trust established and funded pursuant to the terms of a deceased person's will. An inter vivos trust is a trust created during the settlor's life. The trustee is the legal owner of the assets held in trust on behalf of the trust and its beneficiaries. The beneficiaries are equitable owners of the trust property. Trustees have a fiduciary duty to manage the trust for the benefit of the equitable owners. Trustees must provide regular accountings of trust incom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Collar Crime
The term "white-collar crime" refers to financially motivated, nonviolent or non-directly violent crime committed by individuals, businesses and government professionals. The crimes are believed to be committed by middle- or upper-class individuals for financial gains. It was first defined by the sociologist Edwin Sutherland in 1939 as "a crime committed by a person of respectability and high social status in the course of their occupation". Typical white-collar crimes could include wage theft, fraud, bribery, Ponzi schemes, insider trading, labor racketeering, embezzlement, cybercrime, copyright infringement, money laundering, identity theft, and forgery. White-collar crime overlaps with corporate crime. Definitional issues Modern criminology generally prefers to classify the type of crime and the topic: *By the type of offense, e.g., property crime, economic crime, and other corporate crimes like environmental and health and safety law violations. Some crimes are onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
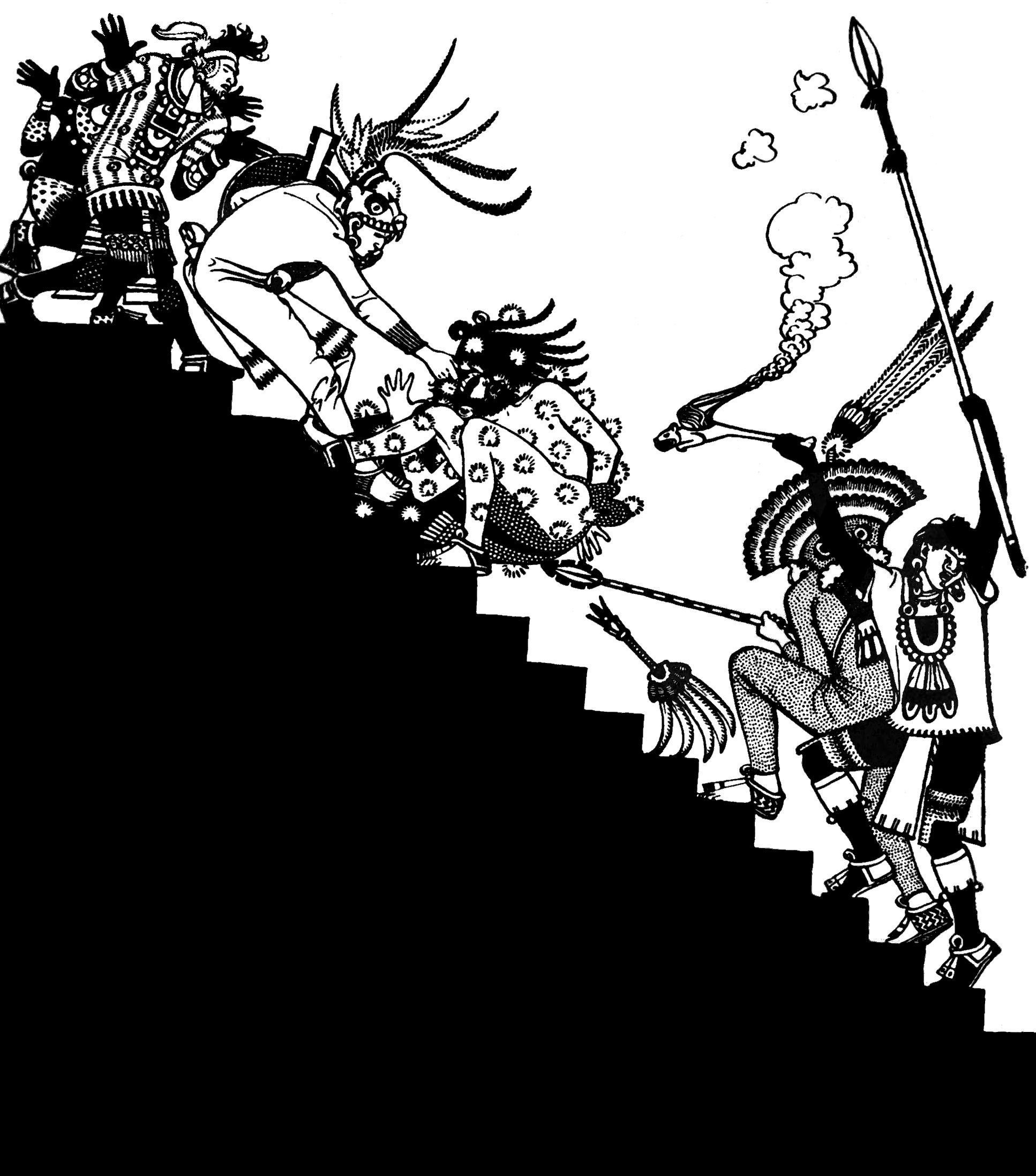
Human Sacrifice In Aztec Culture
Human sacrifice was a common practice in many parts of Mesoamerica. The rite was not new to the Aztecs when they arrived at the Valley of Mexico, nor was it something unique to pre-Columbian Mexico. Other Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Purépecha culture, Purépechas and Toltecs, and the Maya peoples, Maya performed sacrifices as well, and from archaeological evidence, it probably existed since the time of the Olmecs (1200–400 BC), and perhaps even throughout the early farming cultures of the region. However, the extent of human sacrifice is unknown among several Mesoamerican civilizations. What distinguished Aztec practice from Human sacrifice in Maya culture, Maya human sacrifice was the way in which it was embedded in everyday life. In 1519, explorers such as Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and made observations of and wrote reports about the practice of human sacrifice. Bernal Díaz del Castillo, who participated in the Cortés expediti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly existed before that. Evidence of ritual human sacrifice can also be found back to at least pre-Columbian civilizations of Mesoamerica as well as in European civilizations. Varieties of ritual non-human sacrifices are practiced by numerous religions today. Terminology The Latin term ''sacrificium'' (a sacrifice) derived from Latin ''sacrificus'' (performing priestly functions or sacrifices), which combined the concepts ''sacra'' (sacred things) and ''facere'' (to make, to do). The Latin word ''sacrificium'' came to apply to the Christian eucharist in particular, sometimes named a "bloodless sacrifice" to distinguish it from blood sacrifices. In individual non-Christian ethnic religions, terms translated as "sacrifice" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Society
Maya society concerns the social organization of the Pre-Hispanic Maya, its political structures, and social classes. The Maya people were indigenous to Mexico and Central America and the most dominant people groups of Central America up until the 6th century. In the Neolithic Age, Maya society has contributed to the fields of astronomy, mathematics, agriculture, art and writing. The Mayans would peak as a civilization between 250 - 900 AD. This included complex cities, social life, and politics. Mayan civilization began to decline after this time period, and remaining Mayans would revert to more of a hunter-gatherer society. These remaining tribes would eventually be conquered by Europeans in the 1500s. The Maya lived in Mesoamerica, concentrated in the Yucatán Peninsula, the Peten district of northern Guatemala and southern Mexico. The Maya reached the height of their civilization during the Classic Period of Maya civilization (A.D 250 to 900) before a decline starting about 90 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire, also known as the Triple Alliance (, Help:IPA/Nahuatl, [ˈjéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥]) or the Tenochca Empire, was an alliance of three Nahuas, Nahua altepetl, city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish and their native allies who ruled under Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, defeated them in 1521. Its people and civil society are historiographically referred to as the ''Aztecs'' or the ''Culhua-Mexica''. The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital became dominant militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1519, the lands of the alliance were effectively ruled from , while other partners of the alliance had taken subsidiary roles. The al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Civilization
The Maya civilization () was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from Ancient history, antiquity to the early modern period. It is known by Maya architecture#Pyramids and temples, its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for Maya art, its art, Maya architecture, architecture, Maya numerals, mathematics, Maya calendar, calendar, and Maya astronomy, astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the Mayan Lowlands, northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt Bondage
Debt bondage, also known as debt slavery, bonded labour, or peonage, is the pledge of a person's services as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation. Where the terms of the repayment are not clearly or reasonably stated, or where the debt is excessively large, the person who holds the debt has thus some control over the laborer, whose freedom depends on the undefined or excessive debt repayment. The services required to repay the debt may be undefined, and the services' duration may be undefined, thus allowing the person supposedly owed the debt to demand services indefinitely. Debt bondage can be passed on from generation to generation. In 2021, the International Labour Organization estimated that, of the 27.6 million people currently participating in forced labour, 20.9%, or about 5.8 million, were in debt bondage. Debt bondage has been described by the United Nations as a form of "Contemporary slavery, modern day slavery", and the Supplementary Convention on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |